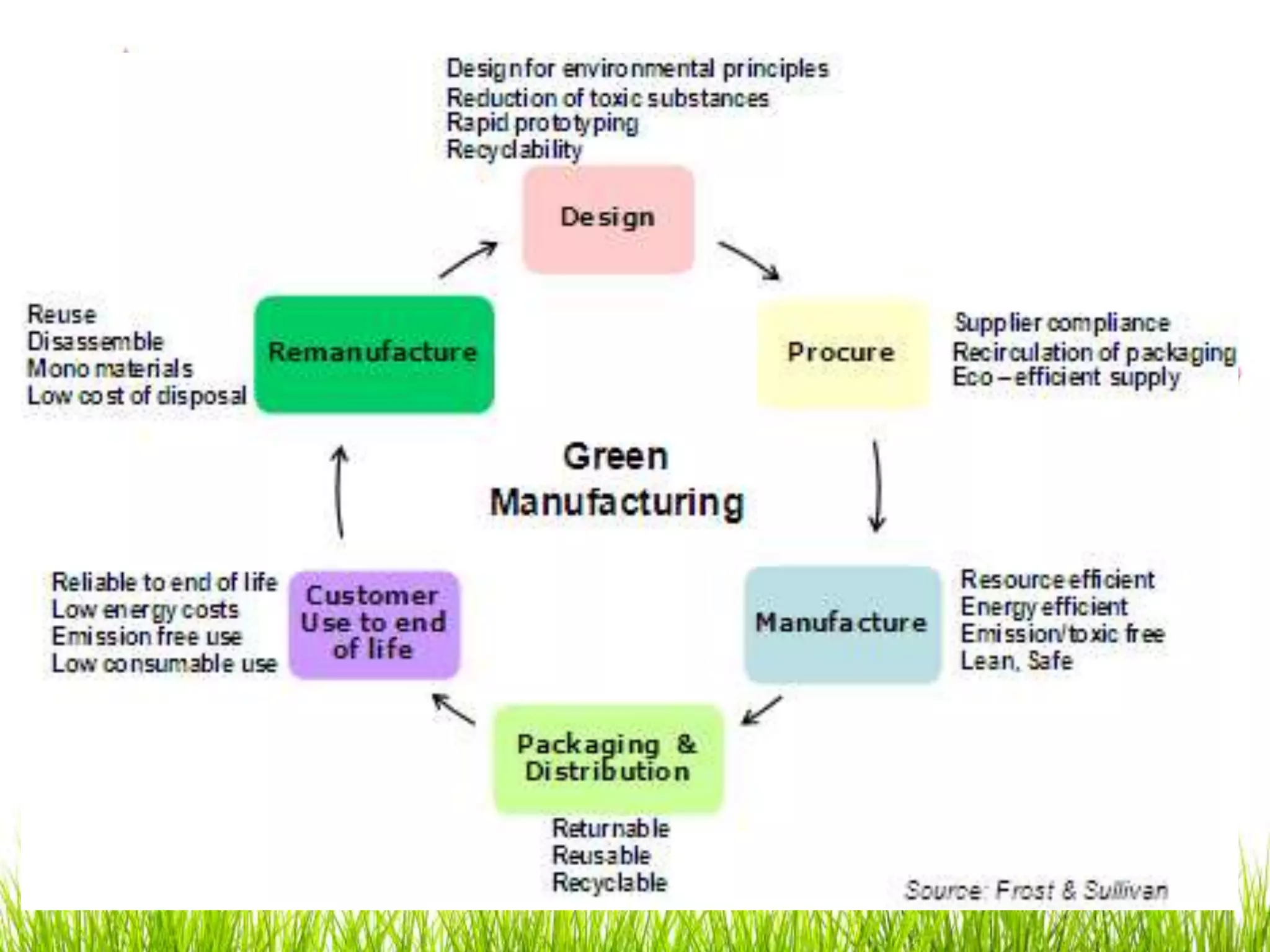
