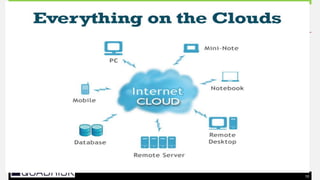
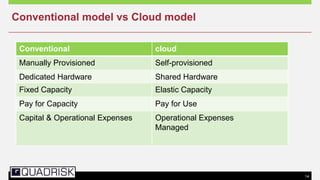
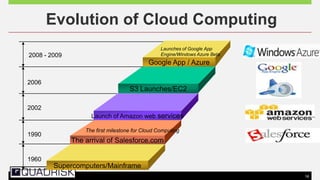
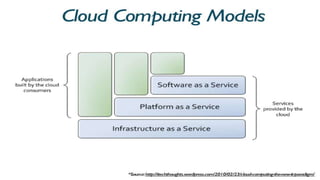
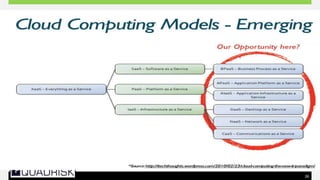
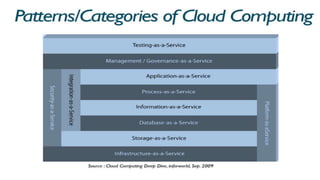
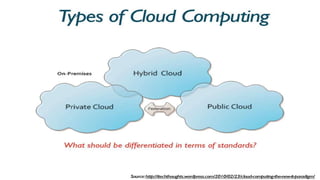
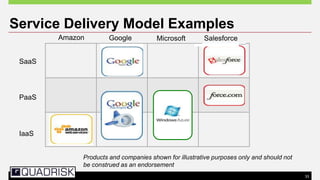
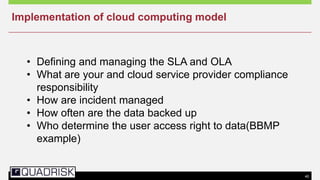
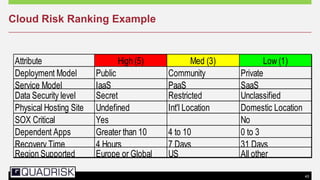
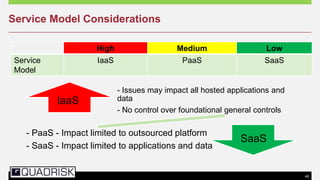
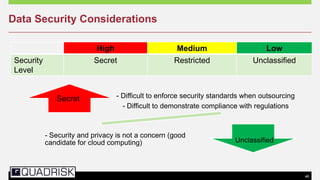
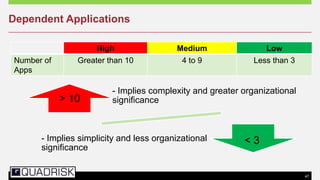
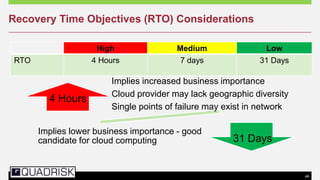
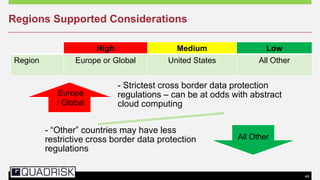
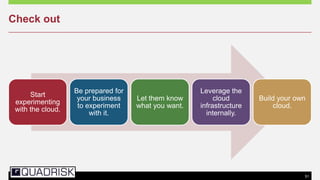
The document provides an extensive overview of cloud computing, defining its service models and key attributes, while highlighting its disruptive potential for traditional IT models. It analyzes different cloud deployment types (public, private, hybrid) and discusses the implications for chartered accountants, including regulatory compliance and risk management. Success stories illustrate the efficiency gains from adopting cloud services, with a call for businesses to experiment with cloud infrastructure.