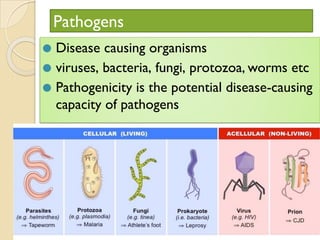
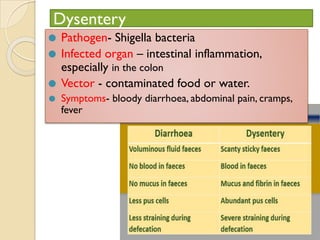
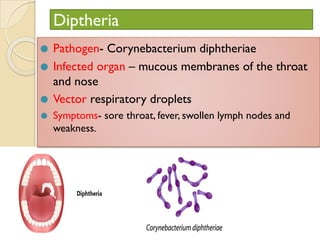
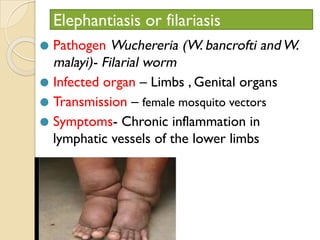
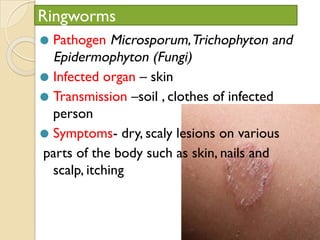
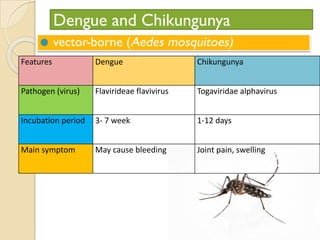
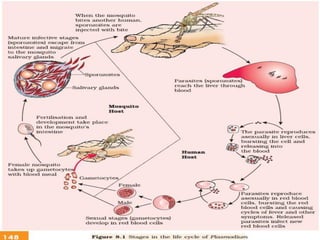
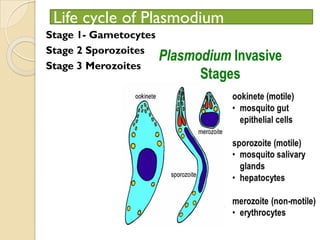
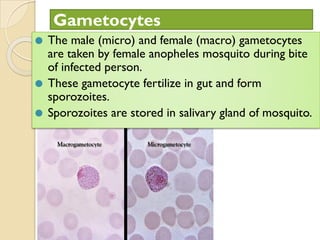
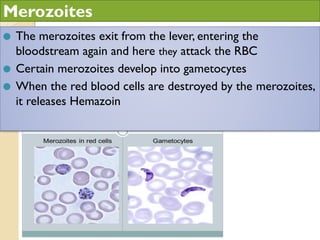
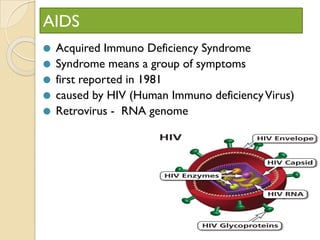
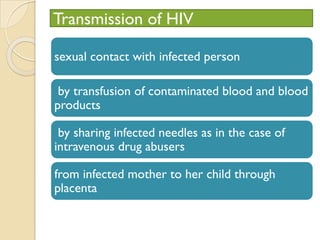
Human health and disease can be affected by genetic disorders, infections, and lifestyle. Diseases can be infectious, spread between people, or non-communicable. Common infectious diseases discussed include typhoid caused by Salmonella bacteria affecting the GI tract, pneumonia caused by bacteria affecting the lungs, and dysentery caused by Shigella bacteria affecting the intestines. Non-infectious diseases include malaria transmitted via mosquitoes which affects the liver and blood cells. HIV/AIDS is also discussed, caused by the HIV virus which attacks immune cells and can be transmitted sexually or via blood.