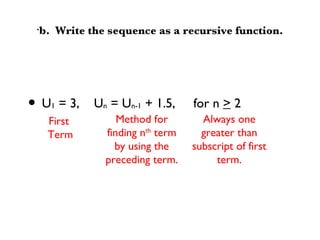
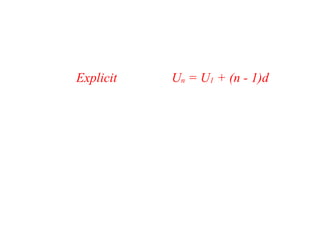
An arithmetic sequence is a sequence where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. The common difference (d) is this constant value. The recursive formula for an arithmetic sequence is Un = Un-1 + d and the explicit formula is Un = U1 + (n - 1)d. Given values for the first few terms, you can find the common difference and write the recursive and explicit formulas to generate all terms of the sequence.