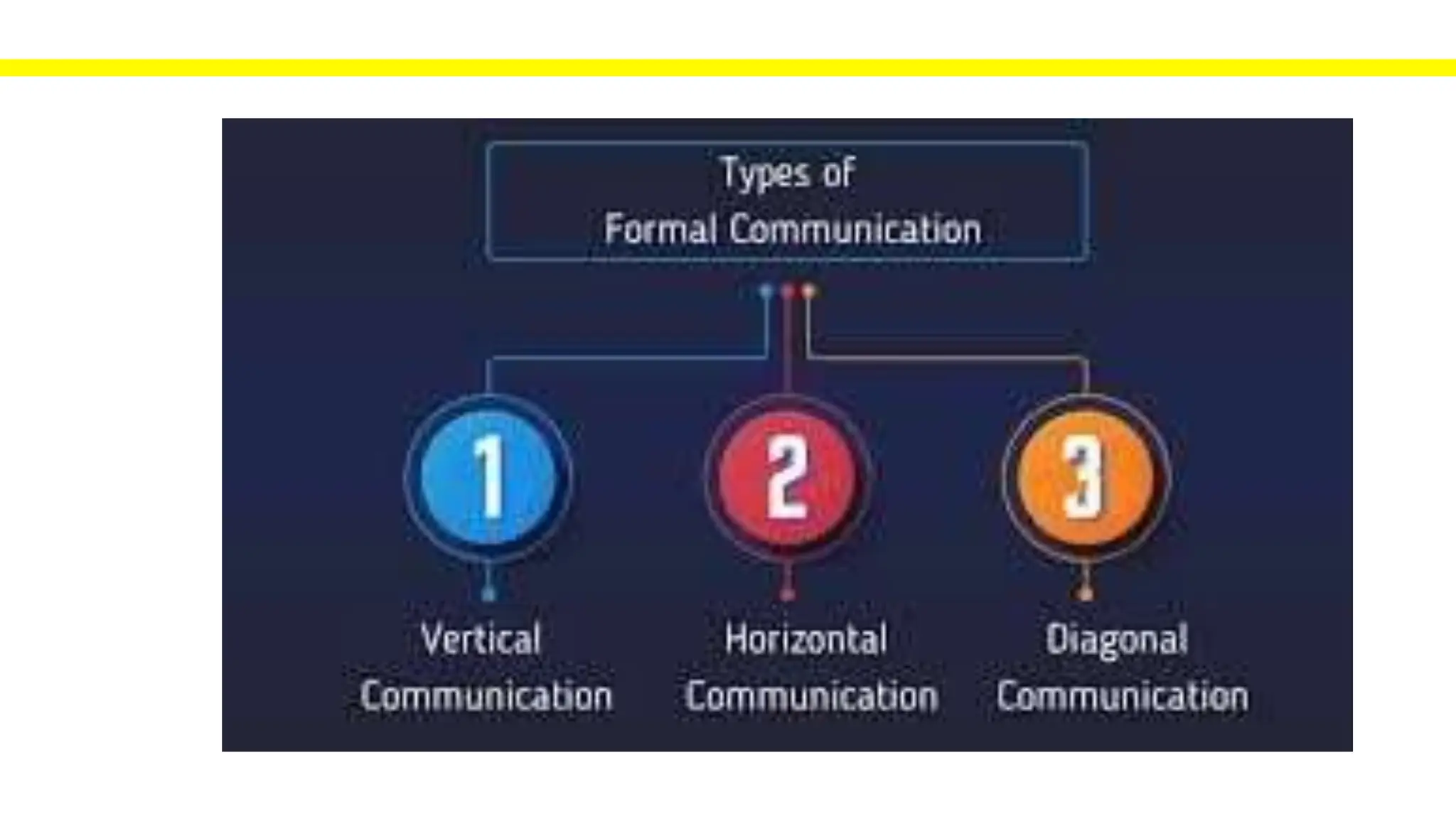
The document discusses various aspects of communication including its meaning, functions, methods, barriers, and types. It defines communication as the act of giving, receiving, and sharing information through talking, writing, listening, and reading. The main functions of communication are listed as control, motivation, emotional expression, and sharing information. Key methods include verbal, non-verbal, written, listening, and visual communication. Barriers to effective communication can be language, organizational, psychological, emotional, or physical. The document also distinguishes between formal communication like meetings and informal communication like casual conversations between coworkers.