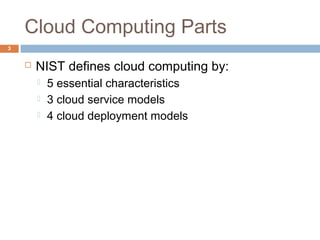
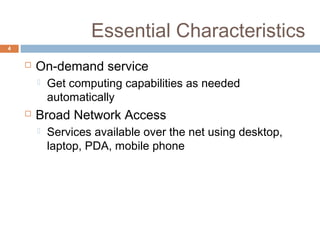
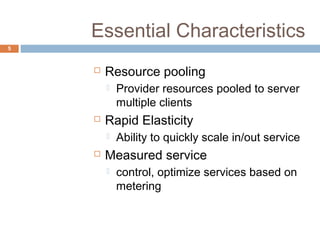
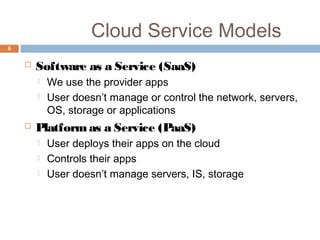
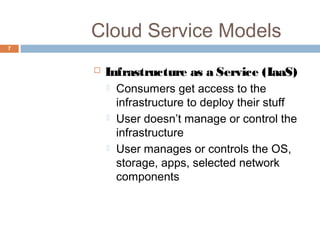
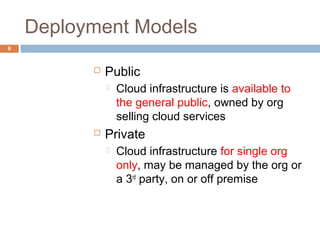
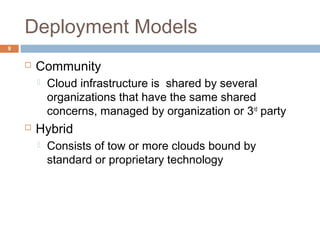
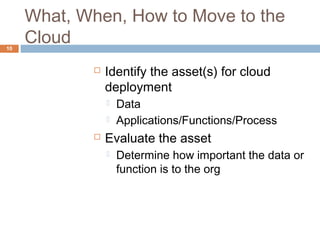
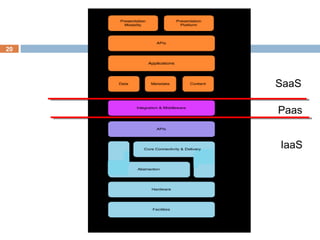
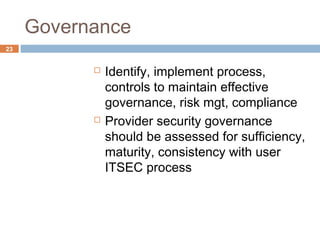
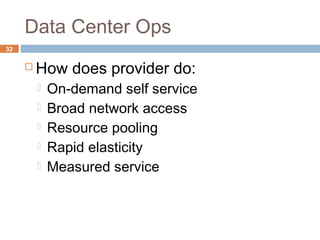
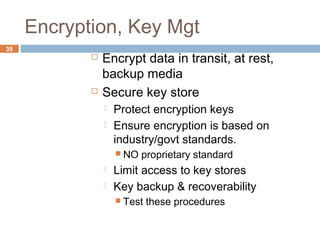
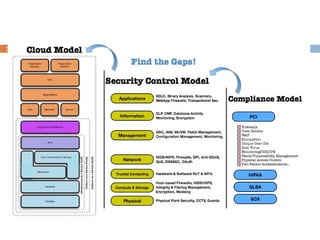
This document discusses security issues related to cloud computing. It defines cloud computing and outlines the essential characteristics, service models, and deployment models. It also addresses key security concerns including governance, legal issues, compliance, information lifecycle management, and risks associated with loss of control over data and applications in the cloud. The document emphasizes that security responsibilities are shared between cloud providers and users, and both parties need to understand their roles.