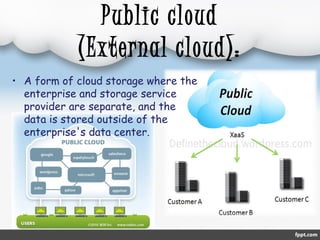
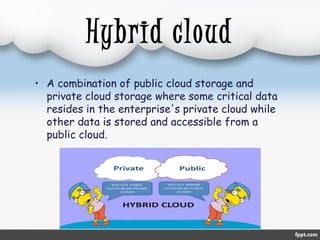
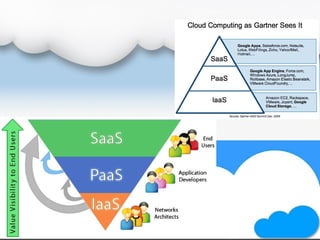
The document outlines cloud computing, including its definition, history, types, service models, advantages, and disadvantages. It defines cloud computing as internet-based computing delivering services such as servers and applications, and presents different types like public, private, and hybrid clouds along with service models like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. While cloud computing offers benefits such as cost reduction and improved performance, it also has drawbacks including reliance on internet connectivity and potential data security risks.