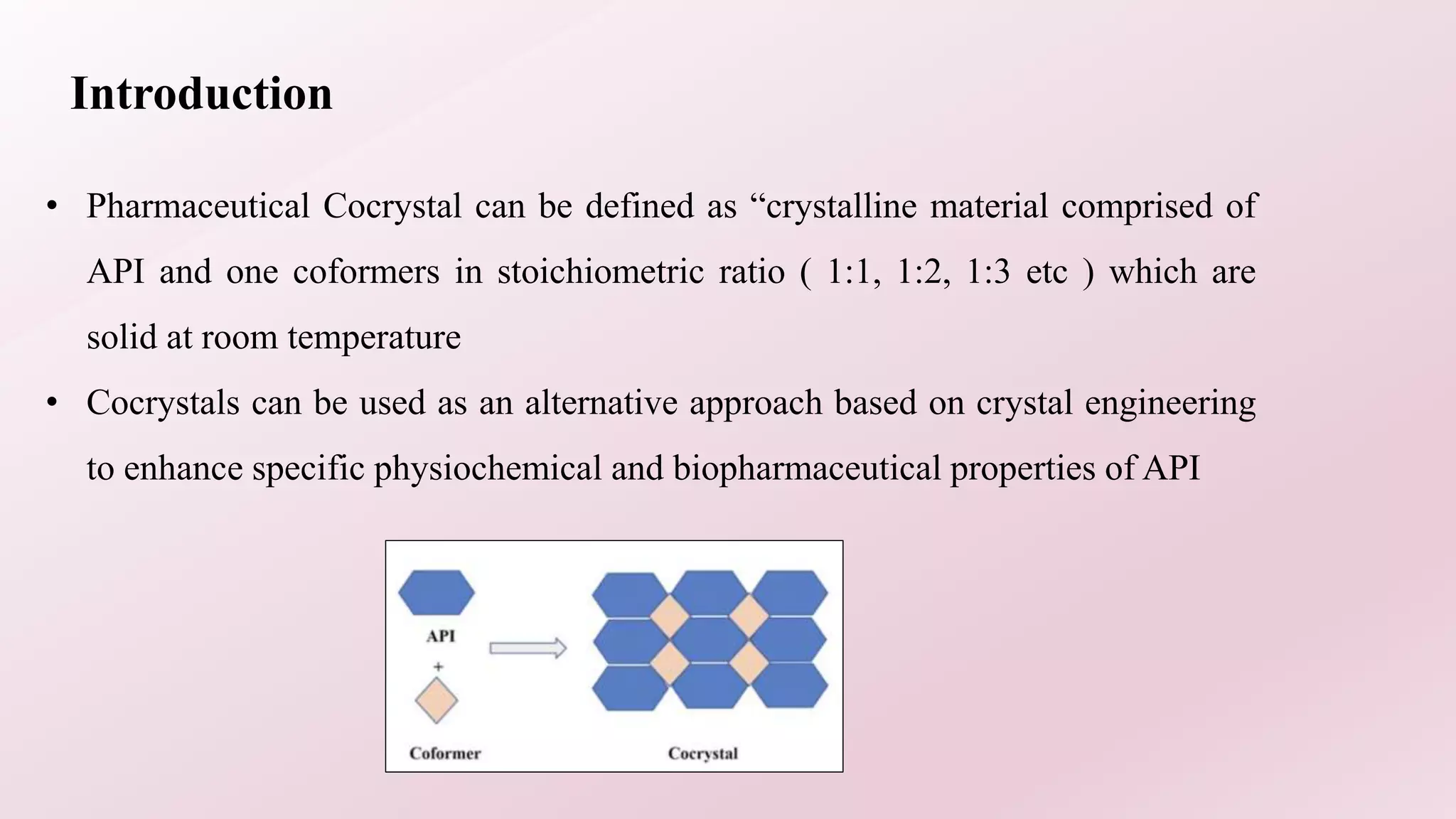
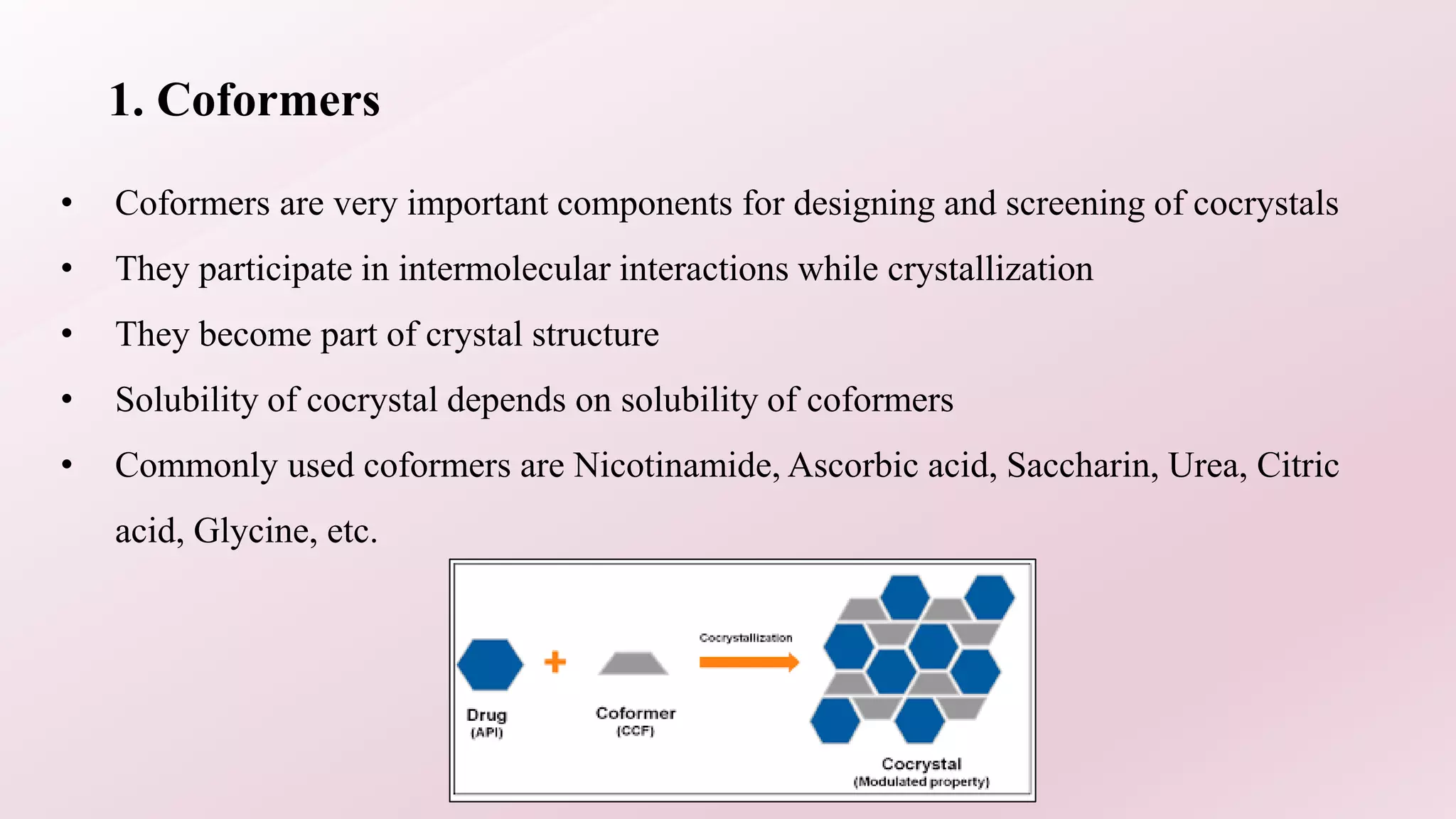
1. The document discusses cocrystals for solubility enhancement of APIs. Cocrystals are crystalline materials made of an API and coformer in a stoichiometric ratio.
