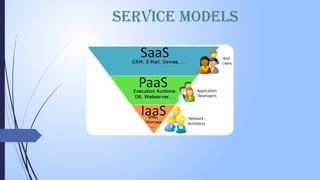
The document is a presentation on cloud computing, detailing its definition, history, benefits, essential characteristics, and various models. It discusses key service models such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, highlighting their features, pros, and cons. The conclusion notes the potential of cloud computing to enhance flexibility and reduce costs, but also emphasizes ongoing security concerns that affect its adoption.