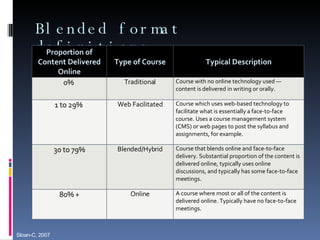
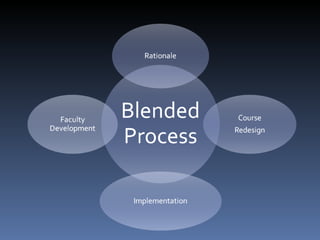
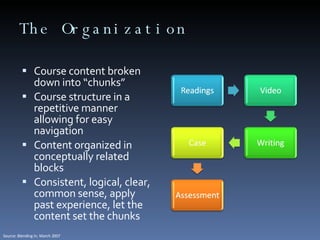
This document summarizes an overview presentation on blended learning. It defines blended learning as combining online and classroom activities to improve student learning outcomes. It discusses implementing blended learning at various levels, from 10% to 70% of course offerings. Key aspects covered include faculty development, course design process breaking content into modules linked to objectives, and supporting faculty with resources and training.




































![Veronica M. Diaz, PhD [email_address] http://www.mcli.dist.maricopa.edu/diaz/ Questions and answers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blended-learning-final-1219088822433484-8/85/MCC-Blended-Learning-44-320.jpg)