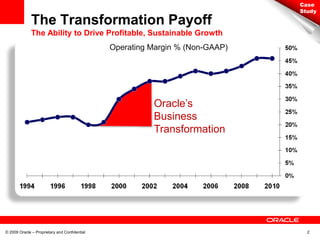
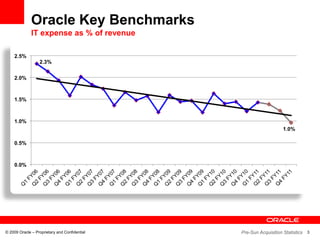
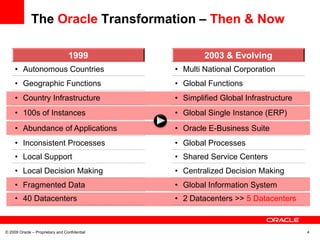
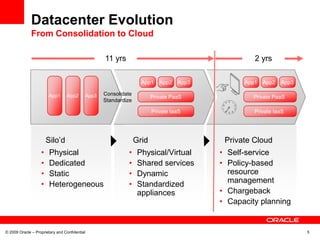
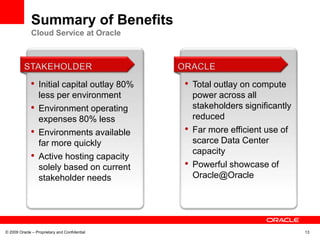
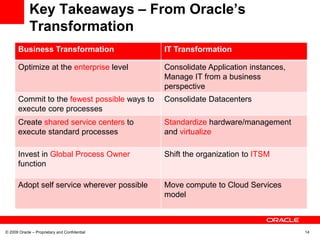
This document discusses Oracle's transformation to enterprise cloud computing. It describes how Oracle moved from siloed and fragmented infrastructure in different countries to a standardized global infrastructure with single instances. This increased efficiency and reduced costs. Oracle now operates large private clouds for development, production applications, and Oracle University. The private clouds provide self-service access, resource pooling, and increased utilization rates. Oracle is further evolving its cloud services to better match consumer needs and provide end user services like desktops in the cloud.