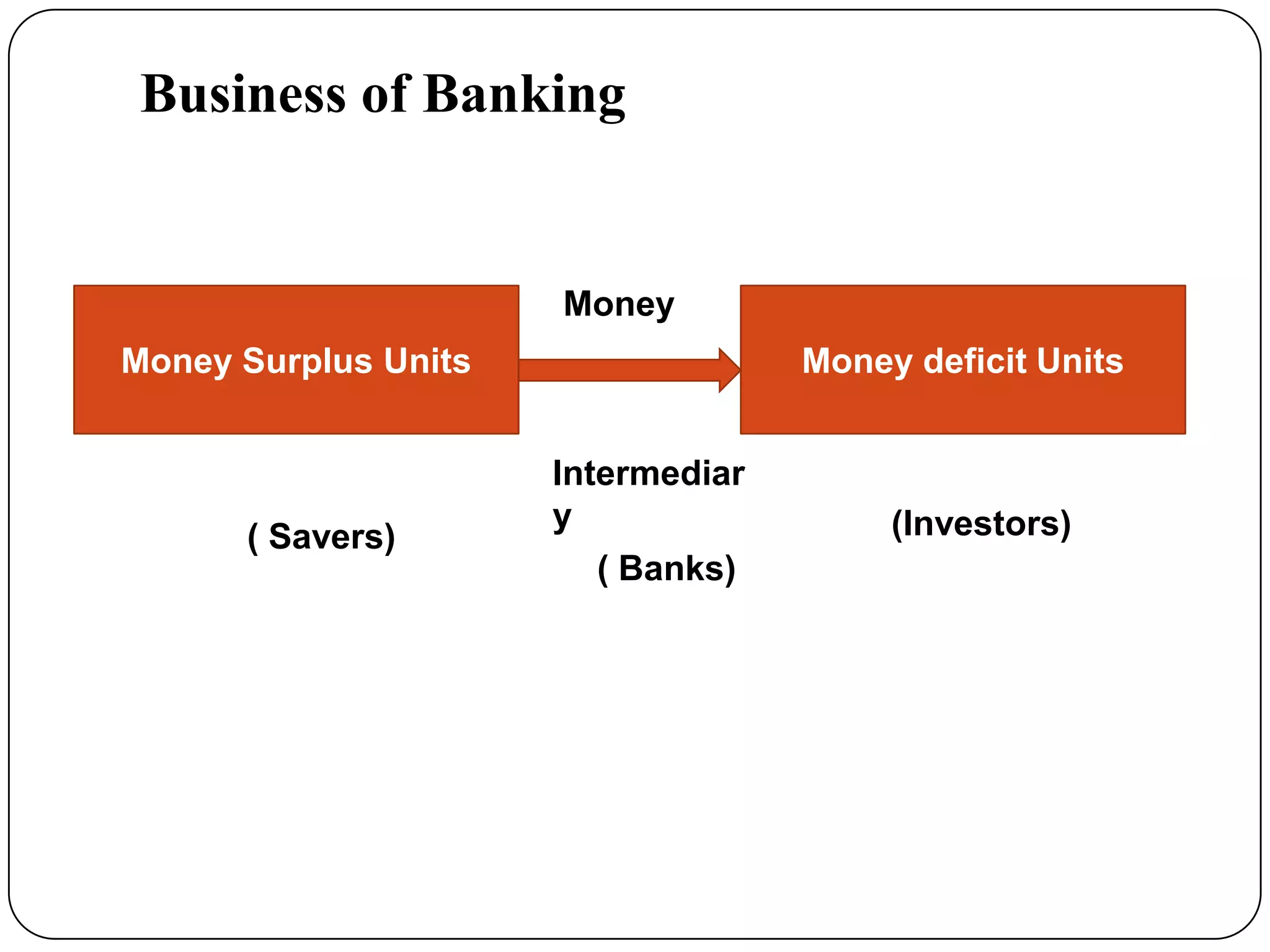
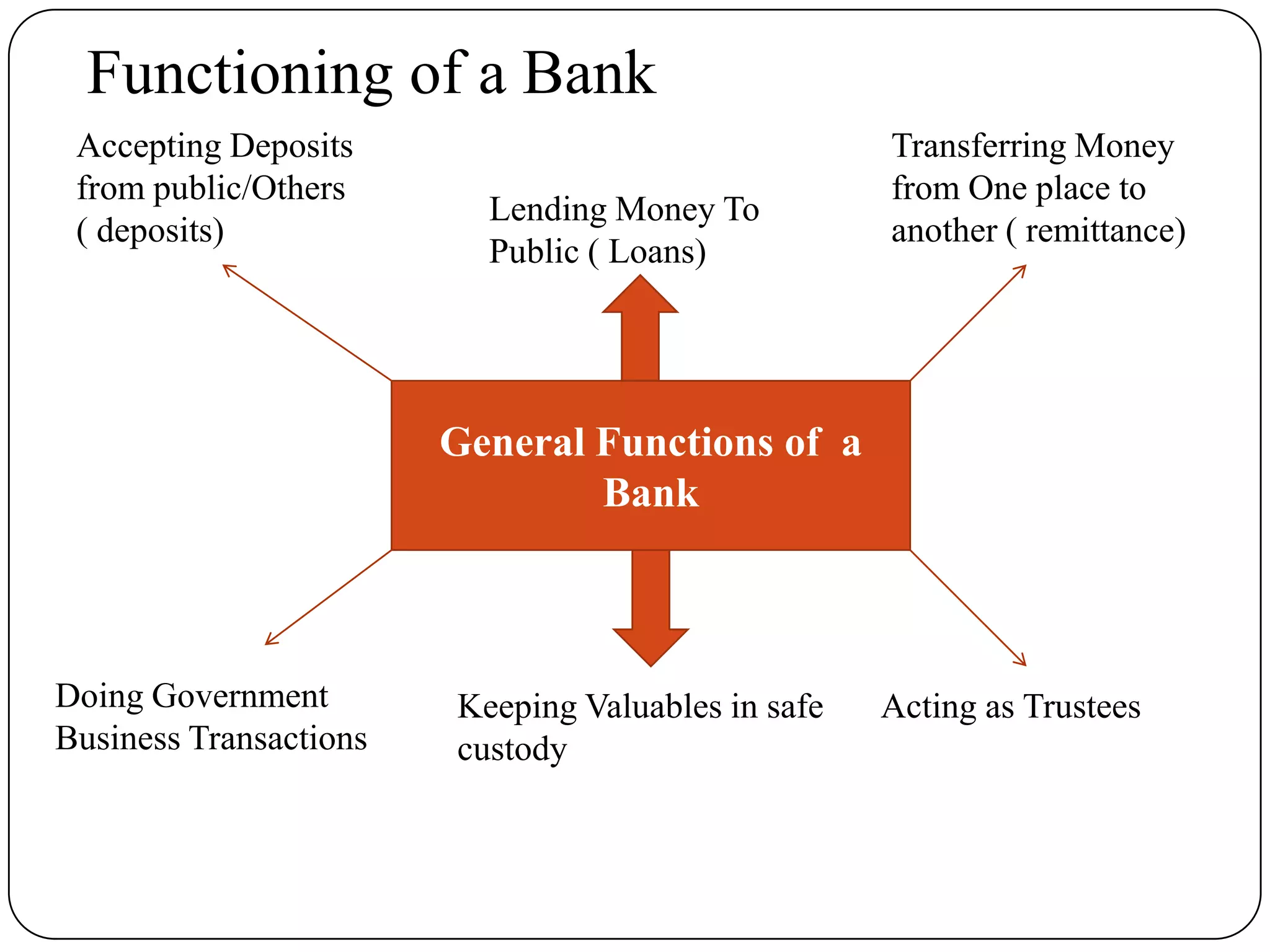
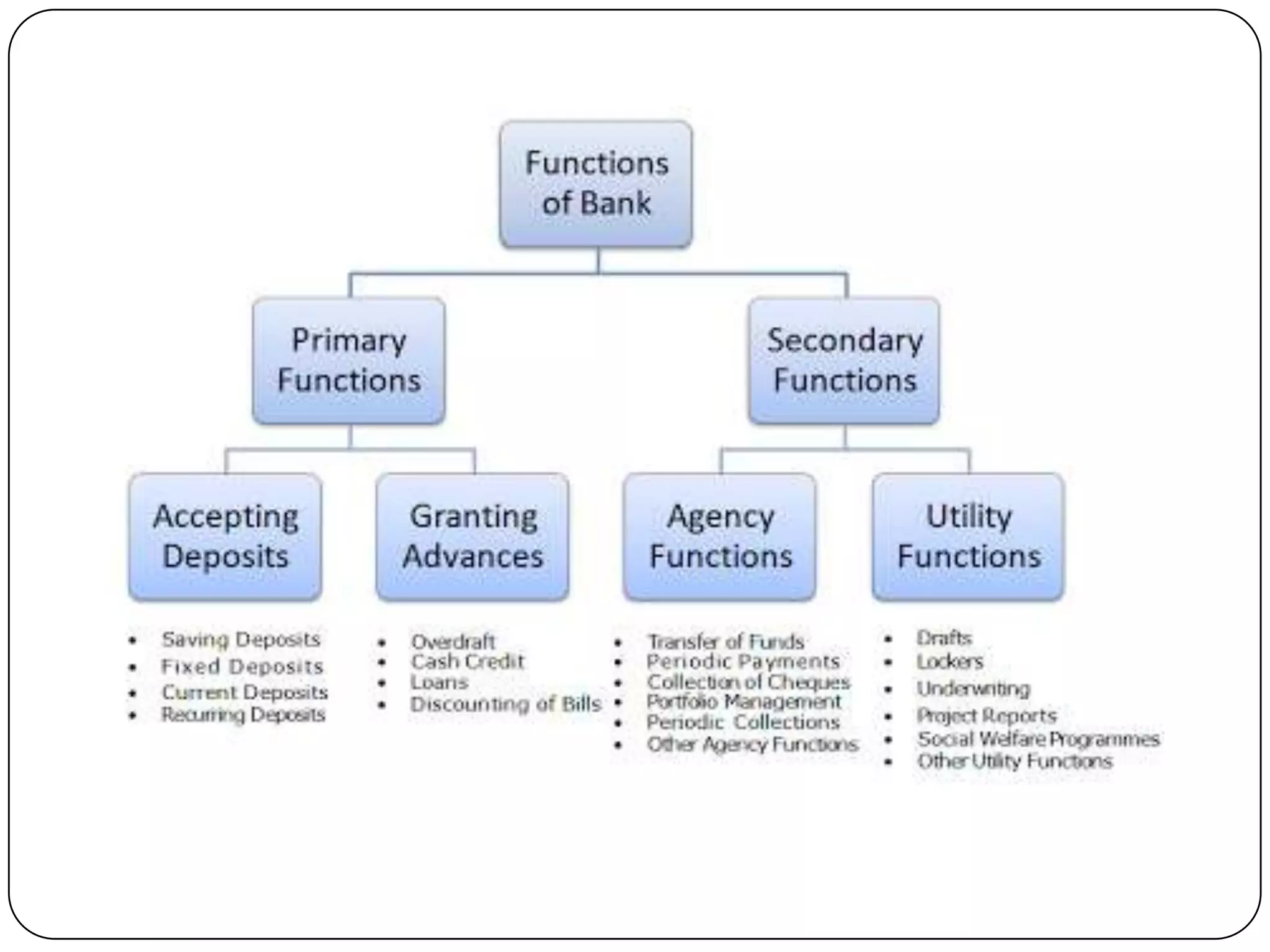
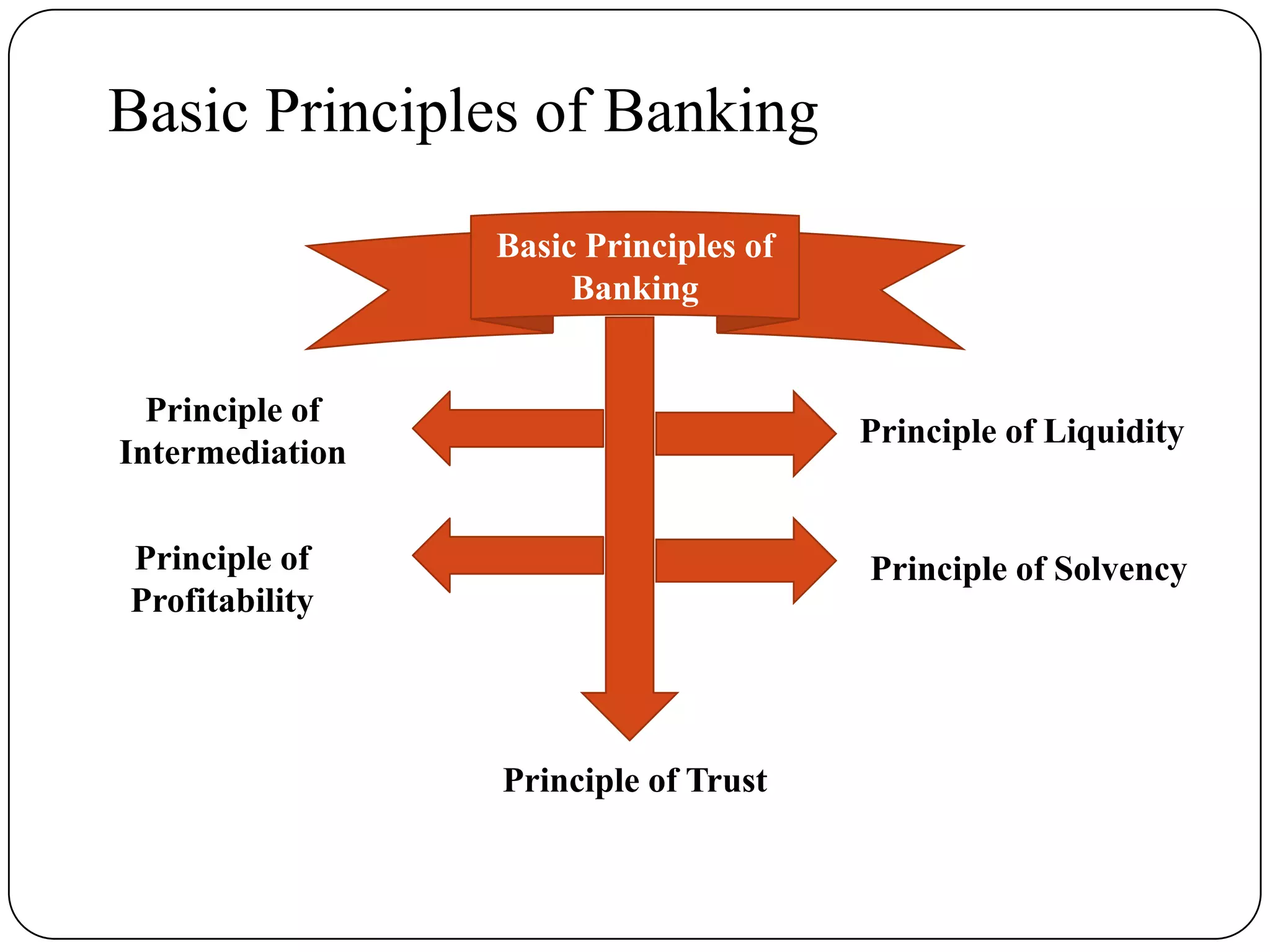
