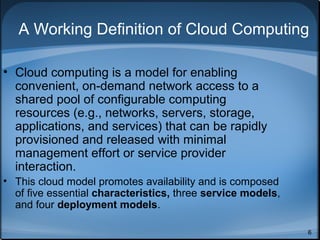
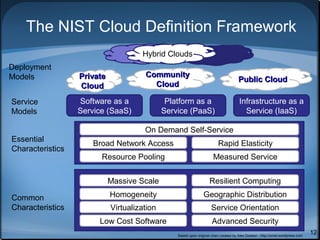
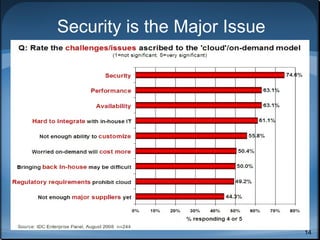
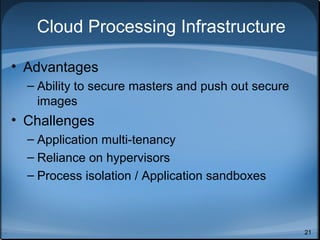
This document discusses cloud computing security and outlines key considerations for both cloud service providers and users. It describes the major cloud service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS) and deployment models (public, private, community, hybrid). The document then covers security pitfalls and responsibilities of providers versus users. Specific areas of focus include governance, compliance, data management, security, encryption, and access control. It emphasizes the importance of effective security controls and trust between providers and users for widespread adoption of cloud computing.



















![Cloud Security
Responsibilities
by Providers and Users
Source: Reference [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudsecurity-130628045203-phpapp01/85/Cloud-security-24-320.jpg)


