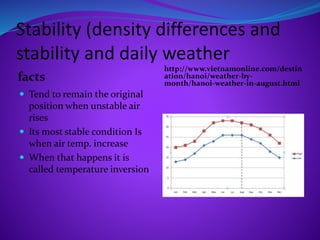
The document discusses various meteorological concepts including adiabatic temperature changes, orographic lifting, frontal wedging, convergence, localized convection lifting, stability, condensation, cloud types, fog formation, precipitation processes, and types of precipitation. It provides definitions and brief explanations of these terms and concepts.