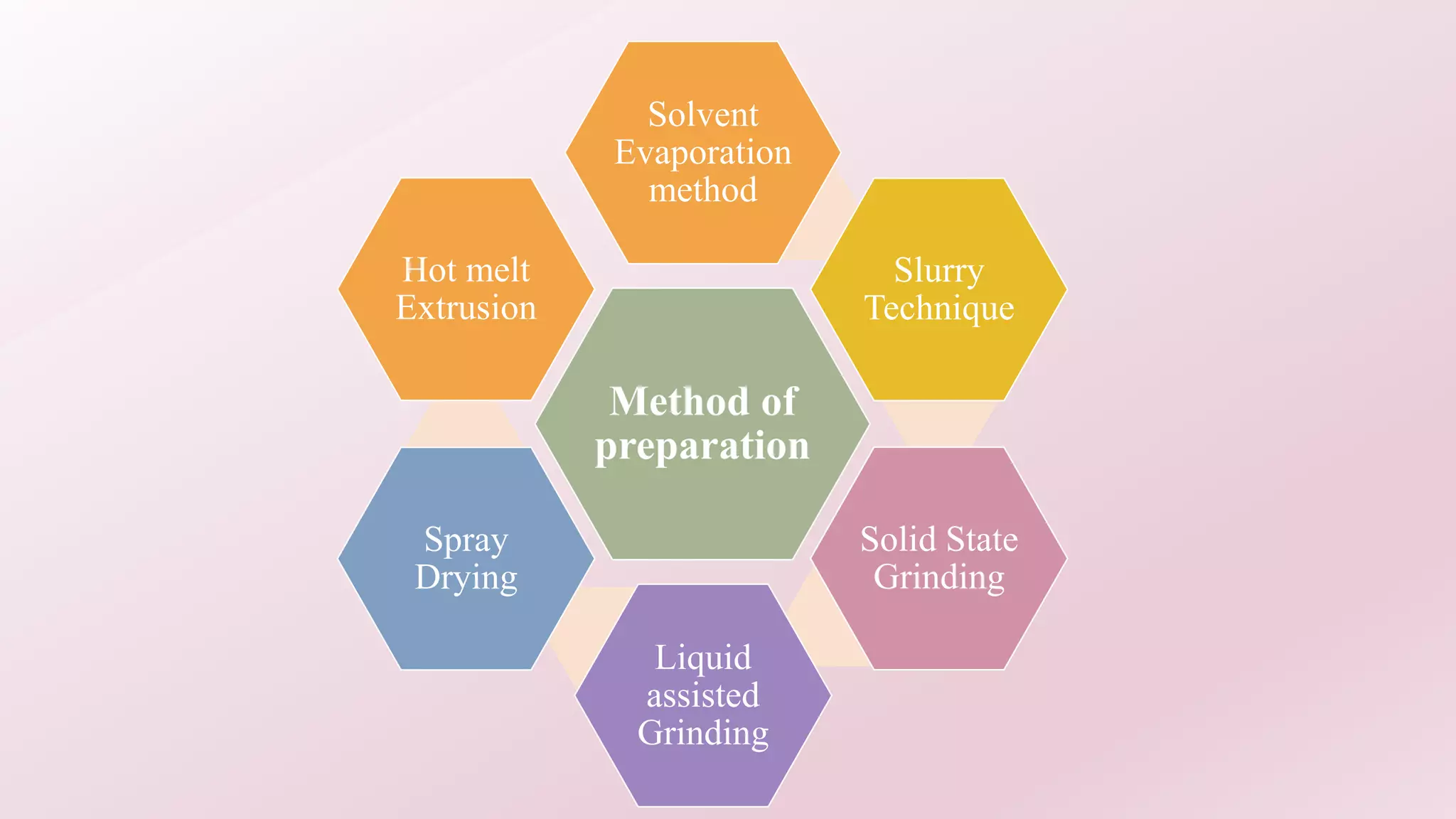
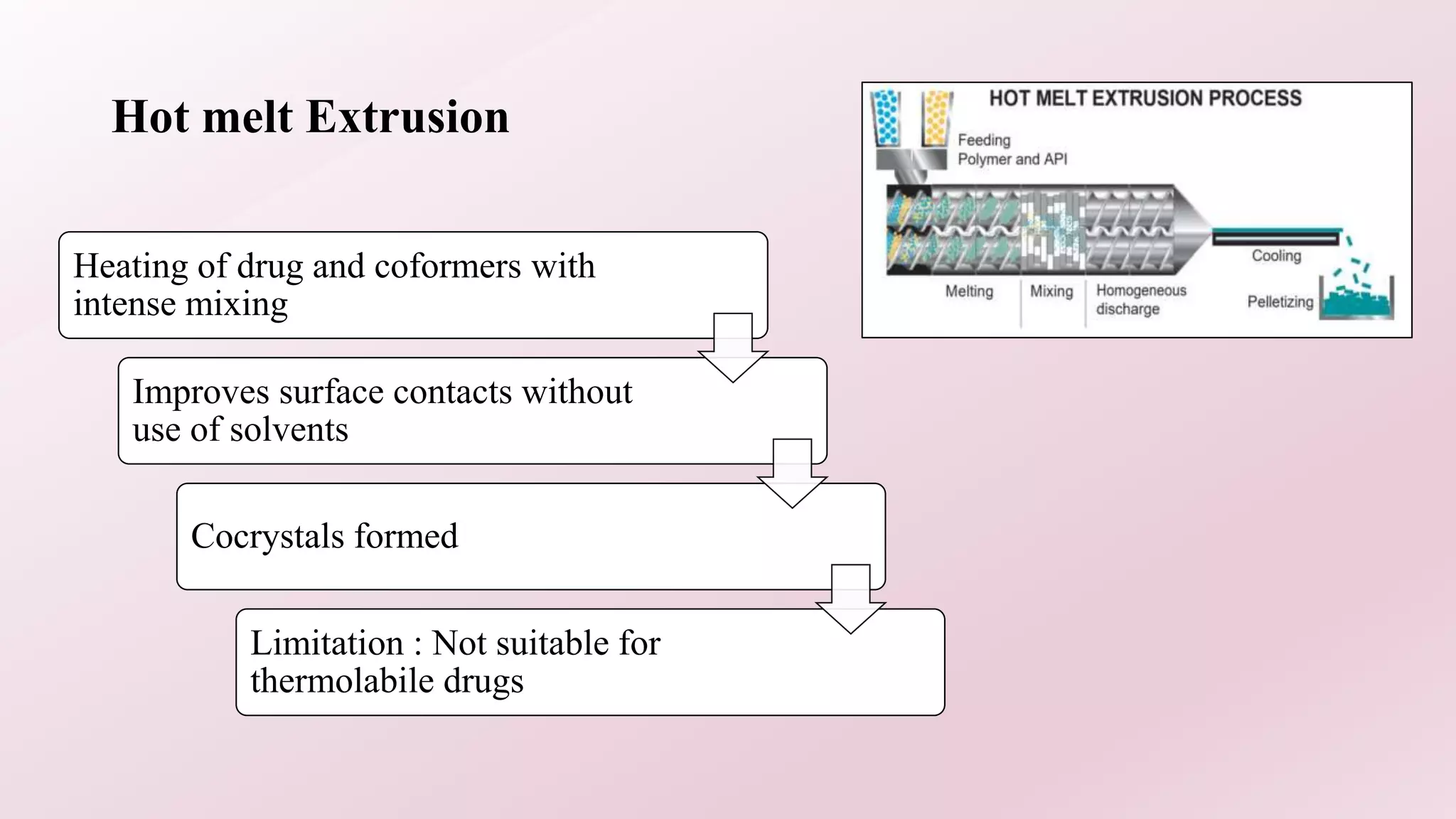
