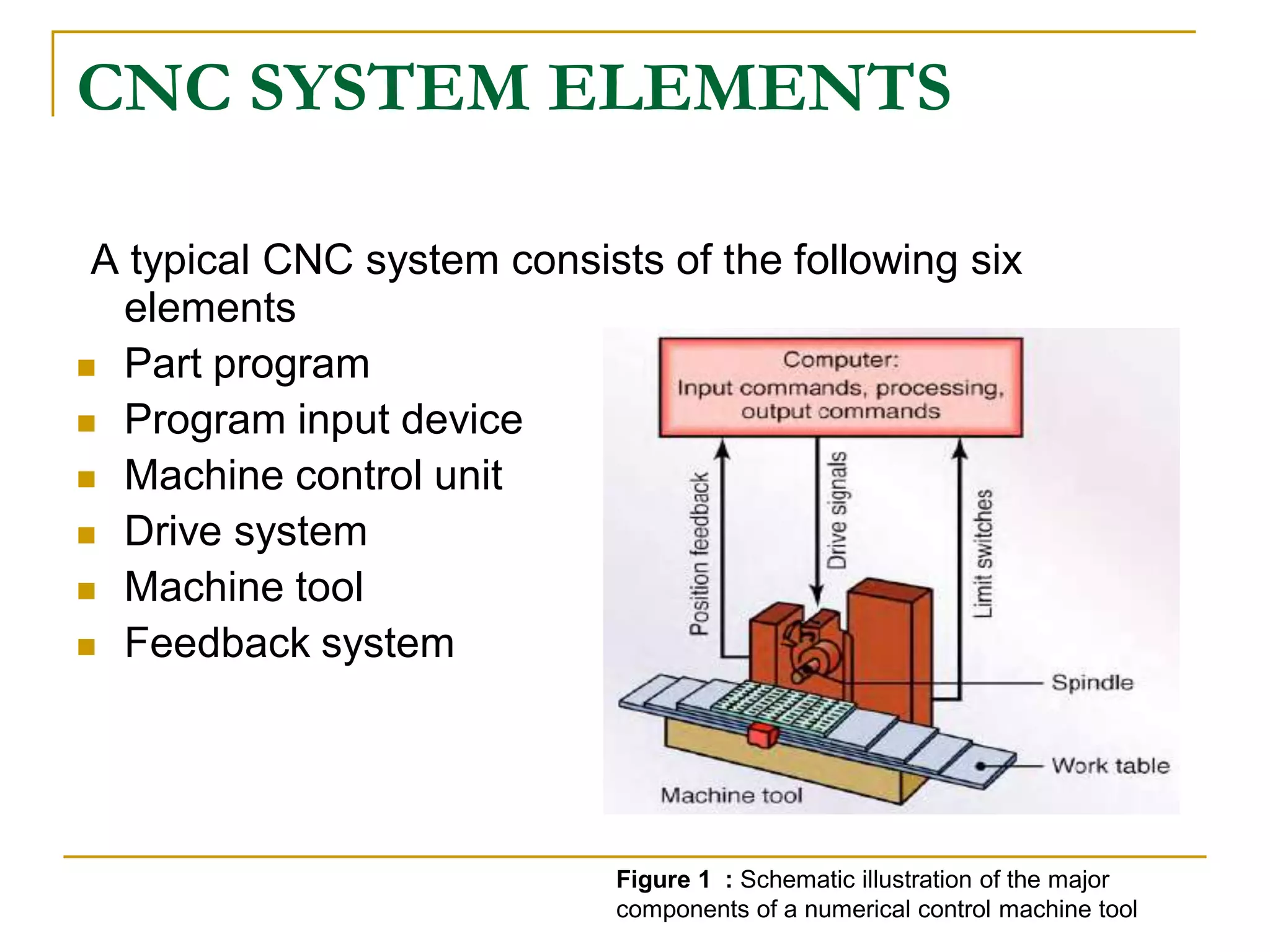
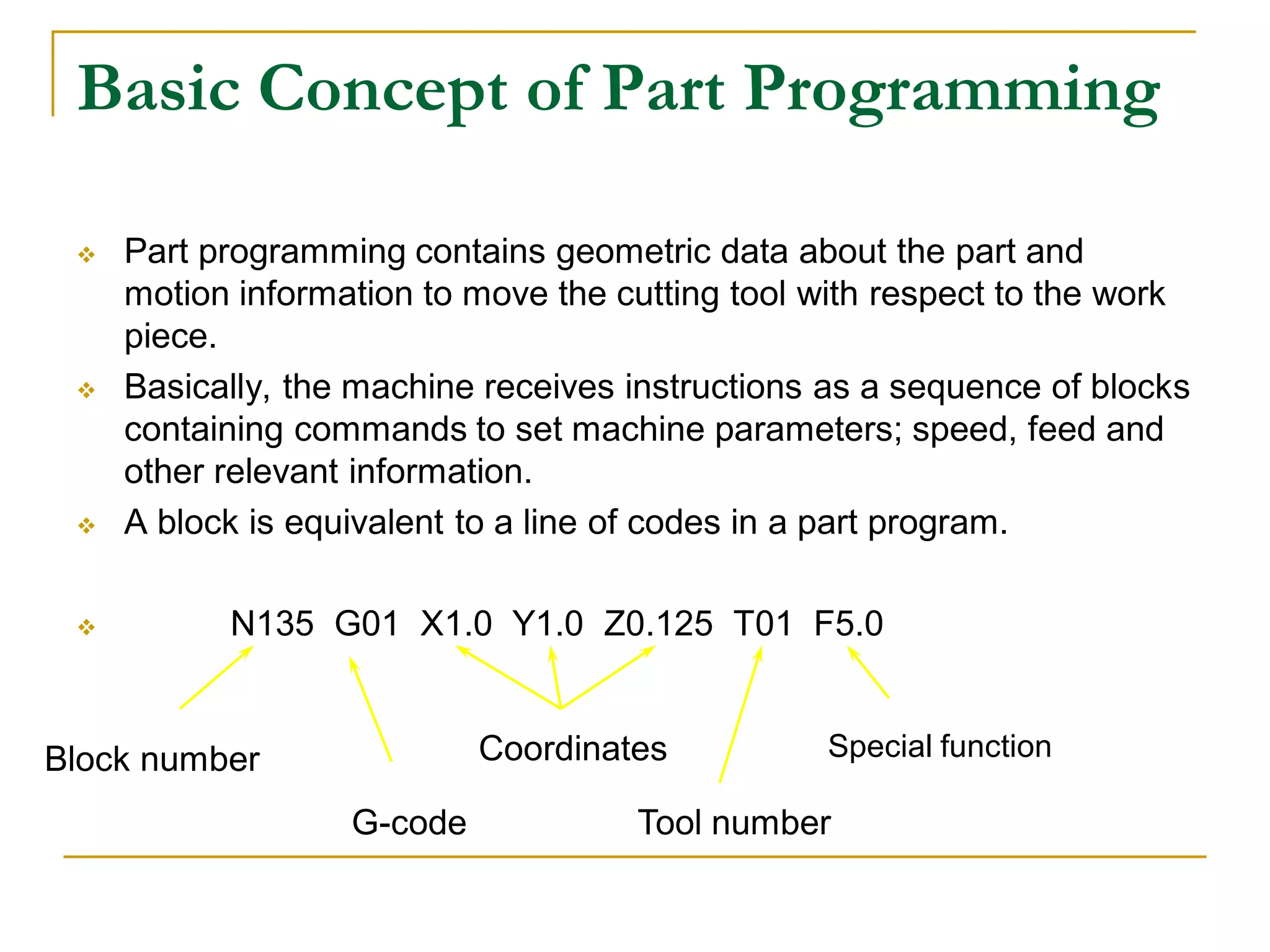
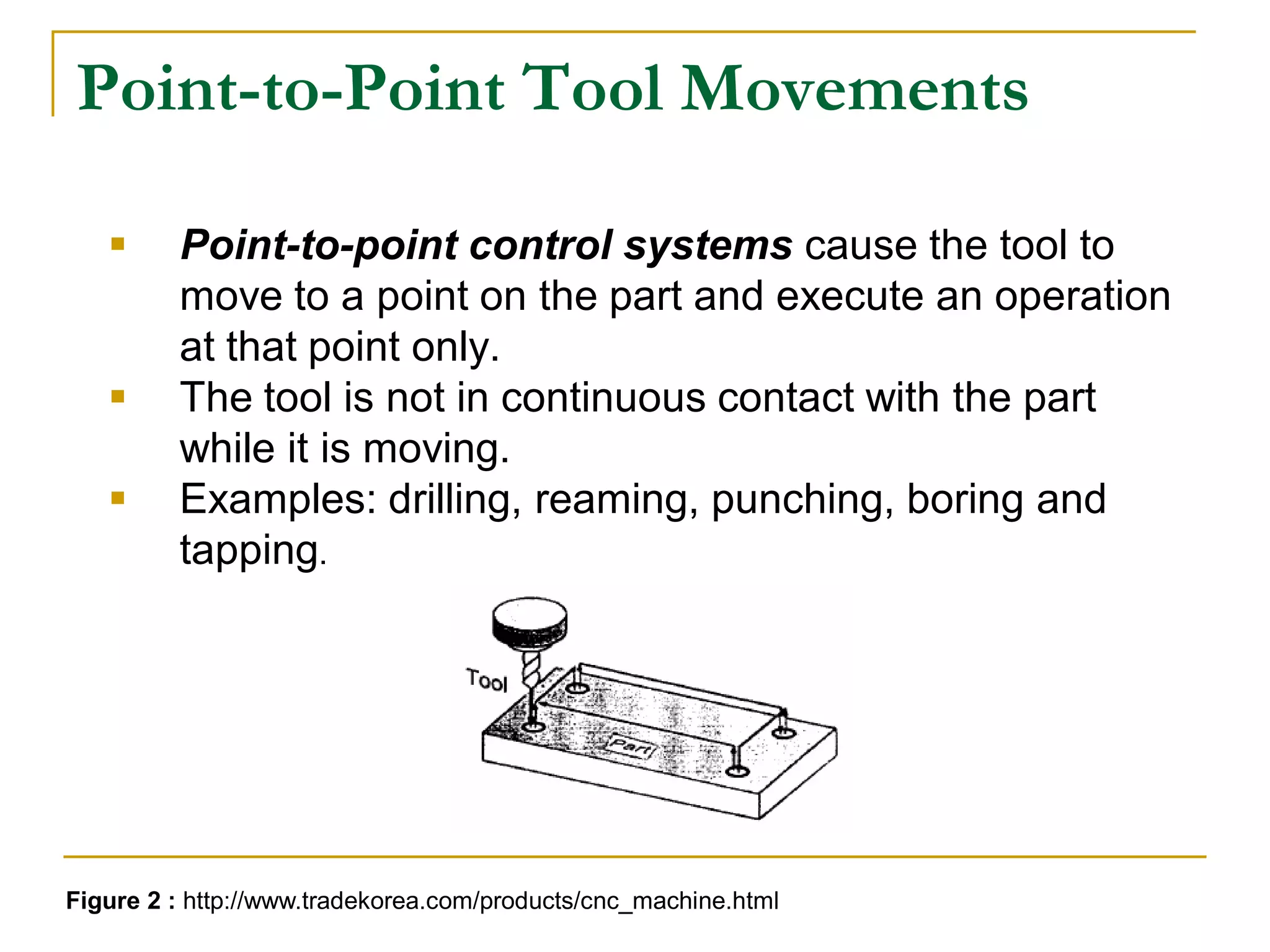
