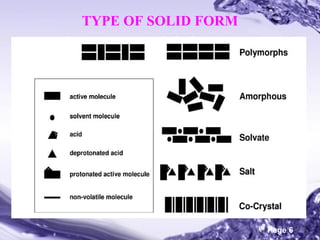
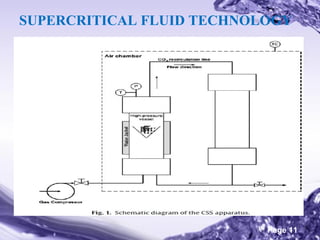
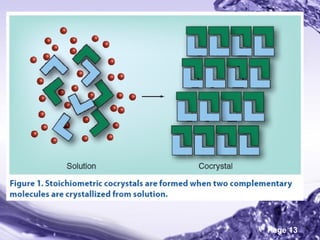
This document discusses the co-crystal technique for enhancing the solubility of poorly water soluble drugs. It introduces co-crystals as crystalline materials comprised of an active pharmaceutical ingredient and one or more co-crystal formers. Co-crystals can improve solubility and bioavailability through interactions like hydrogen bonding and pi-stacking. The document outlines various methods for preparing co-crystals, including solution methods, grinding, and supercritical fluid technology. It also discusses selecting appropriate co-formers, solvents, and evaluation methods like powder X-ray diffraction and solubility analysis. Several marketed drug products incorporating co-crystal technology are presented as examples.