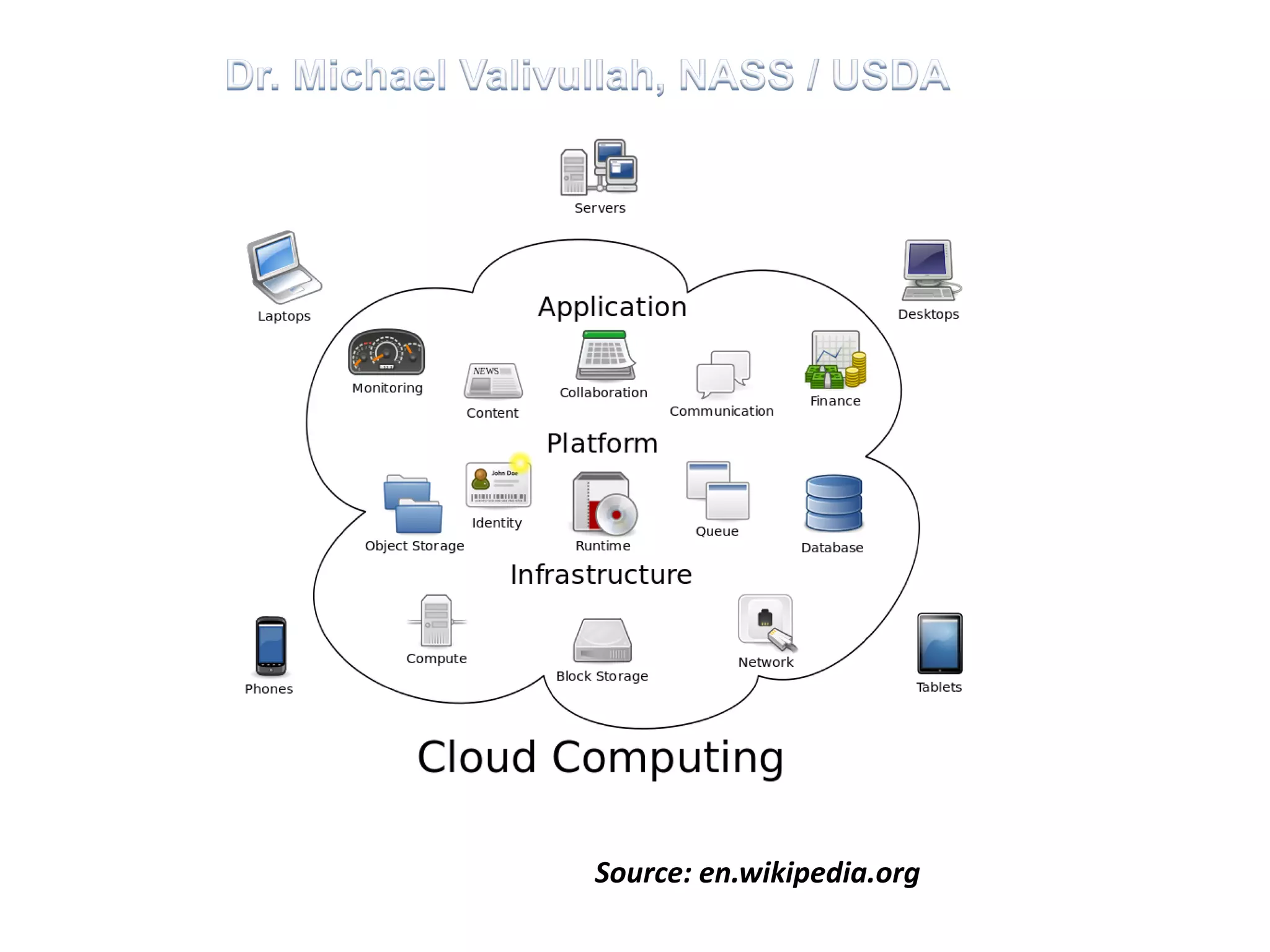
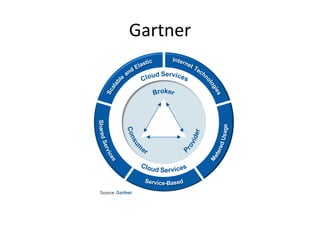
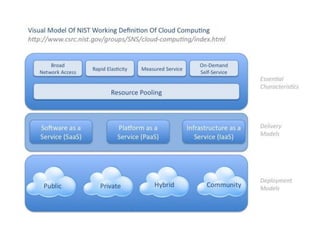
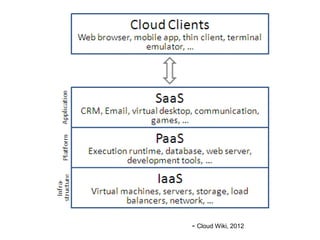
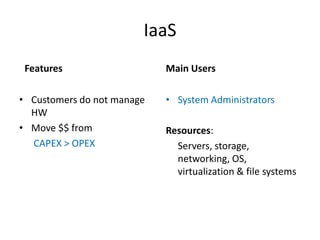
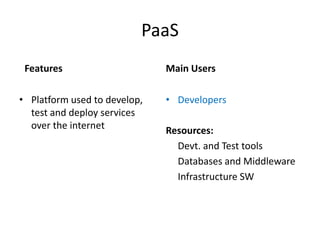
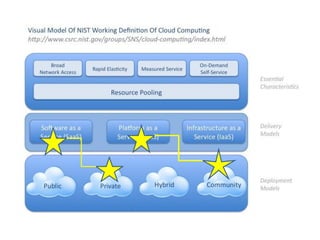
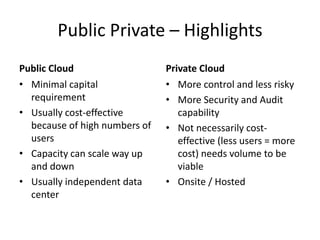
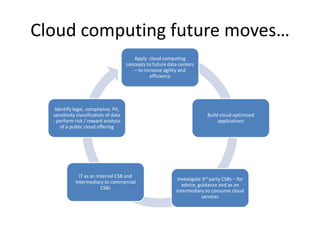
This document provides an overview of cloud computing. It defines cloud computing as a model enabling ubiquitous, convenient access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned with minimal management effort. The document discusses different types of cloud services including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). It also covers public and private cloud models and highlights benefits of cloud computing such as agility, cost reduction, and increased efficiency.