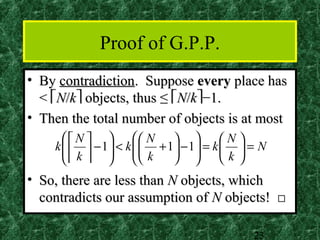
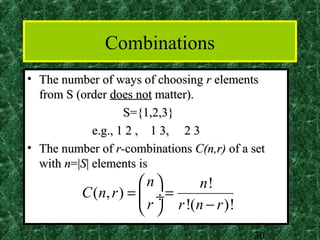
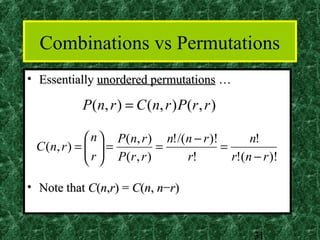
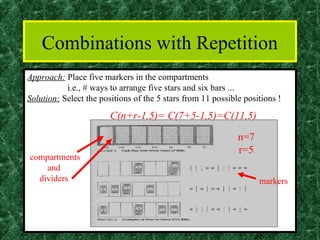
This document provides an introduction to combinatorics including the sum rule, product rule, permutations, and combinations. The sum rule states that if tasks are independent, the number of ways to do either task is the sum of the number of ways to do each individually. The product rule states that if tasks are independent, the number of ways to do both tasks is the product of the number of ways to do each. Permutations refer to ordered arrangements and combinations refer to unordered arrangements. The document includes examples of applying these concepts.