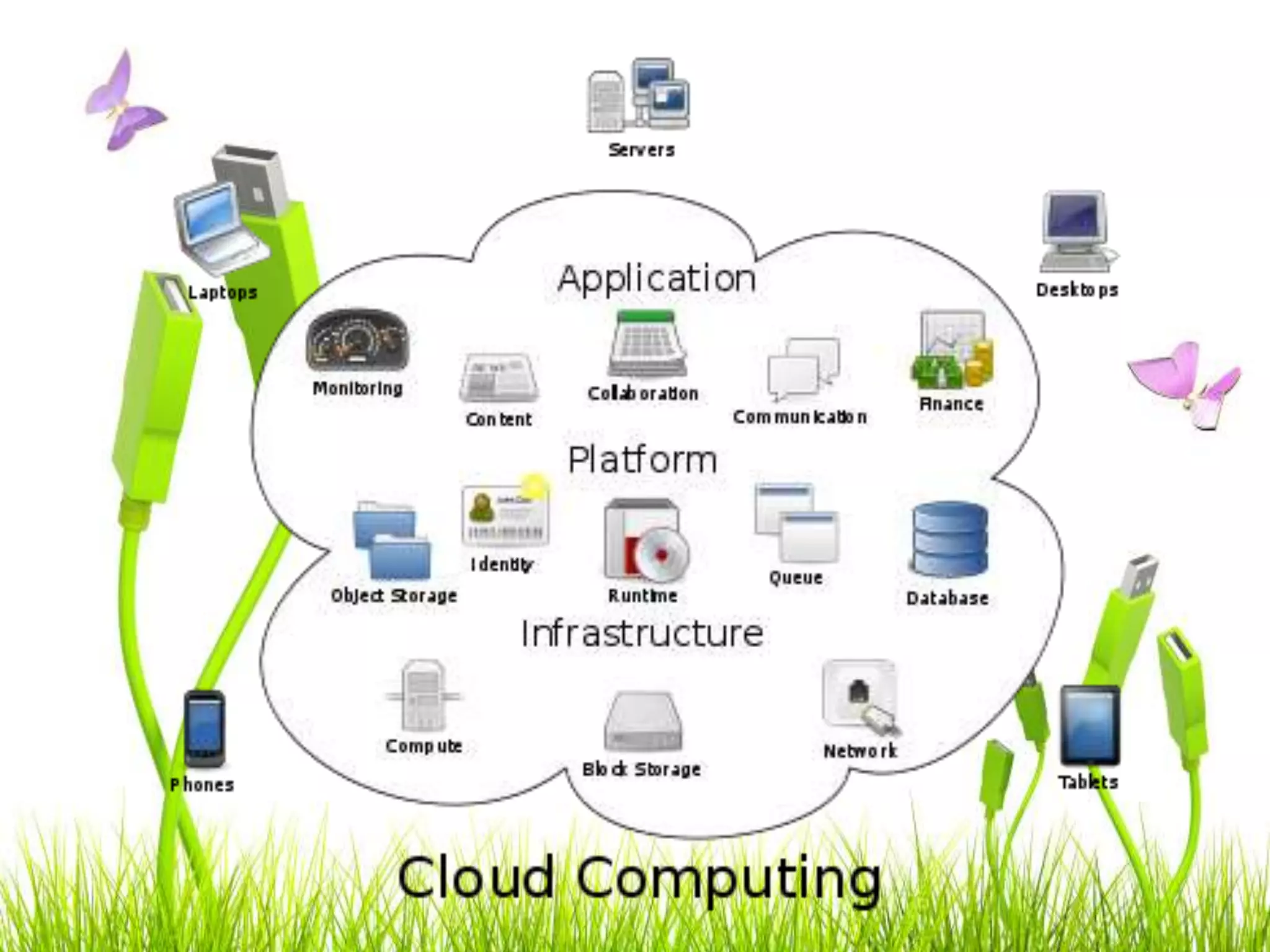
