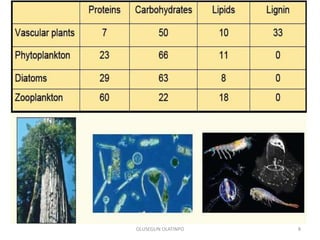
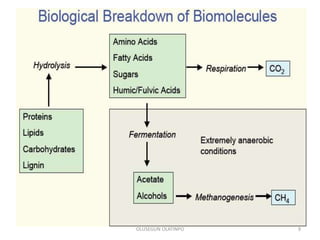
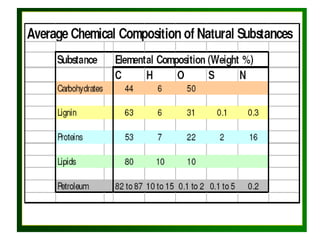
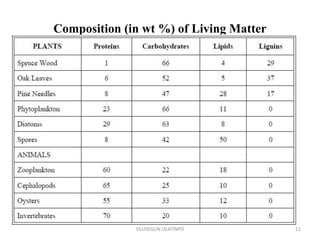
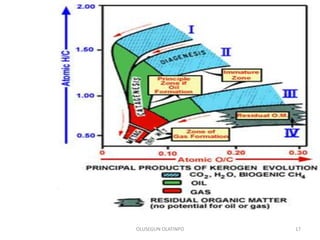
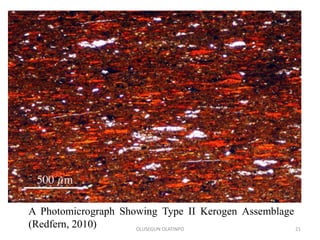
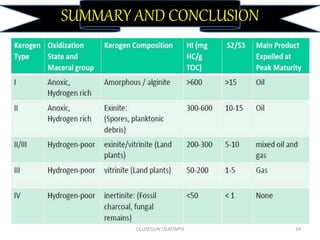
Kerogen is composed of the insoluble organic matter in sedimentary rocks that is capable of generating petroleum. It is formed from the decomposed remains of organisms like bacteria, algae, and plants. Kerogen is classified into four main types - Type I kerogen forms from algal matter and yields large amounts of oil; Type II kerogen is a mix of marine and terrestrial organic matter and is the most prolific source; Type III kerogen derives from woody plant debris and yields more gas; Type IV kerogen is highly carbonaceous but incapable of generating petroleum. The composition and source of the organic matter determines the type of kerogen formed and ultimately influences the hydrocarbon products generated during maturation.