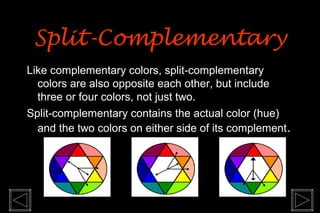
The document discusses color theory and color wheel principles. It defines primary, secondary, tertiary, warm, cool colors. It explains how to create tints and shades using black and white. Color schemes like monochromatic, complementary, split-complementary and analogous are described. Key elements of hue, chroma, tone and achromatic colors are also summarized. Examples of paintings using different color schemes are provided.