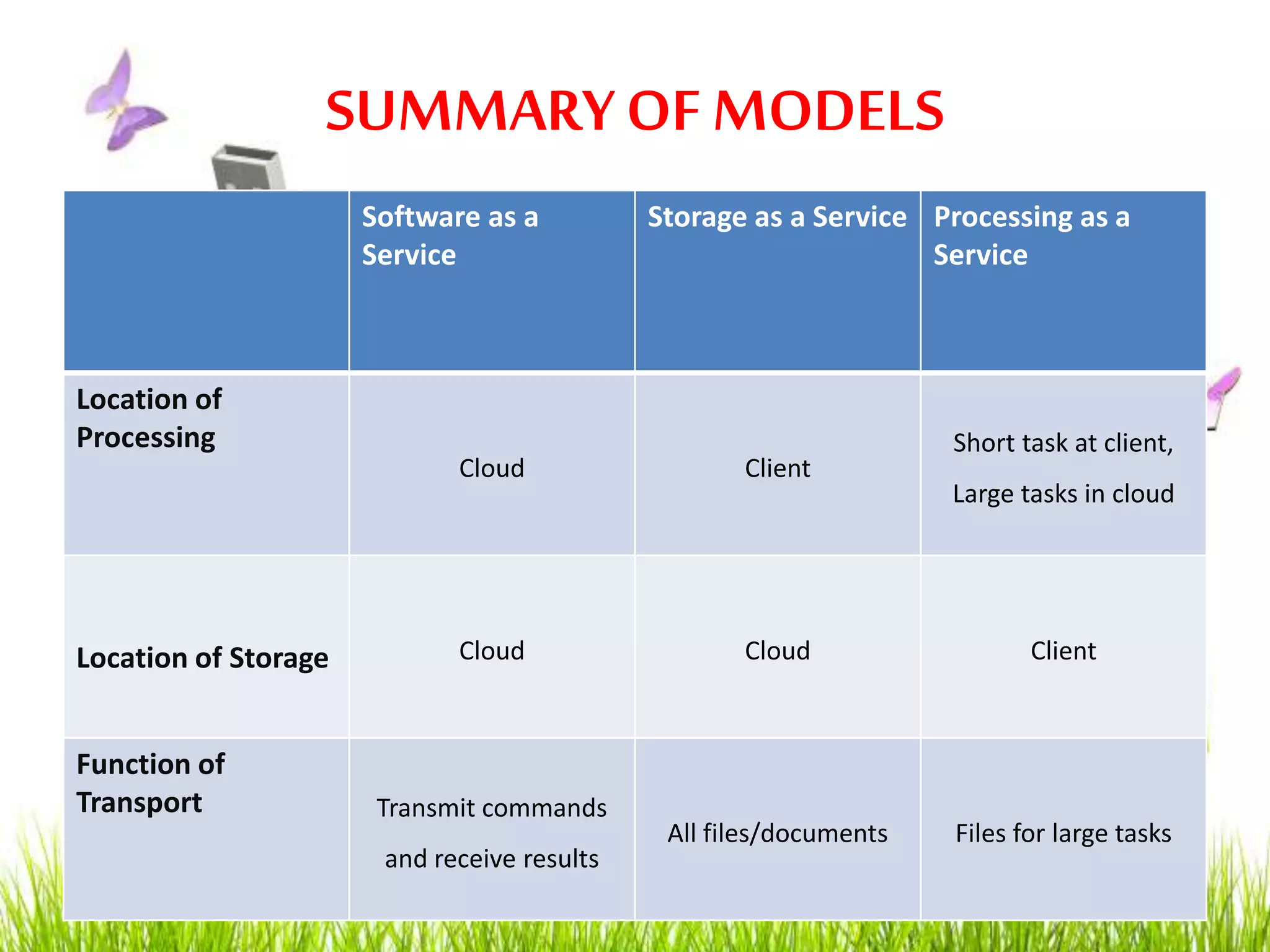
