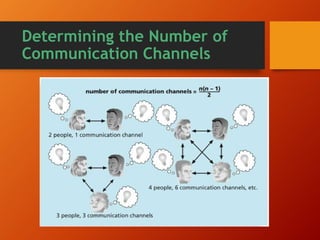
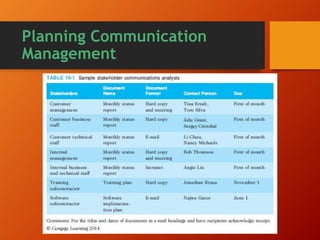
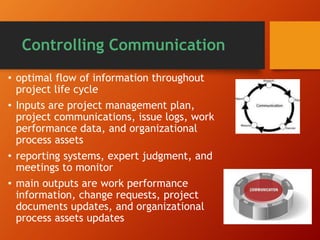
The document discusses the importance of project communications management. It emphasizes planning, managing, and controlling communications through various formal and informal methods. This includes understanding individual and group communication needs, distributing important information in an effective and timely manner, and using technology to enhance information creation and distribution. The key is having the right communication skills and running effective meetings to optimize the flow of information throughout the project life cycle.