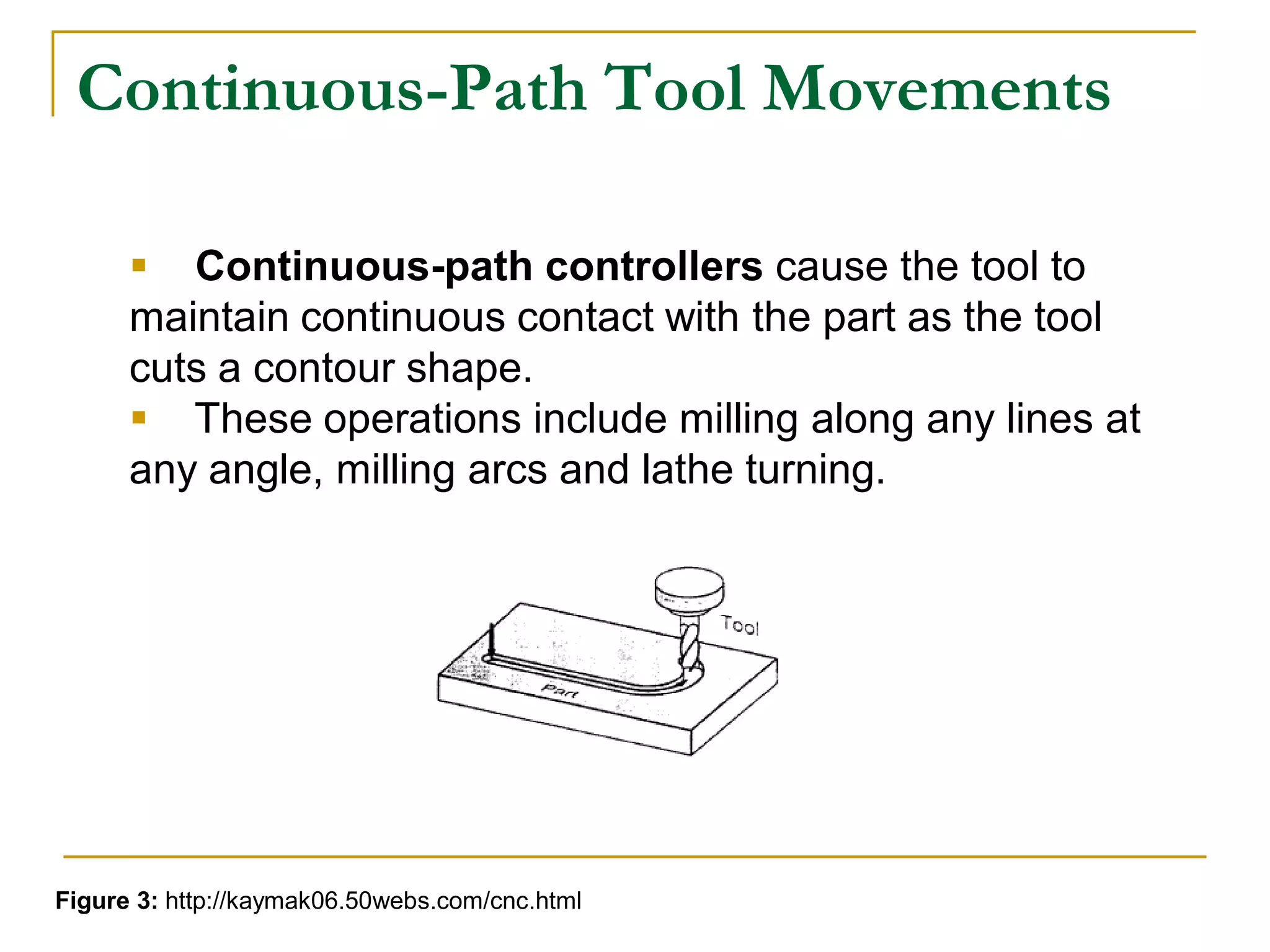
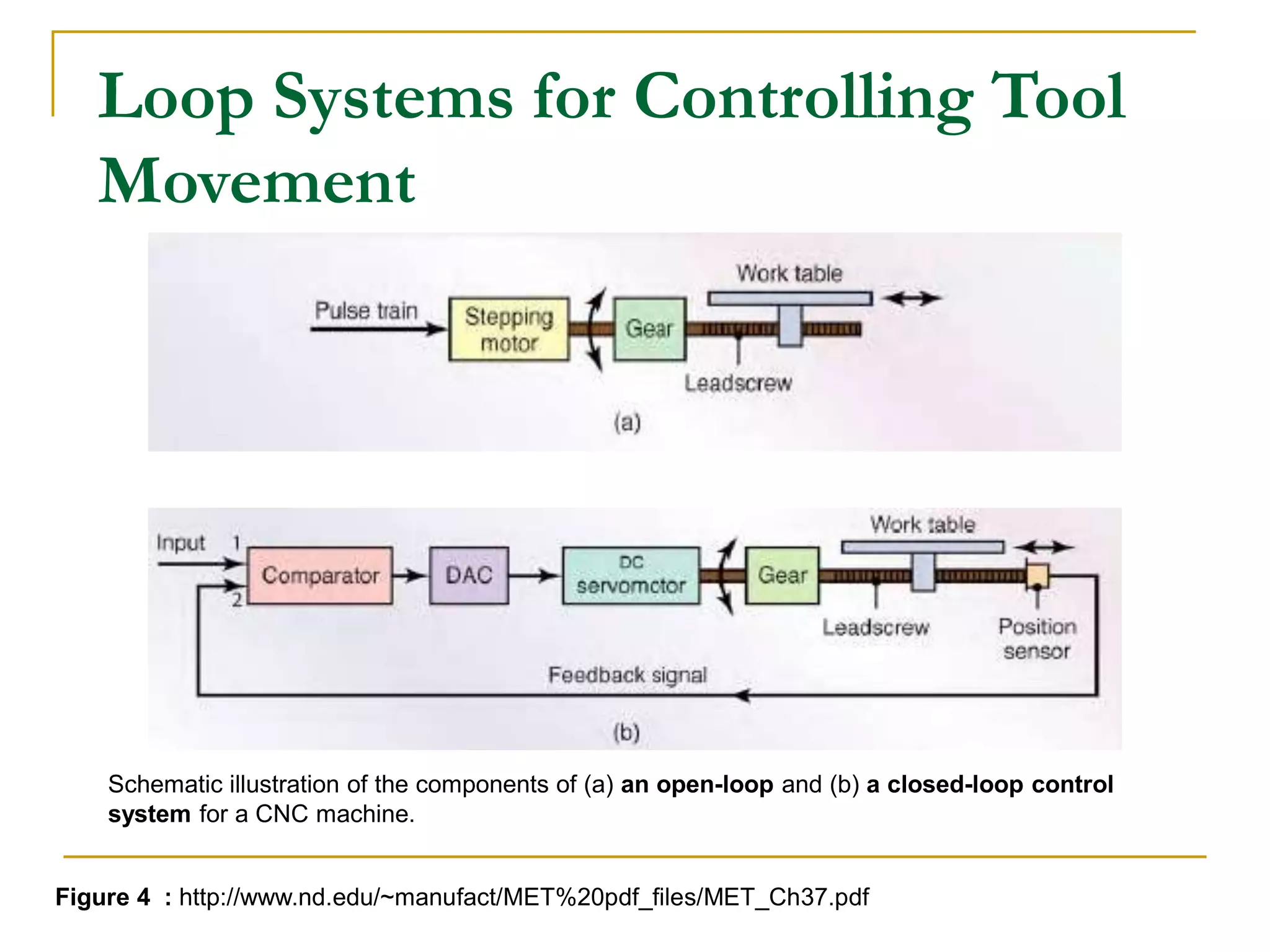
