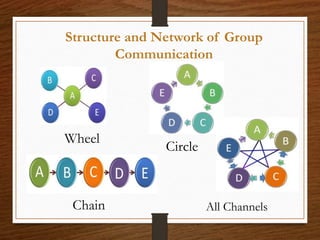
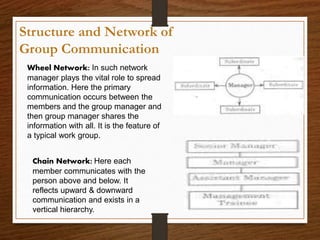
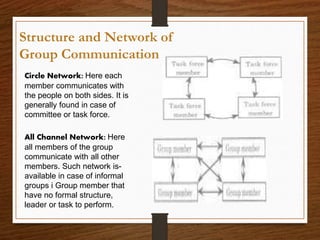
This document discusses group communication in organizations. It defines group communication as communication between employers, employees, and employee teams/groups. The importance of group communication is highlighted as sharing ideas, solving problems, delegating tasks, and developing a sense of group identity. Small group communication refers to interactions among 3 or more people connected by a common purpose, while large group communication describes communication in large organizations. Different structures and networks of group communication are described, including wheel, chain, circle, and all channel networks. A case study examines how Facebook was used to facilitate project-based learning in an EFL context in Taiwan.