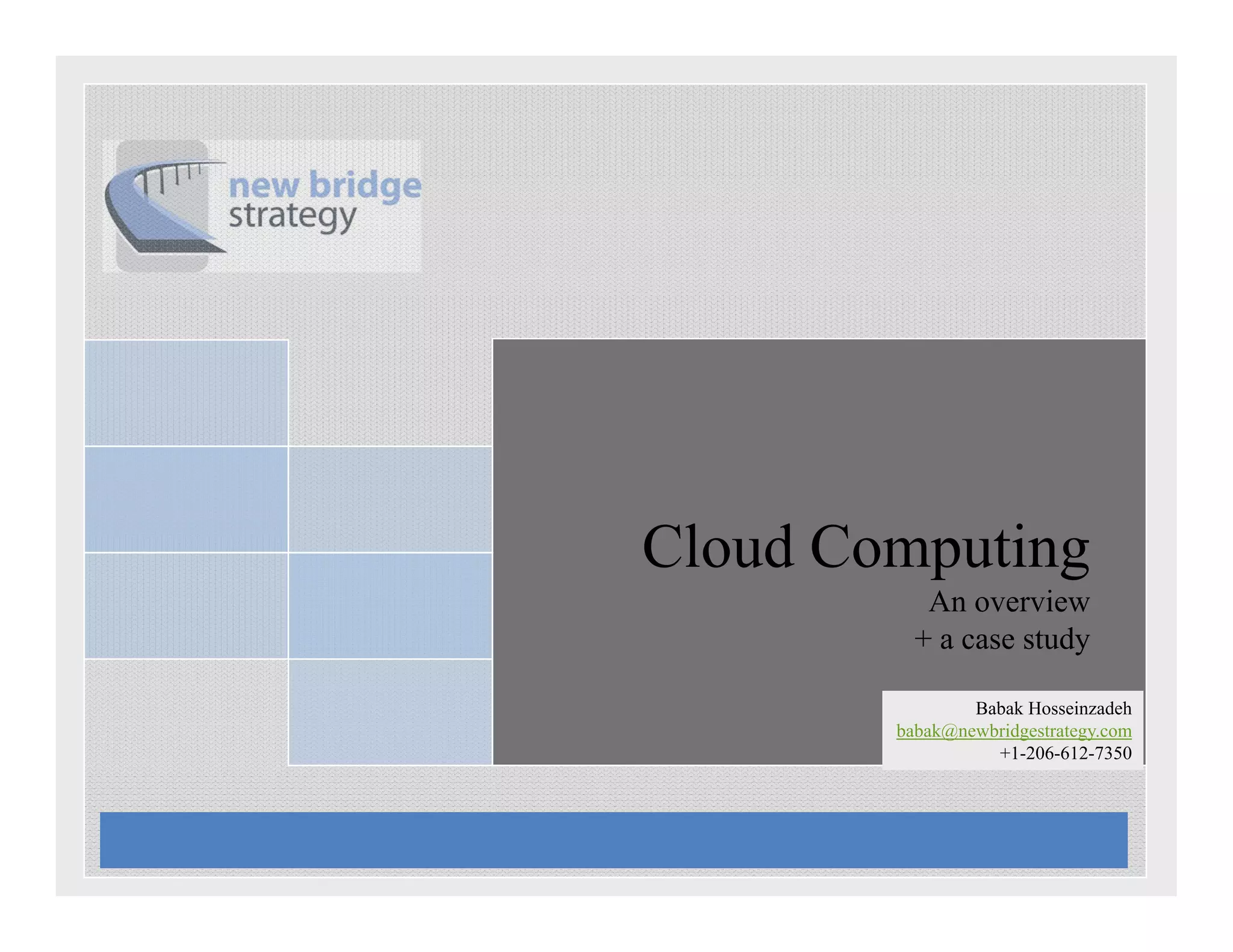
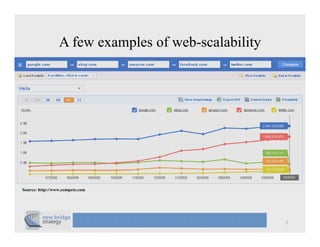
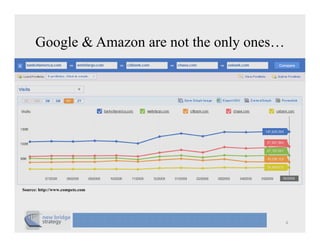
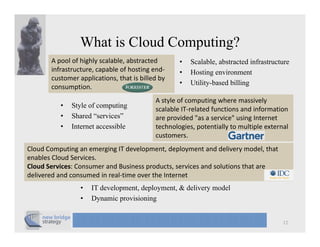
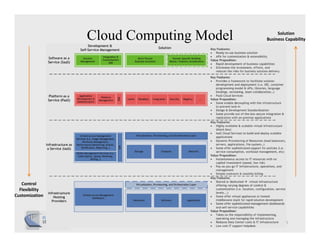
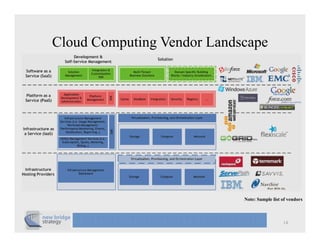
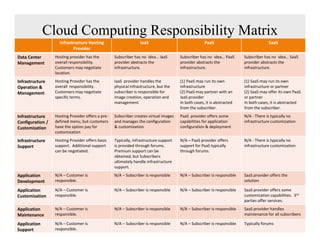
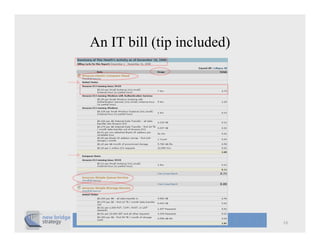
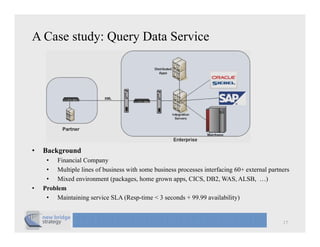
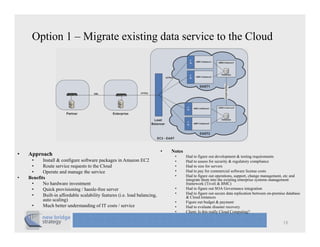
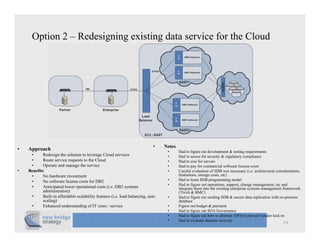
The document discusses cloud computing and provides a case study on moving a financial company's data service to the cloud. It outlines two options: 1) migrating the existing service to Amazon EC2, which would require addressing various technical and operational challenges, or 2) redesigning the service to leverage cloud databases and services, which could reduce costs but would require significant development work. The document cautions that moving workloads to the cloud requires careful analysis and that the hype around cloud computing should be taken in perspective, as integration and other business issues are more significant than technical challenges. It emphasizes establishing metrics to measure the benefits of cloud initiatives.