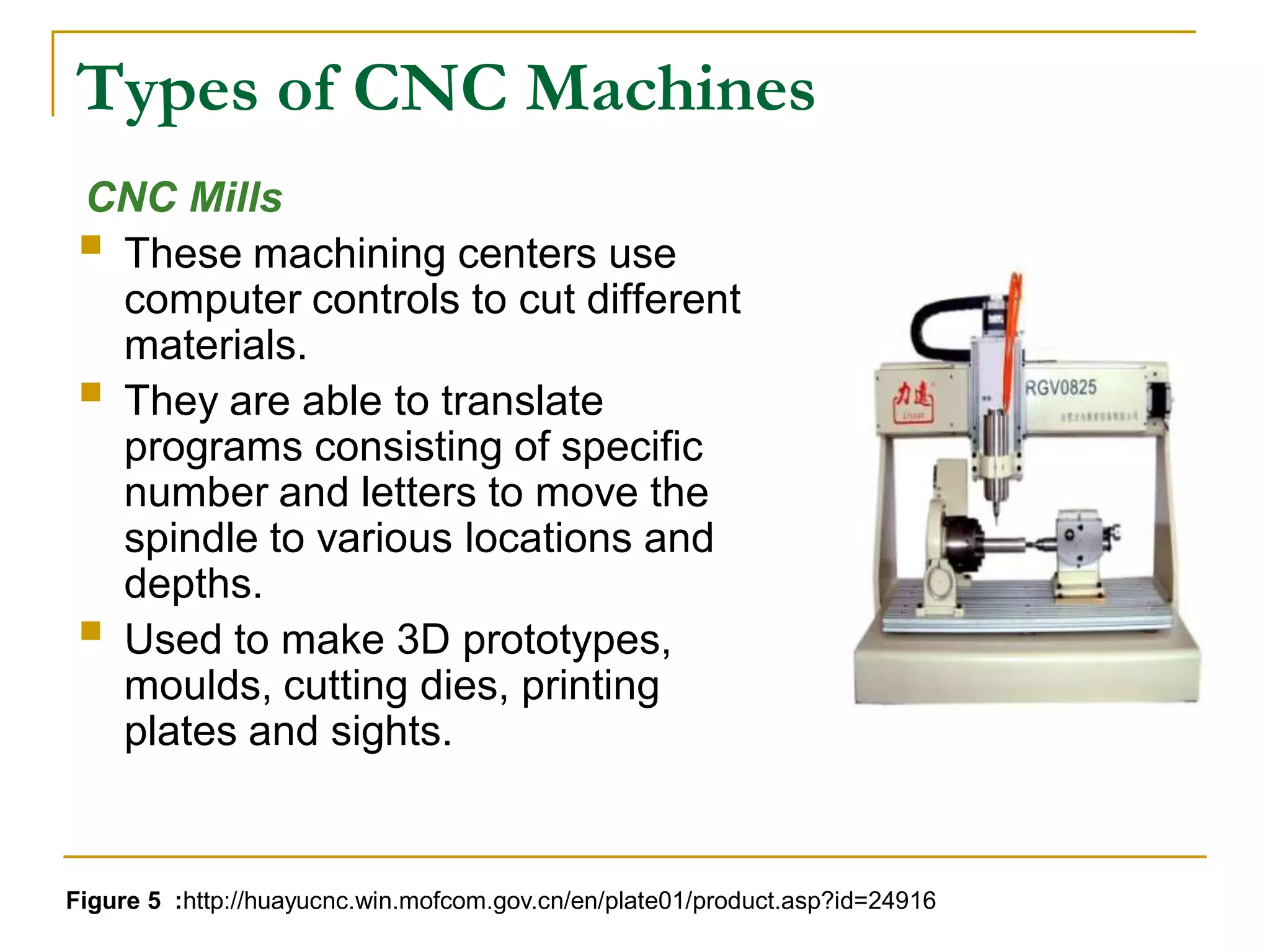
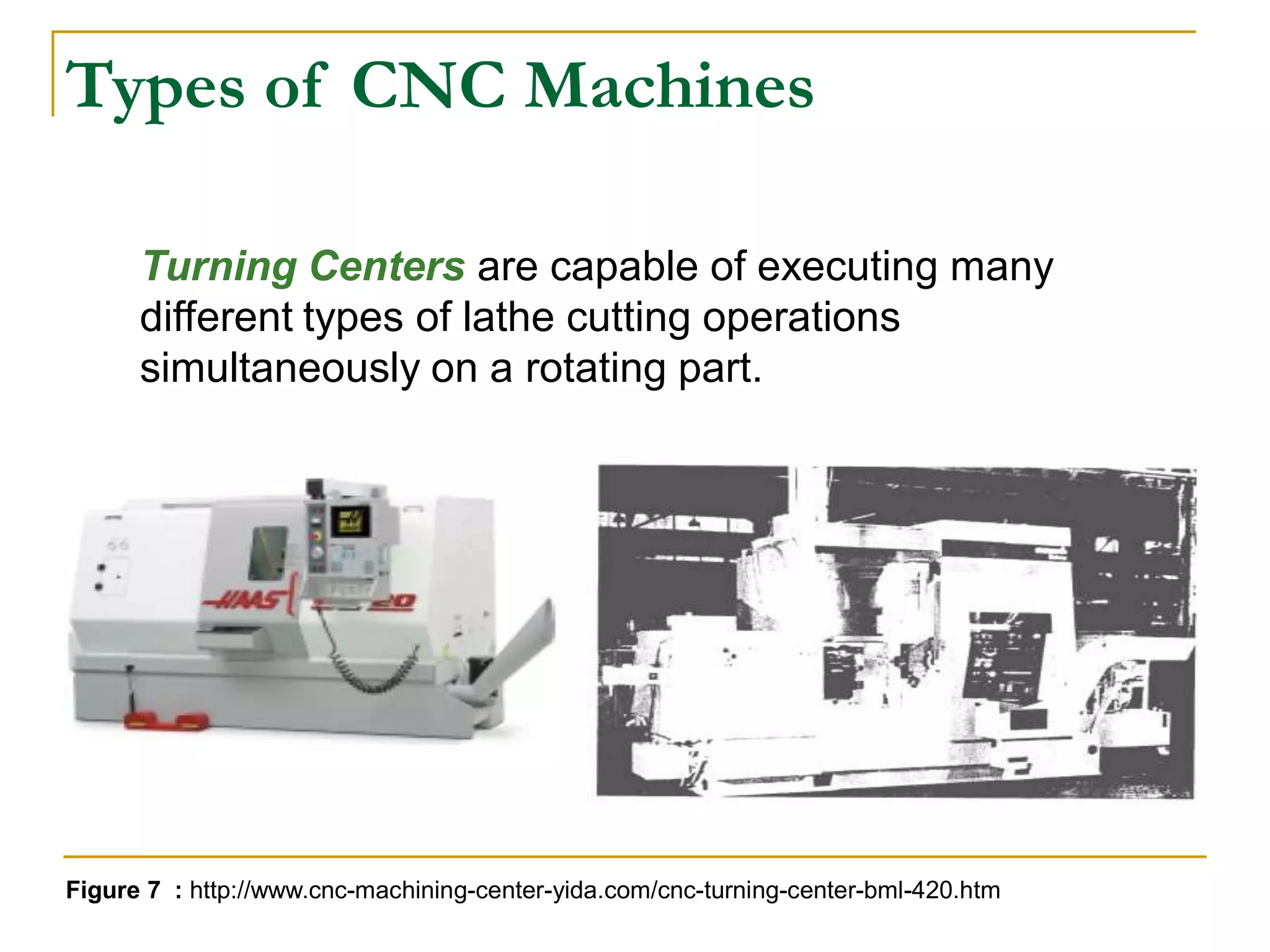
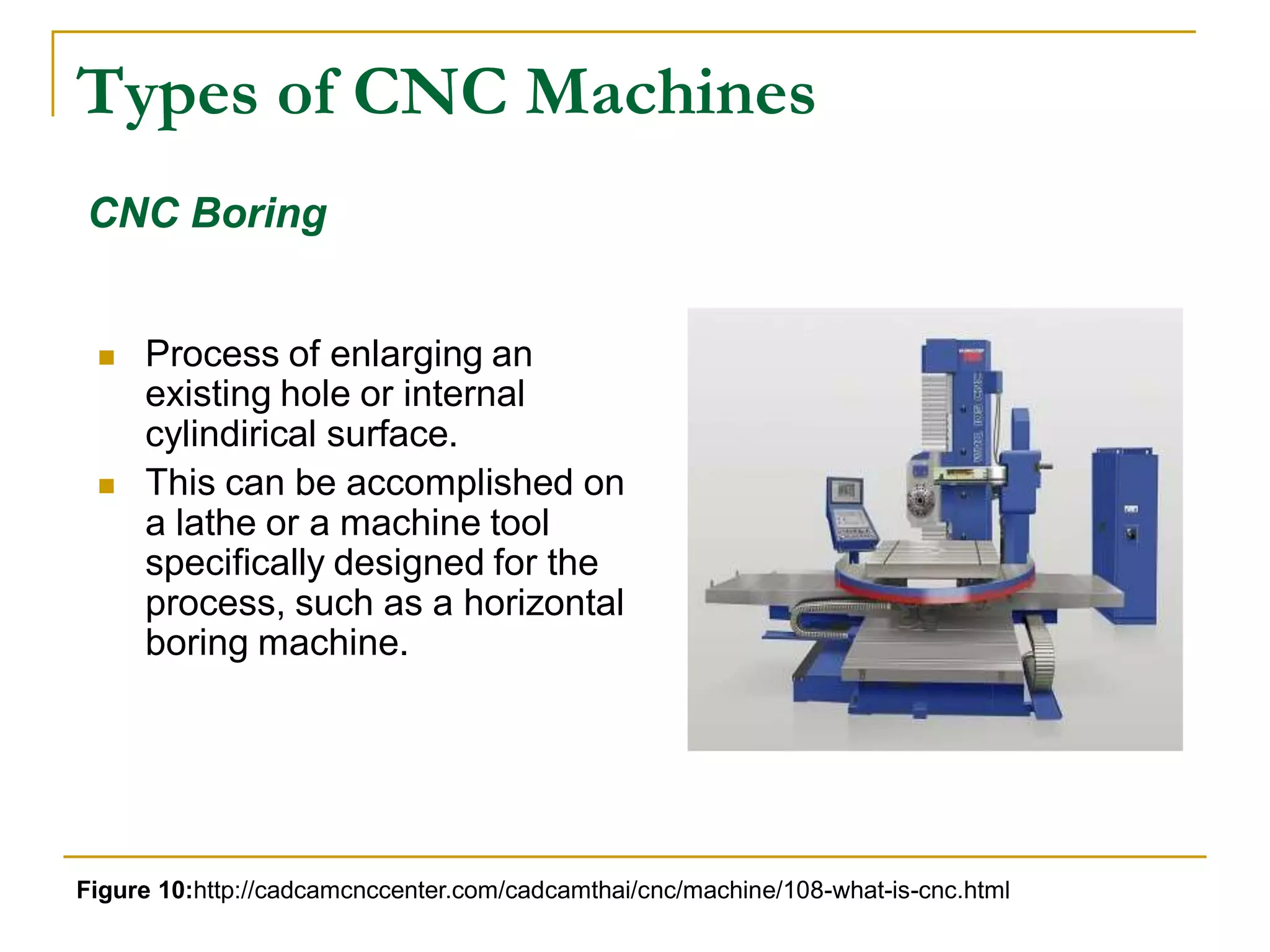
