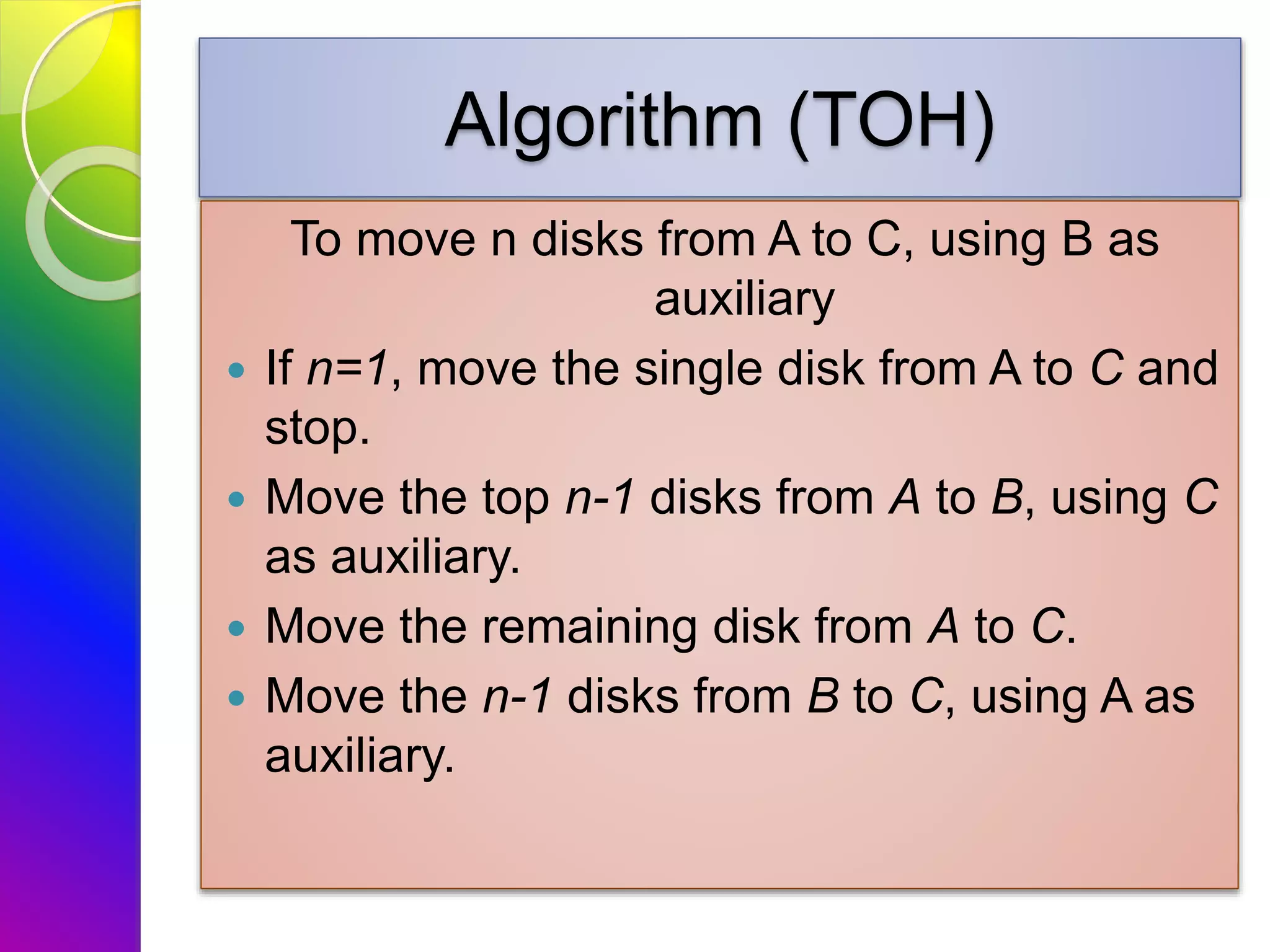
The document discusses recursion, explaining that it refers to a function that can call itself to solve a problem until a specific condition is met. It highlights the advantages, such as efficiency and reduced coding, as well as disadvantages including the risk of infinite loops if not managed correctly. Additionally, the document provides examples of recursive functions, such as the factorial function and the Tower of Hanoi problem, illustrating the principles of recursion in action.