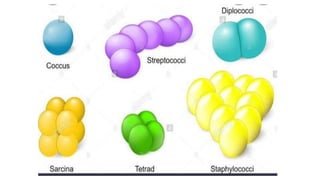
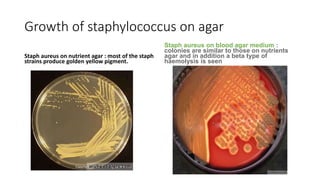
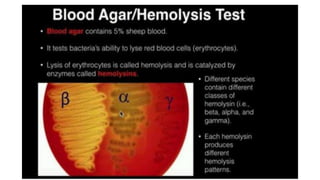
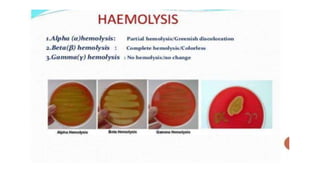
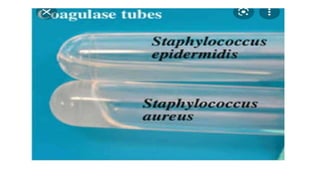
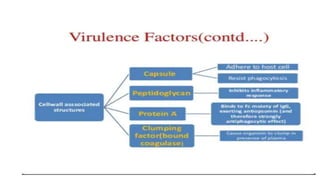
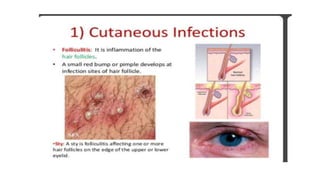
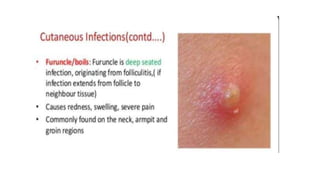
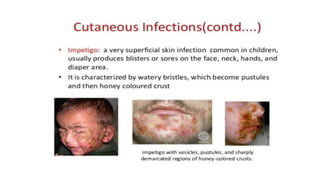
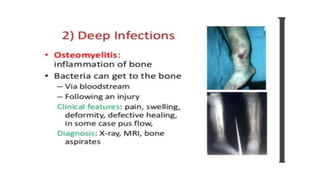
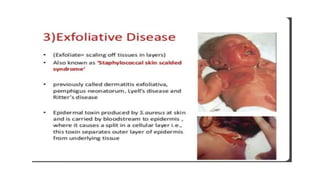
Cocci are spherical or oval shaped bacteria that can be arranged in pairs, chains, or clusters. Staphylococcus aureus is a gram positive coccus that grows in grape-like clusters and is an important human pathogen. S. aureus is identified by its beta-hemolytic activity on blood agar, ability to coagulate plasma, and production of golden pigment and acid from mannitol fermentation. Treatment involves penicillin for sensitive strains, or other antibiotics like cephalosporins, clindamycin, or vancomycin depending on the infection severity and patient allergy profile.