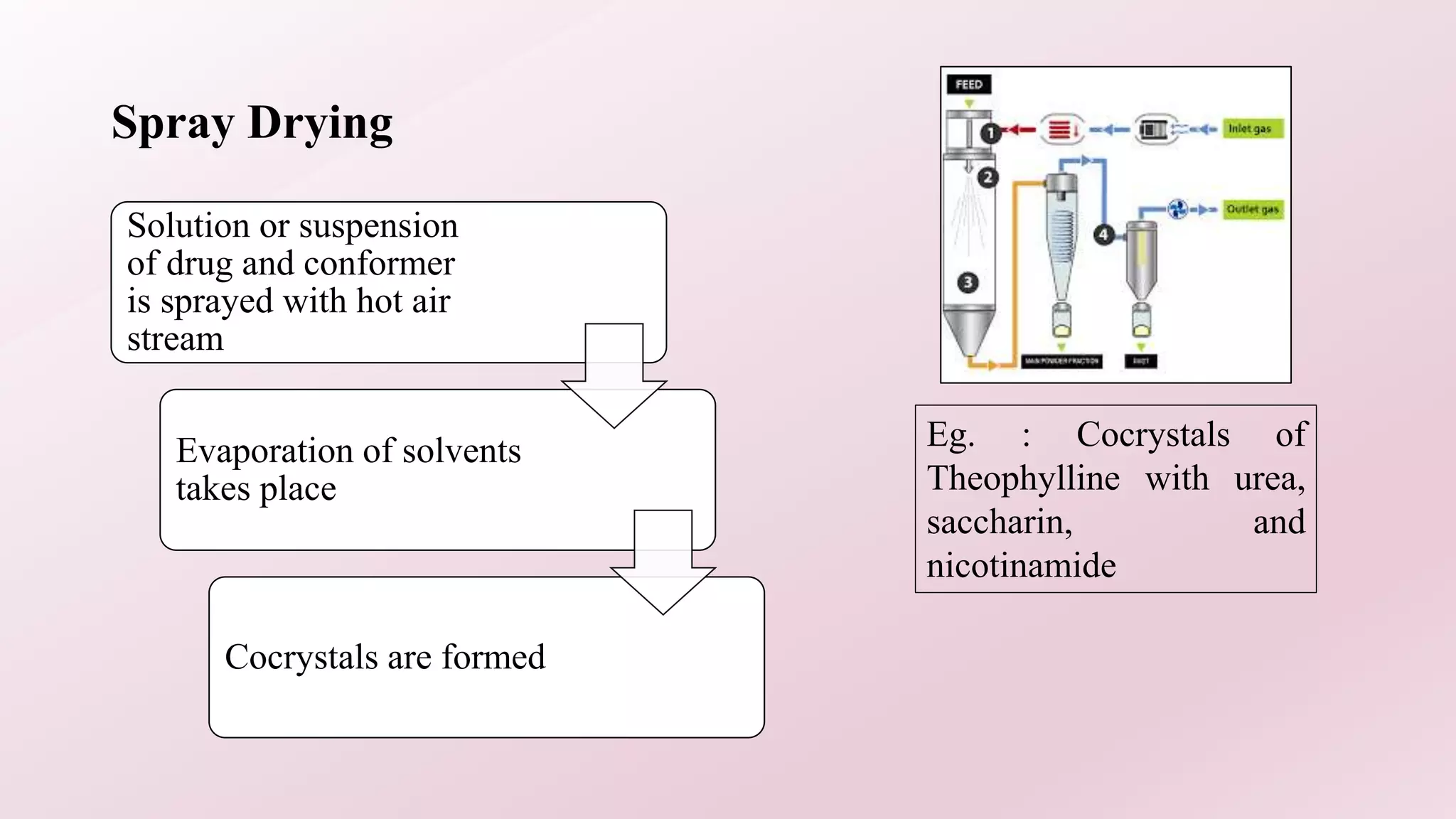
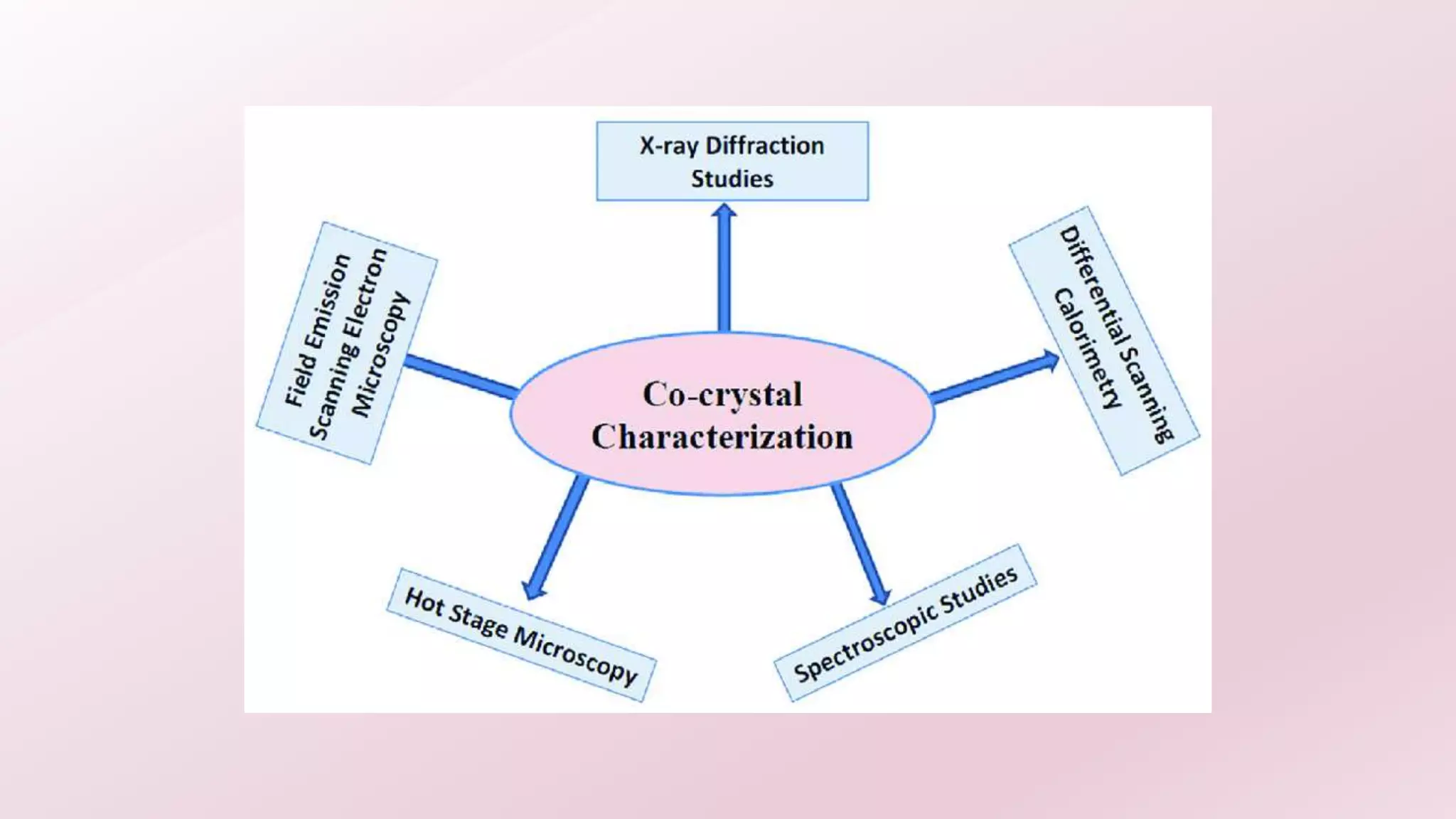
2. Several methods are described for preparing cocrystals including solvent evaporation, slurry technique, solid state grinding, and spray drying. Characterization techniques like XRD, DSC, and IR are used to analyze the cocrystals.