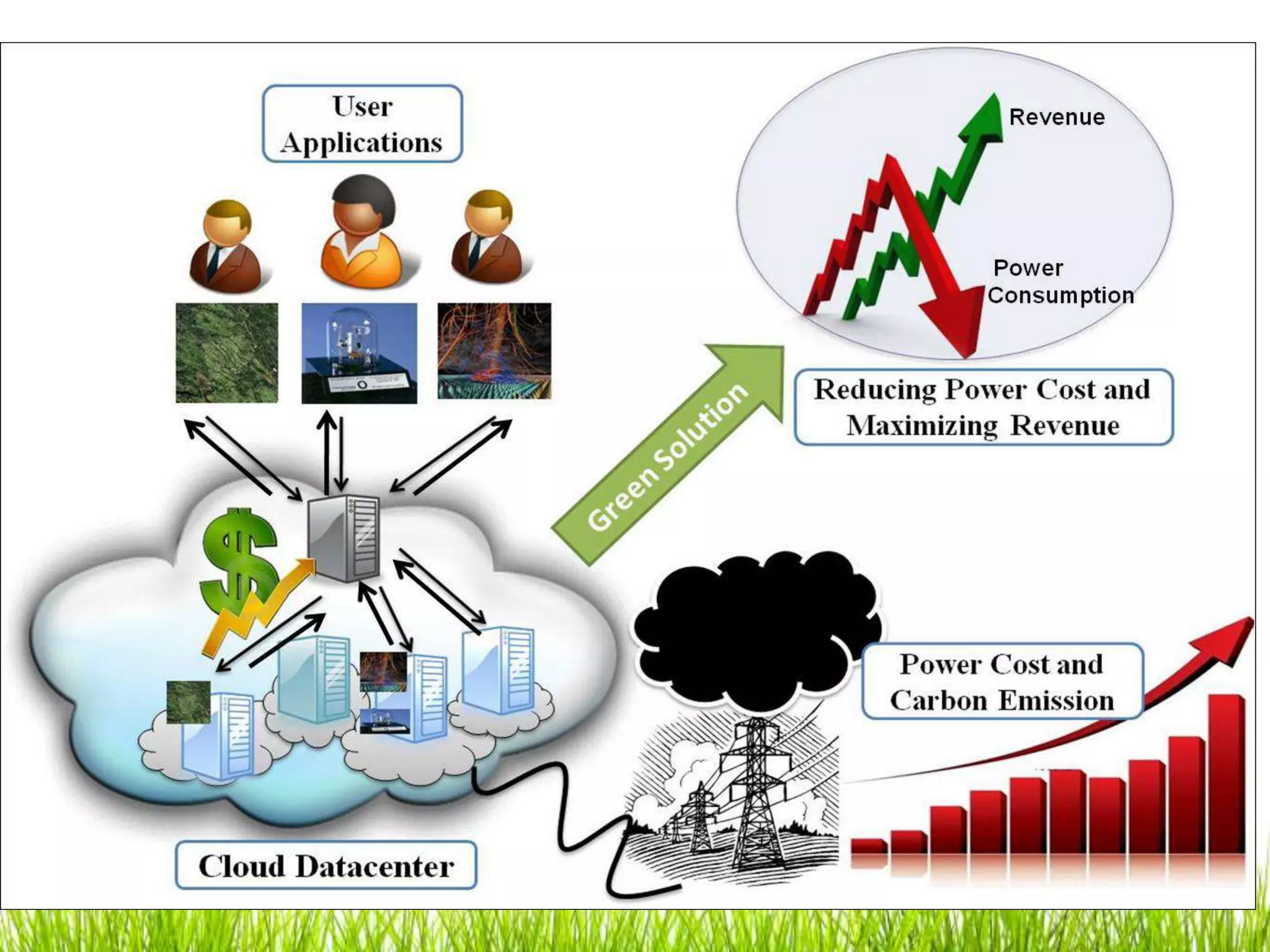
