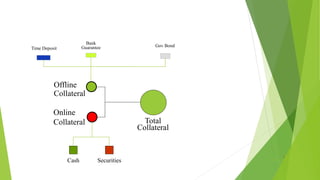
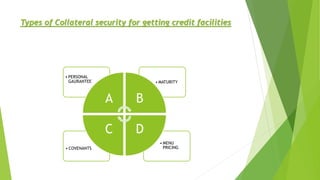
This document discusses different types of collateral security that can be used to secure loans. It defines collateral security as property or other assets offered by a borrower to a lender to secure a loan. If the borrower defaults, the lender can seize the collateral. The document provides examples of acceptable collateral like cash, securities, land, buildings, and personal guarantees. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of different types of collateral security and how they can help mitigate risk for the lender.