This document discusses combustion and related topics. It defines combustion as a chemical reaction between a substance and oxygen that produces heat. It describes the types of combustion as rapid, spontaneous, or explosive. It explains that the ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a substance will catch fire. Substances with low ignition temperatures are called inflammable. Burning fuels produces harmful byproducts like carbon particles, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and sulfur dioxide, which can damage health, environment and property.







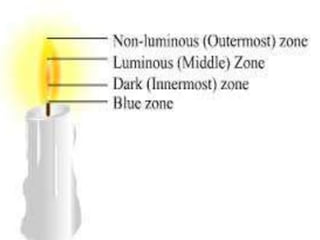
![FLAME& STRUCTURE
Flame is a hot glowing body of ignited gas that is
generated by something on fire. The substances
which vaporize during burning give flames.
Example: Candle
Flames have 3 types of zones:
1. Outer Zone[blue]
2. Middle Zone[yellow]
3. Inner Zone[black]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/combustionandflame-151101115901-lva1-app6892/85/Combustion-and-flame-8-320.jpg)