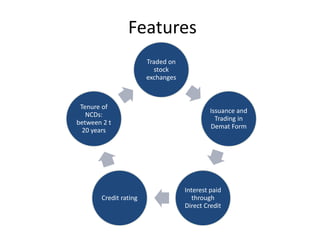
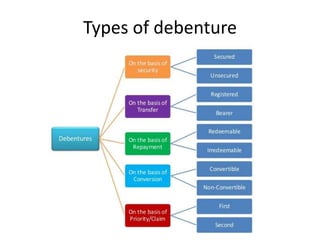
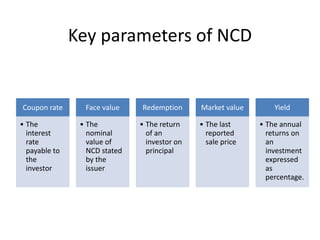
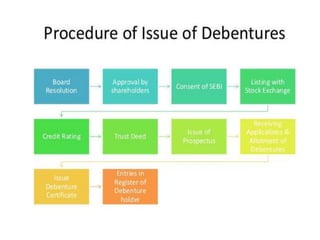
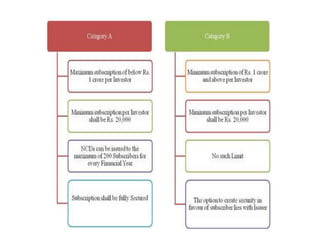
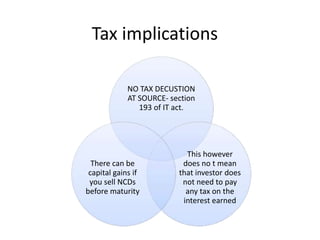
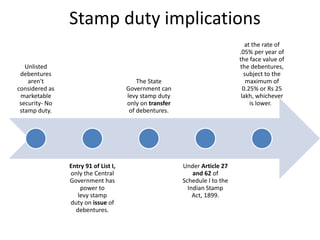
The document provides a detailed overview of non-convertible debentures (NCDs), including features, types, regulatory frameworks, and issuance processes. It outlines specific criteria for private placements, the role of debenture trustees, and tax implications associated with NCDs. Key parameters such as coupon rate, face value, redemption, and market value are also discussed.