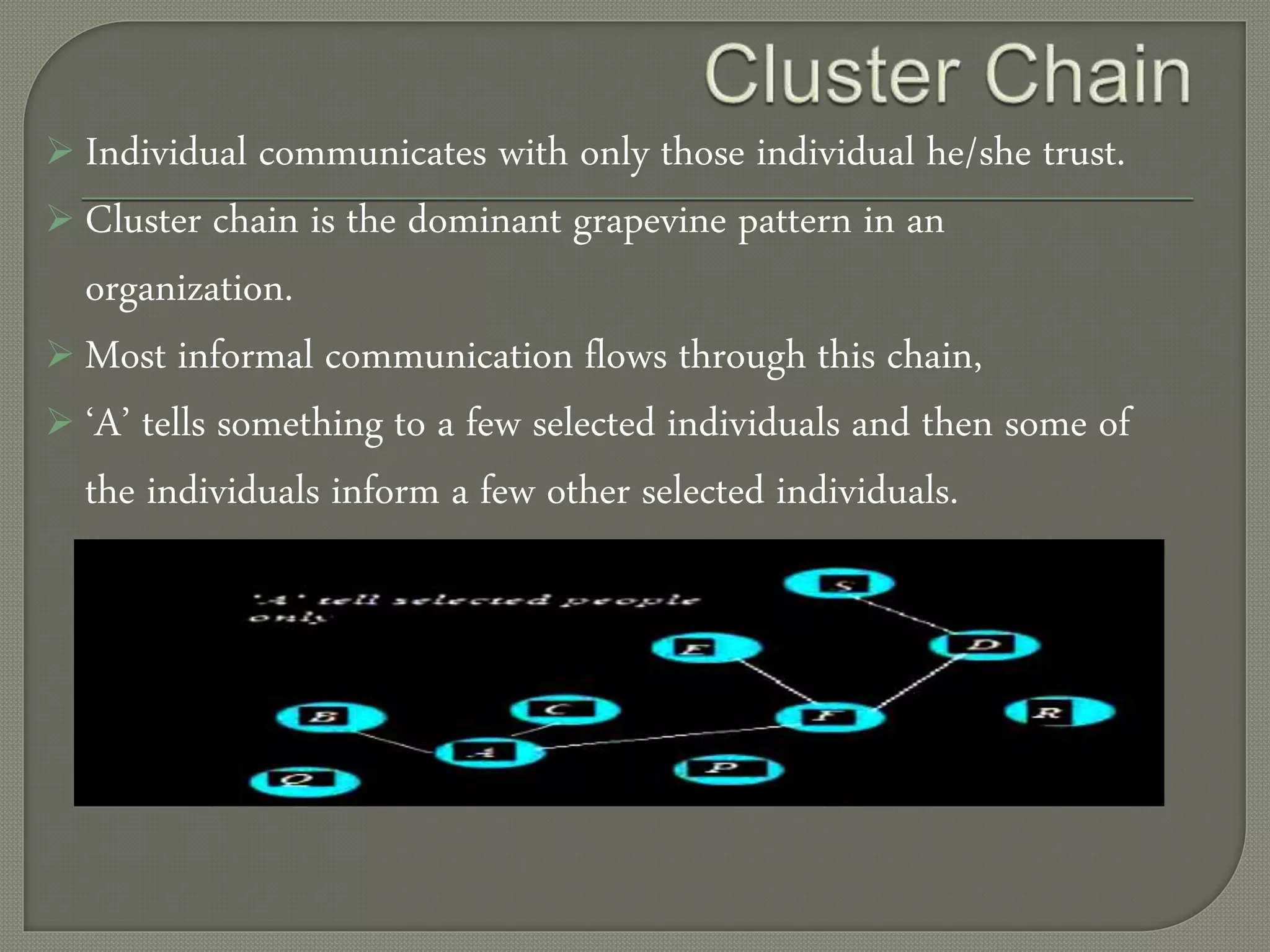
The document discusses the concept of the organizational grapevine, which refers to the informal flow of information through gossip and rumors within an organization. It outlines various characteristics, types, advantages, and disadvantages of this communication method, emphasizing its rapid transmission and potential inaccuracies. The text suggests maintaining clear and timely formal communication to mitigate the negative impacts of grapevine communication.