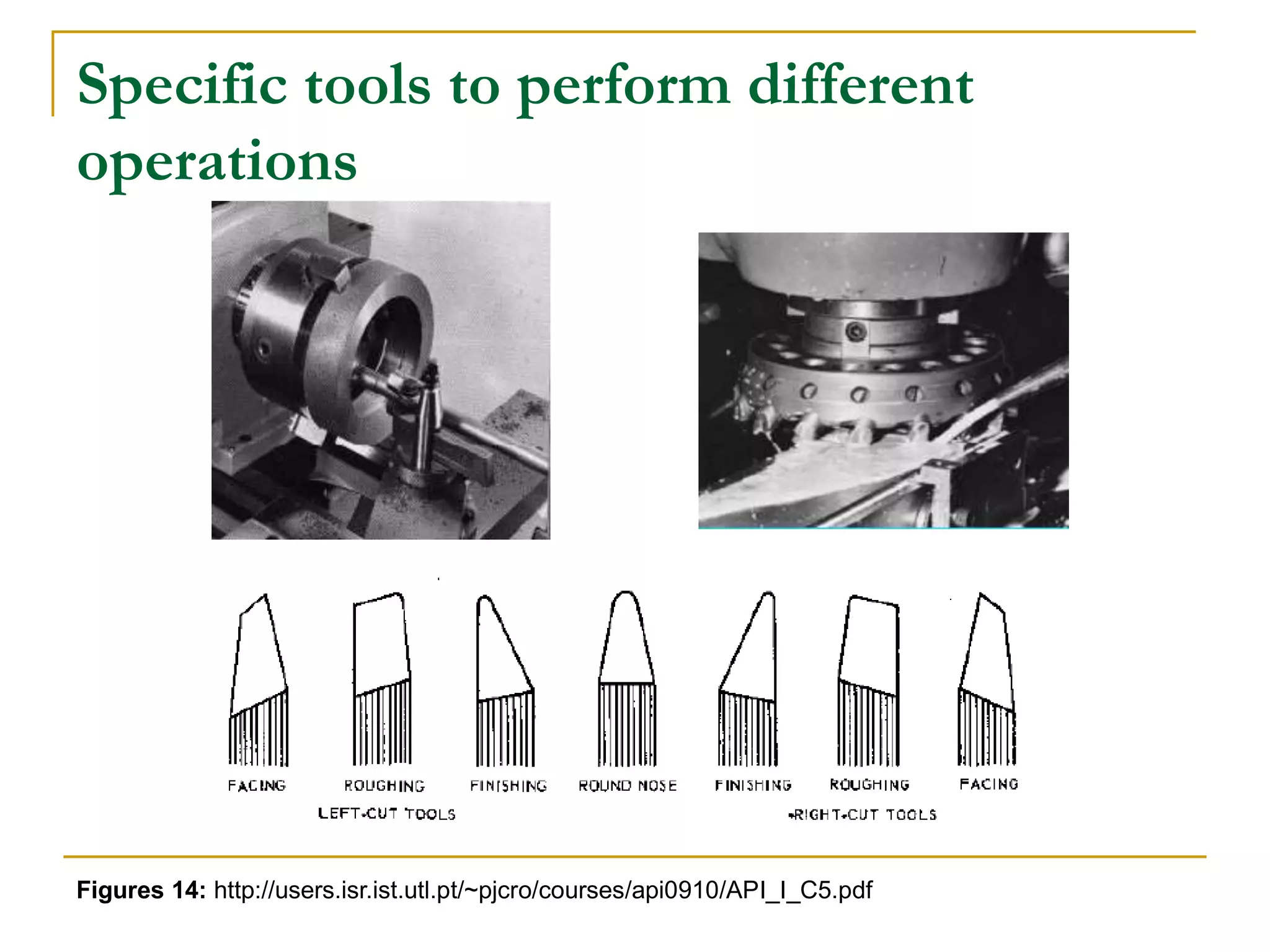
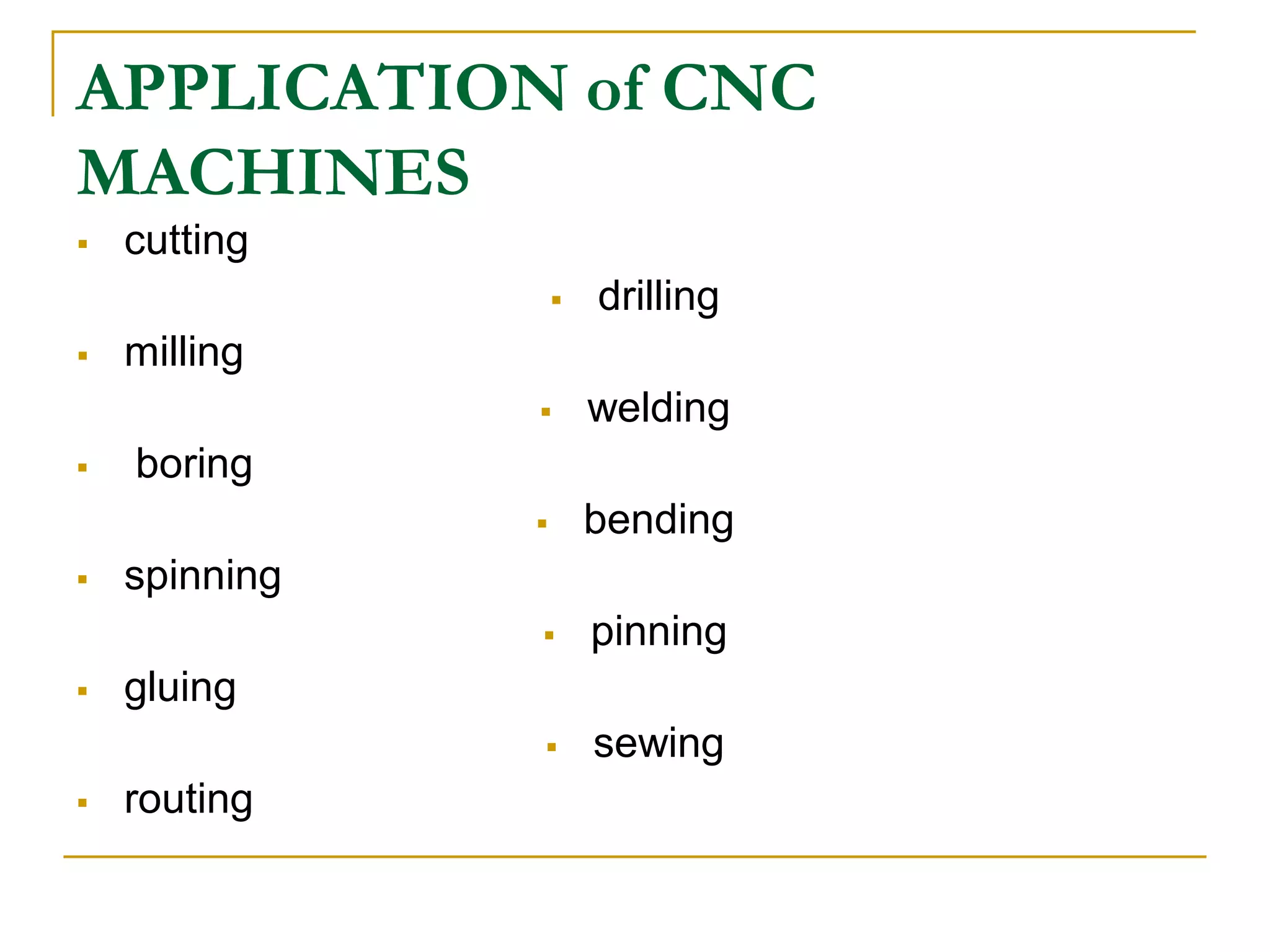
This document provides an overview of computer numerical control (CNC) machines. It discusses what NC and CNC are, the history of NC machines, the typical elements of a CNC system including the part program and control unit. It also describes different types of CNC machines such as lathes, mills, drills, and lasers. Advantages of CNC machines include precision, efficiency, and reducing waste, while disadvantages include higher costs.