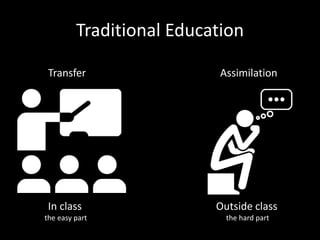
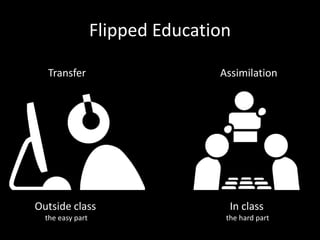
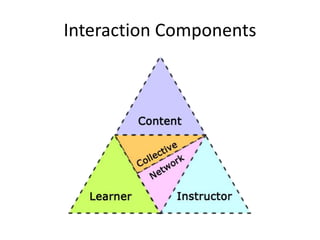
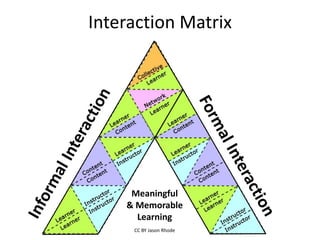
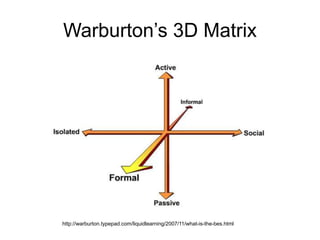
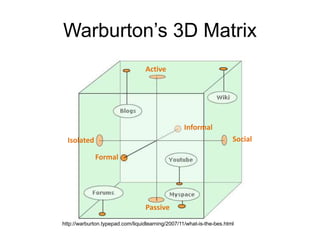
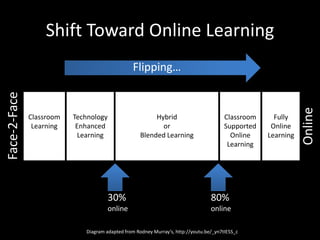
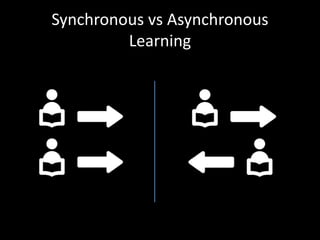
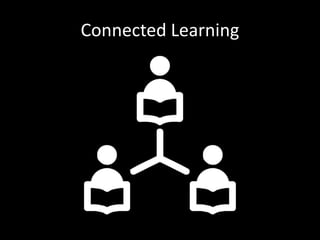
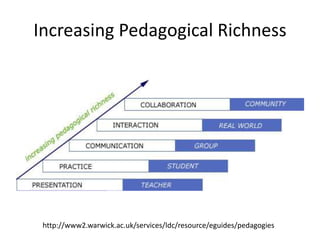
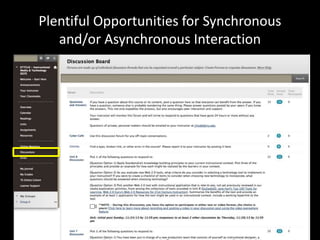
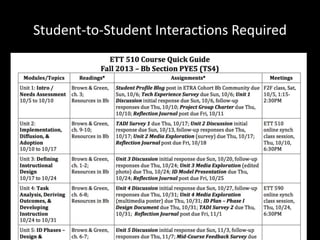
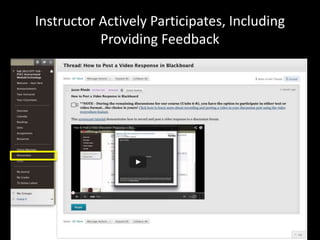
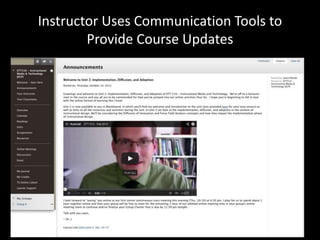
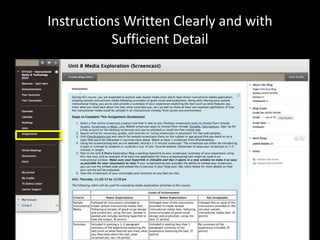
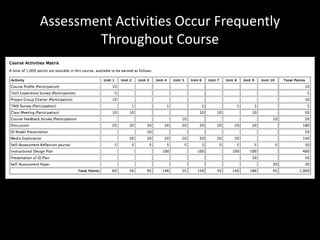
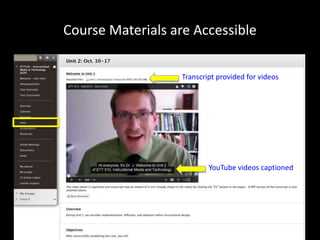
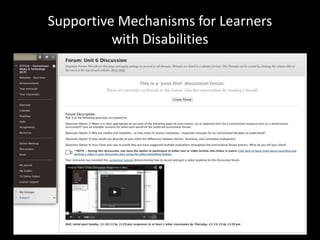
The document discusses the concept of flipping traditional education by leveraging technology for active learning in online and blended courses. It outlines the importance of meaningful interaction and engagement in course design, emphasizing quality learning experiences through clear standards, assessment, and collaboration. Additionally, it references the Blackboard Catalyst program, highlighting innovative teaching practices and support for faculty development.