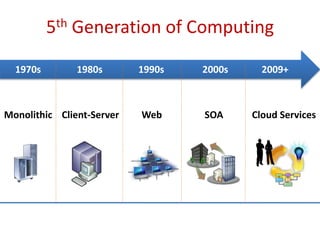
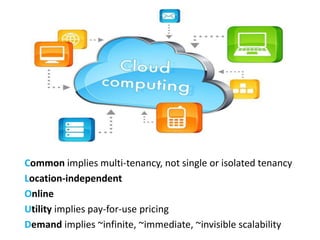
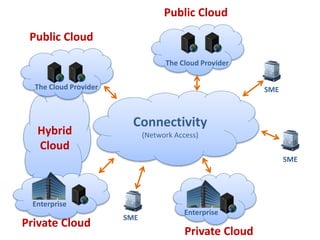
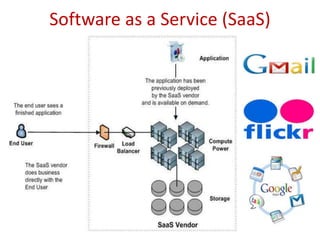
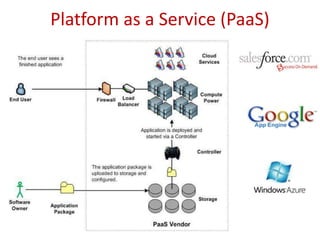
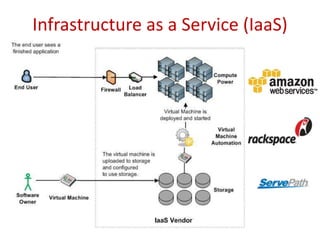
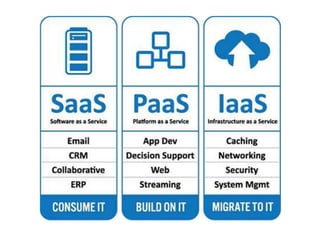
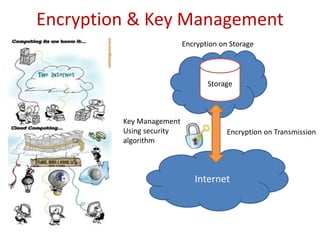
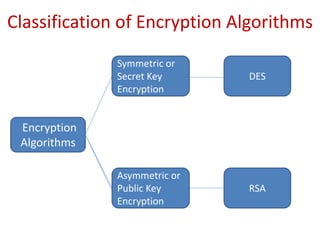
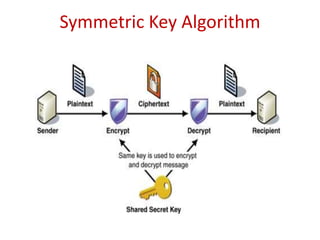
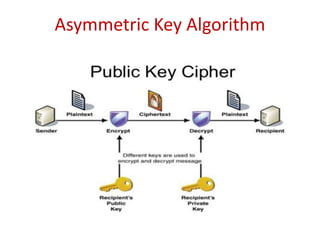
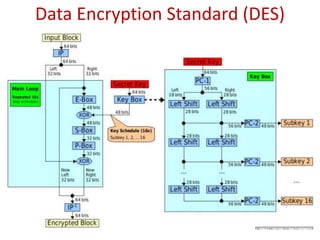
The document discusses the evolution and architecture of cloud computing, emphasizing security issues and cryptographic techniques used in cloud environments. It highlights various encryption algorithms and recent research on enhancing data security and accessibility in cloud storage. The conclusion underscores the need for stronger security algorithms and innovative techniques to address the unique challenges of cloud computing.






![RSA CRYPTOSYSTEM WITH EXAMPLE
SETUP
Step 1: Choose two primes:- p=3 , q=11 [for encrypting small message]
Step 2: n=p*q=3*11=33
Step 3: phi or ɸ(n)=(p-1)(q-1)=(3-1)(11-1)=2*10=20
Step 4: Choose e i.e., public exponent/encryption exponent
e must 1) be an integer
2) not be a factor of n
3) 1<e<ɸ (n)
Let, e=7
Step 5: Calculate d i.e., secret exponent/decryption exponent
(d*e)mod ɸ(n) = 1
(d*7)mod 20=1 => d=3
KEYS
Public Key: KE=( n, e)=(91,7)
Private Key: KD=d=3
ENCRYPTION
Let’s encrypt “BE” where B=2 and E=5 alphabetically.
1<M<n is a condition to encrypt messages within a range.
So, the plaintext, M=25.
Cipher text, C=M^e mod n= 25^7 mod 33=31
DECRYPTION
M=C^d mod n= 31^3 mod 33=25 = “BE”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudencryptionfinal-150829173342-lva1-app6892/85/Cloud-Encryption-19-320.jpg)
![RECENT SCHEMES OF CLOUD ENCRYPTION
1. Rashmi Nigoti et. al[1] have surveyed different security issues to cloud and
different cryptographic algorithms adoptable to better security for the cloud and
the benefits of cloud storage viz. easy access , scalability, cost efficiency, and
high reliability of the data.
2. Brian Hay et. al [2] have focused on data authentication, data integrity,
querying and outsourcing the encrypted data.
3. Ashalatha R [3] discussed in her paper about the significance of data security
and the various existing security techniques for the cloud.
4. S.Monikandan et.al[4] proposed a new cloud cryptography technique . It
conveys that since the user has no control over the data once their session is
logged out, the encryption key acts as the primary authentication for the user.
By applying this encryption algorithm, user ensures that the data is stored only
on secured storage and it cannot be accessed by administrators or intruders.
5. Rajeev Bedi et.al[5] developed a retrieval system in which the data is retrieved
by the user in encrypted form and is decrypted by the user at its own site using
a public and private key encryption both the keys working at the user level.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudencryptionfinal-150829173342-lva1-app6892/85/Cloud-Encryption-20-320.jpg)

![BIBLIOGRAPHY
[1] Rashmi Nigoti et al., “ A Survey of Cryptographic Algorithms for Cloud
Computing” International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational and
Applied Sciences,4(2), March-May 2013.
[2] Brian Hay, Kara Nance, Matt Bishop, “Storm Clouds Rising: Security
Challenges f for IaaS Cloud Computing” Proceedings of the 44th Hawaii
International Conference on System Sciences -2011.
[3] Ashalatha R,Faculty of Computer Science, Dayananda Sagar College of
Engineering, Bangalore,” A Survey On Security As A Challenge In Cloud
Computing” International Journal of Advanced Technology & Engineering
Research (IJATER) National Conference on Emerging Trends in Technology (NCET-
Tech), Volume 2, Issue 4, July 2012.
[4] S. Monikandan et al., “Data Security and Privacy in Cloud Storage using Hybrid
Symmetric Encryption Algorithm” International Journal of Advanced Research in
Computer and Communication Engineering Vol. 2, Issue 8, August 2013.
[5] Rajeev Bedi et al., “Applying Encryption Algorithm for Data Security and Privacy
in Cloud Computing” Punjab Technical University, Beant College of Engineering
and Technology,Gurdaspur, Punjab, India, IJCSI International Journal of Computer
Science Issues, Vol. 10, Issue 1, No 1, January 2013.
JOURNALS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudencryptionfinal-150829173342-lva1-app6892/85/Cloud-Encryption-22-320.jpg)


