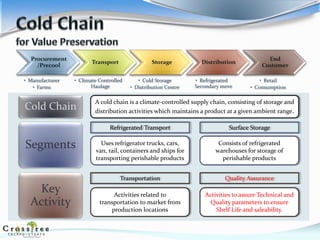
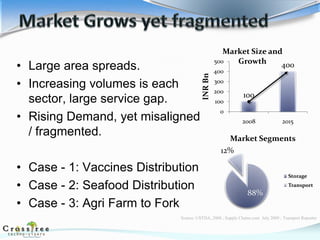
The document provides an overview of the cold chain industry in India. It discusses key segments like refrigerated transport and storage. It notes that the market is estimated at $9 billion in 2015 and is growing due to factors like organized retail, horticultural crops, and processed foods. Challenges include a lack of logistical support and human resources. Trends include public-private partnerships and rail-based refrigerated transport. Competition is currently minimal but increasing. The government is taking initiatives to support the industry through policies and funding. The future of the cold chain industry in India looks promising.