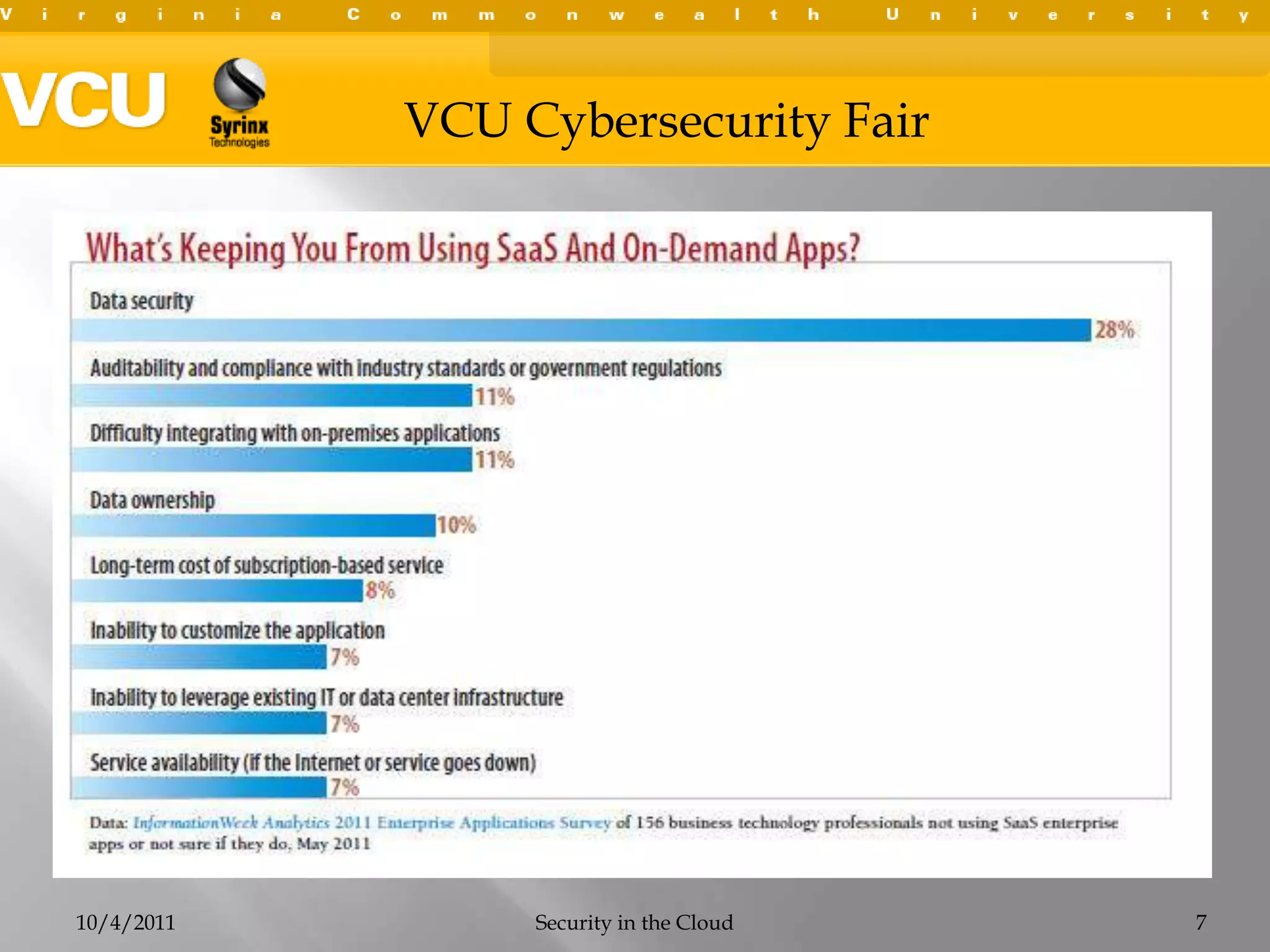
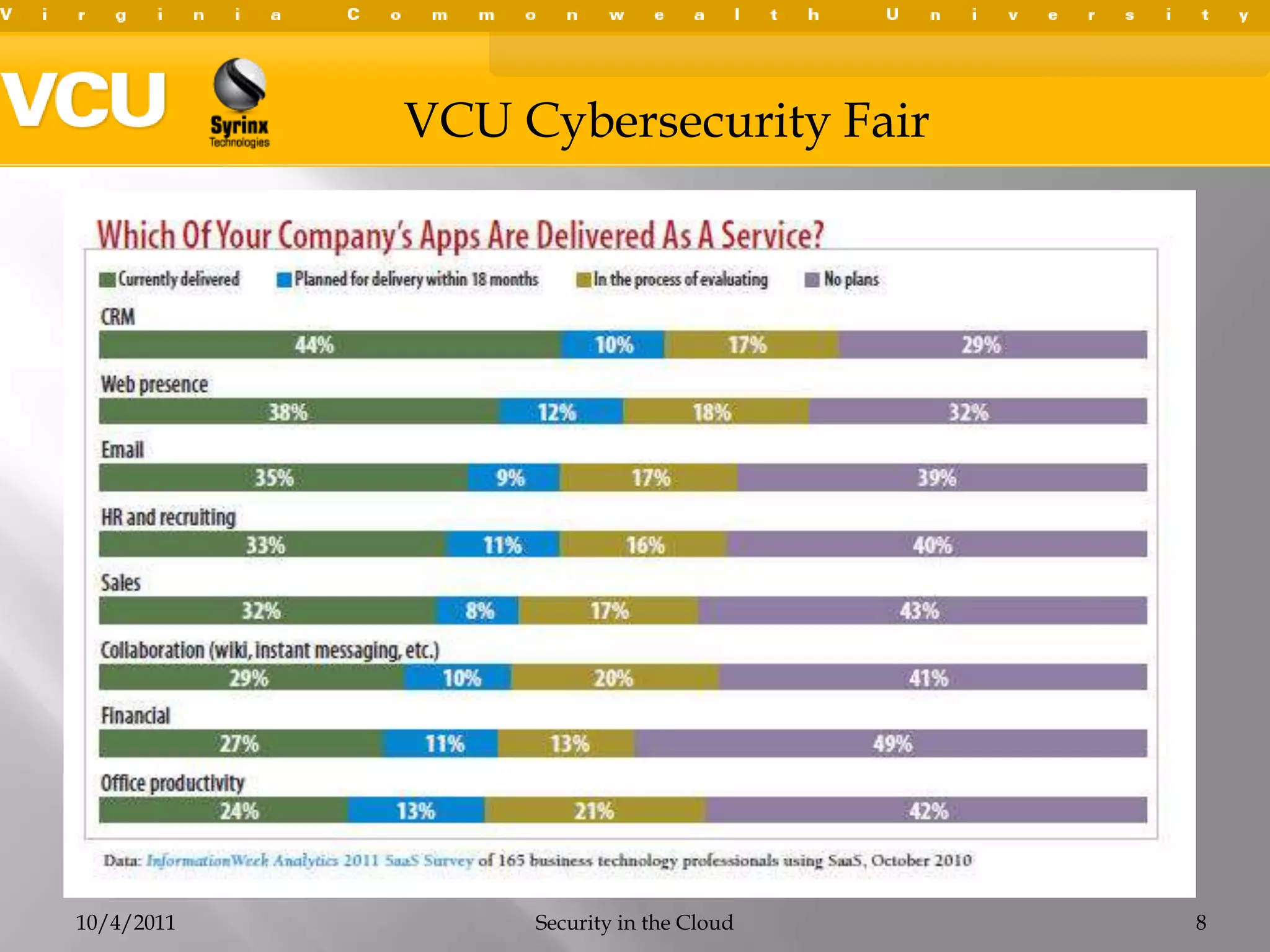
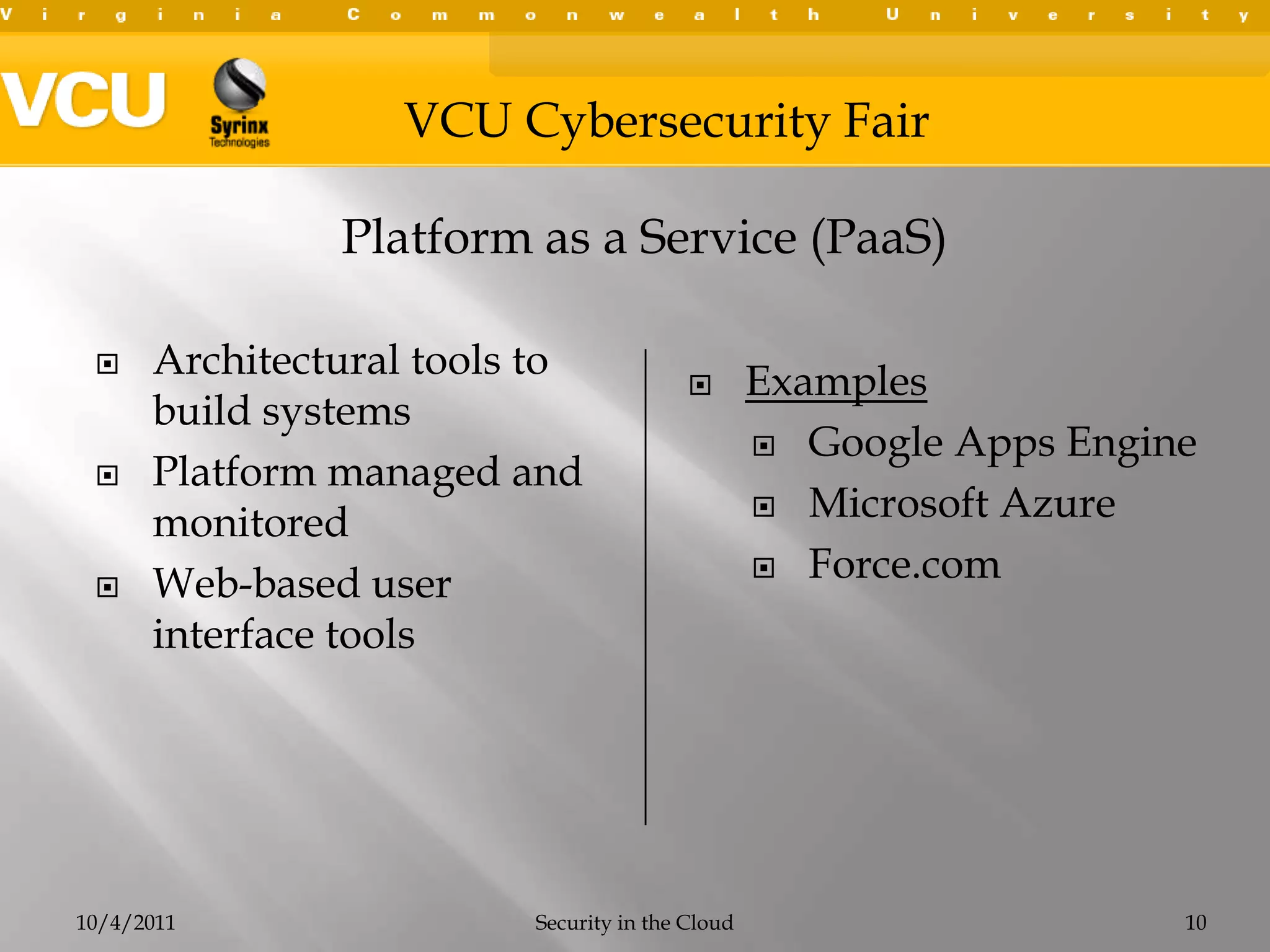
This document summarizes a presentation on cybersecurity in the cloud. The presentation covered cloud computing definitions and models including SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and public, private and hybrid clouds. It discussed major cloud vendors like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and OpenStack. The presentation addressed security issues in the cloud like outages, data breaches, and regulatory compliance. It emphasized the importance of service level agreements, testing disaster recovery plans, and monitoring metrics when adopting cloud services.