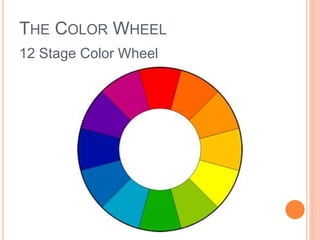
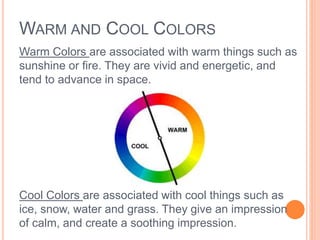
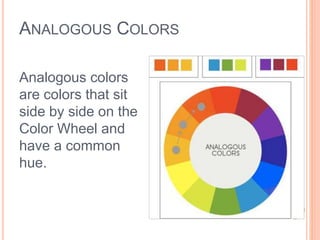
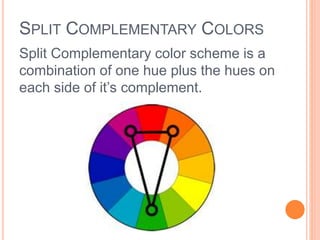
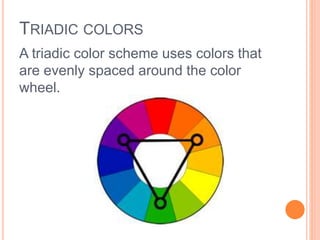
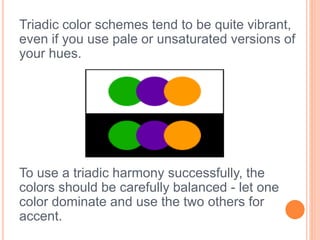
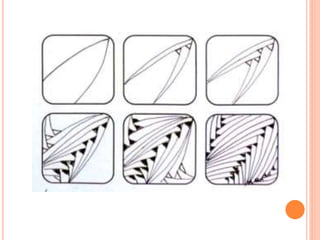
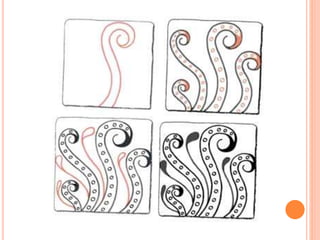
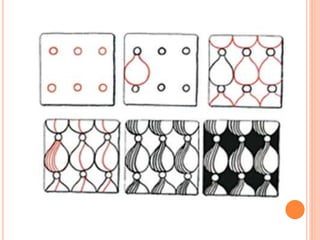
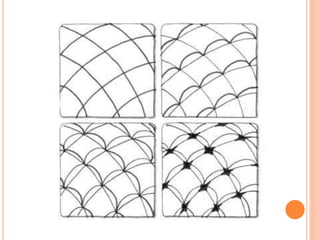
Color is produced when light reflects off objects into our eyes. There are three properties of color: hue (name of color), intensity (strength of color), and value (lightness or darkness). There are two color wheels - the additive color wheel used in technology with primary colors red, green, blue and secondary cyan, yellow, magenta, and the subtractive color wheel used in printing with primary colors cyan, magenta, yellow and secondary red, blue, green. The document then discusses primary, secondary, tertiary, warm, cool, complementary, analogous, split complementary, monochromatic, and triadic color schemes. It concludes with instructions for Zentangle art which uses repetitive patterns and doodling within a