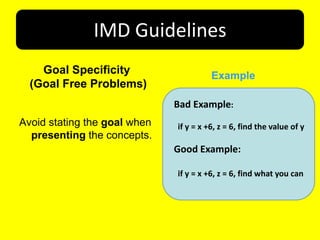
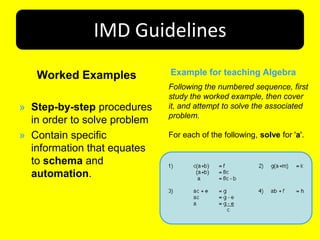
This document provides an overview of Cognitive Load Theory for instructional designers. It discusses the theory's focus on optimizing learner's intellectual performance given the limitations of working memory. It describes three types of cognitive load - intrinsic, extraneous, and germane. Key researchers who developed the theory such as John Sweller and Jeroen van Meriënboer are mentioned, as well as their contributions. Guidelines for Instructional Model Design (IMD) derived from the theory are presented, including examples of goal specificity, worked examples, and completion tasks. References for further information are provided at the end.