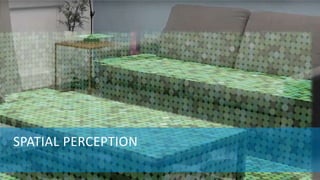
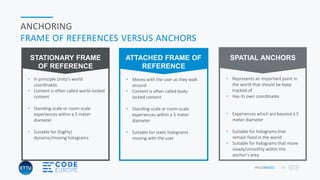
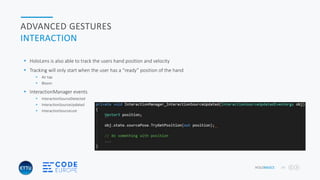
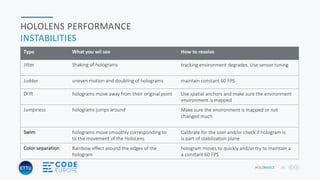
This document presents an overview of advanced mixed reality applications for Microsoft HoloLens, highlighting its functionalities, hardware specifications, and development tools. It discusses key concepts such as spatial perception, coordinate systems, anchoring, and advanced gesture recognition. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of optimizing applications for performance and stability while providing resources for further development and community engagement.