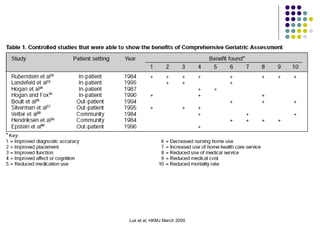
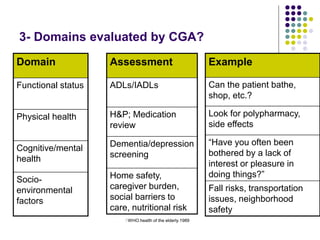
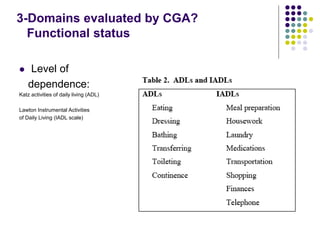
The document discusses comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA), which is a multidisciplinary evaluation of elderly patients to develop a treatment plan. It defines CGA and explains its importance in evaluating multiple domains, including functional status, physical health, mental health, and socio-environmental factors. Several assessment tools are described for each domain. The document also analyzes a clinical case study of an elderly patient who fell and demonstrates how CGA would evaluate her across different areas.