The document discusses several models of communicative competence:
1. Canale and Swain's model includes grammatical, sociolinguistic, and strategic competence. It emphasizes the demonstration of knowledge in actual performance.
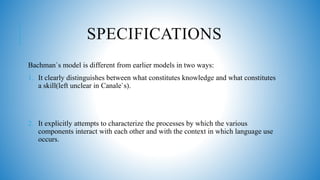
2. Bachman's model distinguishes knowledge from skills. It includes language competence, strategic competence, and psychophysiological mechanisms.
3. Celce-Murcia et al.'s model has five components: discourse competence, actional competence, sociocultural competence, linguistic competence, and strategic competence. It aims to generate detailed content for curriculum design.