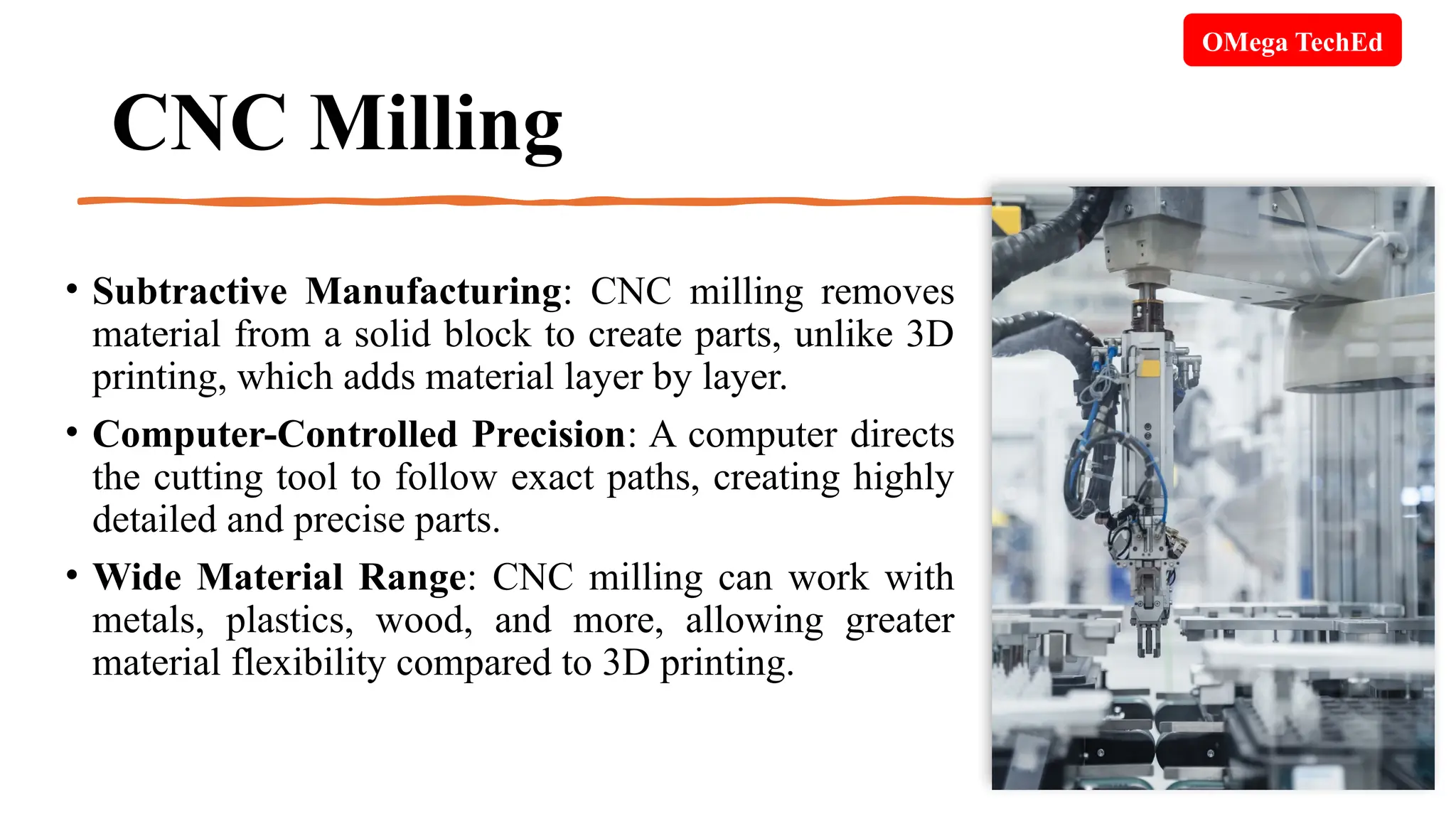
CNC milling is a precise manufacturing process that utilizes computer control to remove material from a workpiece, enabling the creation of complex shapes. This method allows for a wide range of materials, is efficient with the ability to perform multiple operations simultaneously, and involves different axes of movement to increase capability. Additionally, the document discusses repurposing and recycling as essential practices for extending the life cycle of materials, emphasizing the benefits of reusing components in connected device projects.