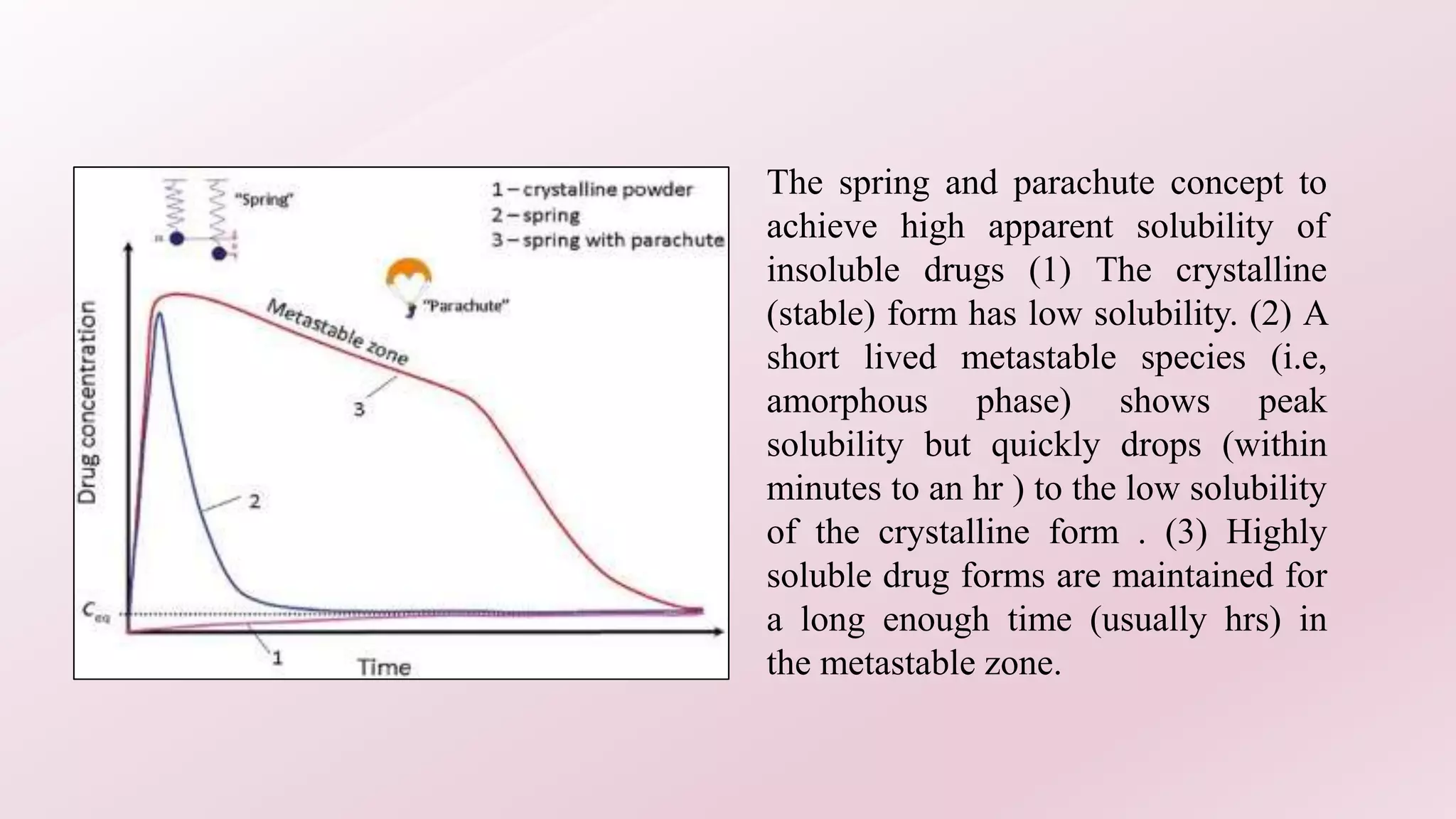
3. Examples demonstrate how cocrystallization can increase solubility and bioavailability of APIs like sildenafil, danazol, and aceclofenac. The "spring and parachute" concept is discussed for maintaining supersaturation of drugs to enhance absorption.