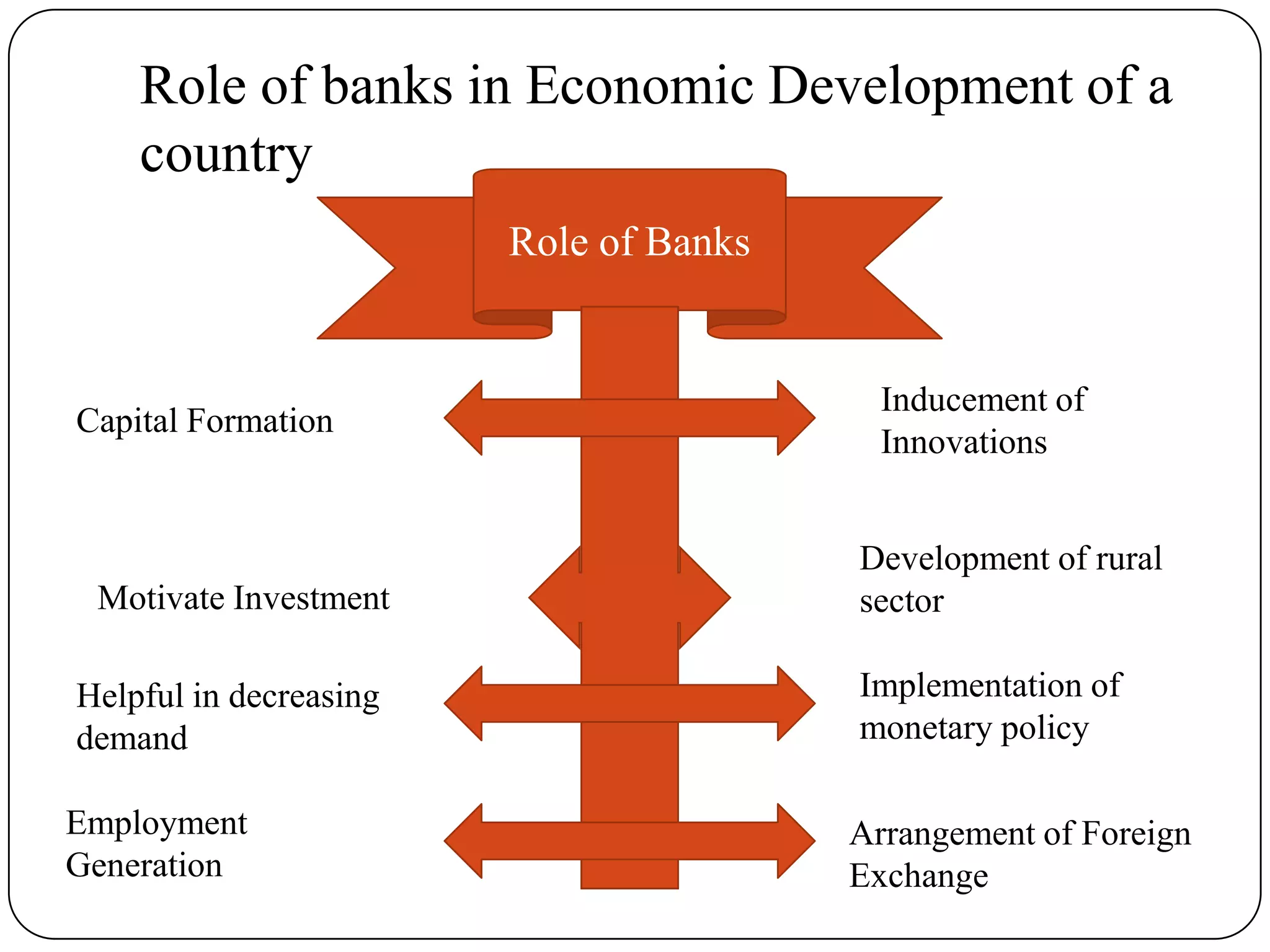
Indian banking originated in the 18th century with the establishment of the General Bank of India. Key events in Indian banking history include the founding of the State Bank of India in 1806 and the nationalization of the Reserve Bank of India in 1947. Banks act as intermediaries between savers and borrowers, accepting deposits and lending money. The basic principles of banking include trust, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and intermediation. Banks play an important role in a country's economic development by facilitating capital formation, investment, employment generation, and implementing monetary policy.