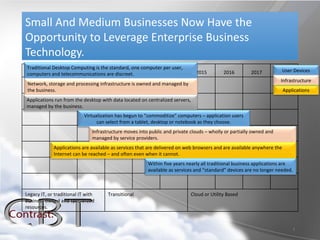
Cloud computing delivers computer services such as software, infrastructure, security and platforms as utilities via the internet. Key benefits include lower costs compared to maintaining internal infrastructure, flexibility and scalability. Major types of cloud services include Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Security as a Service (SecaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Emerging specialized cloud services also provide opportunities for on-demand access to communication, storage, backup and file sharing resources.