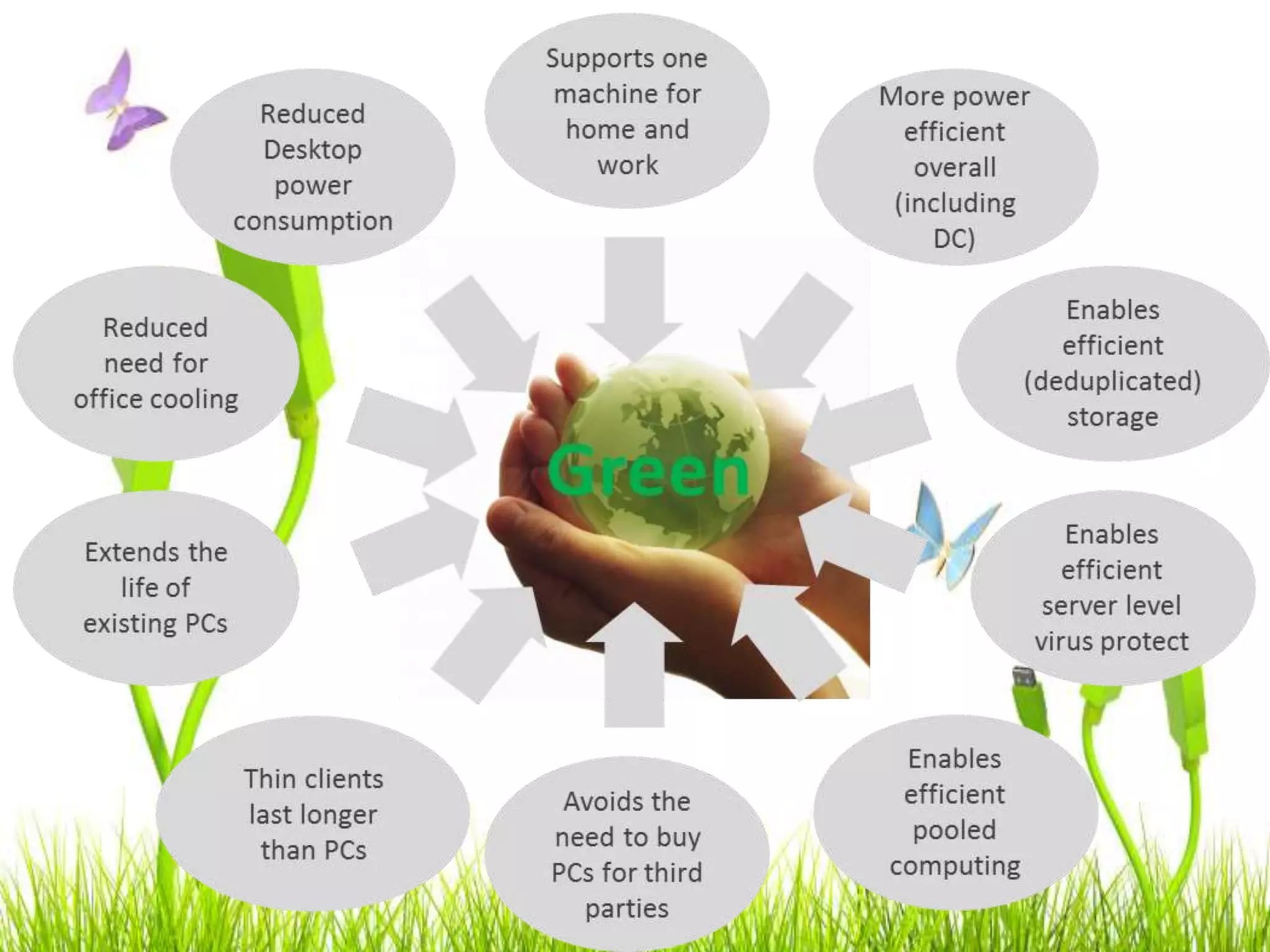
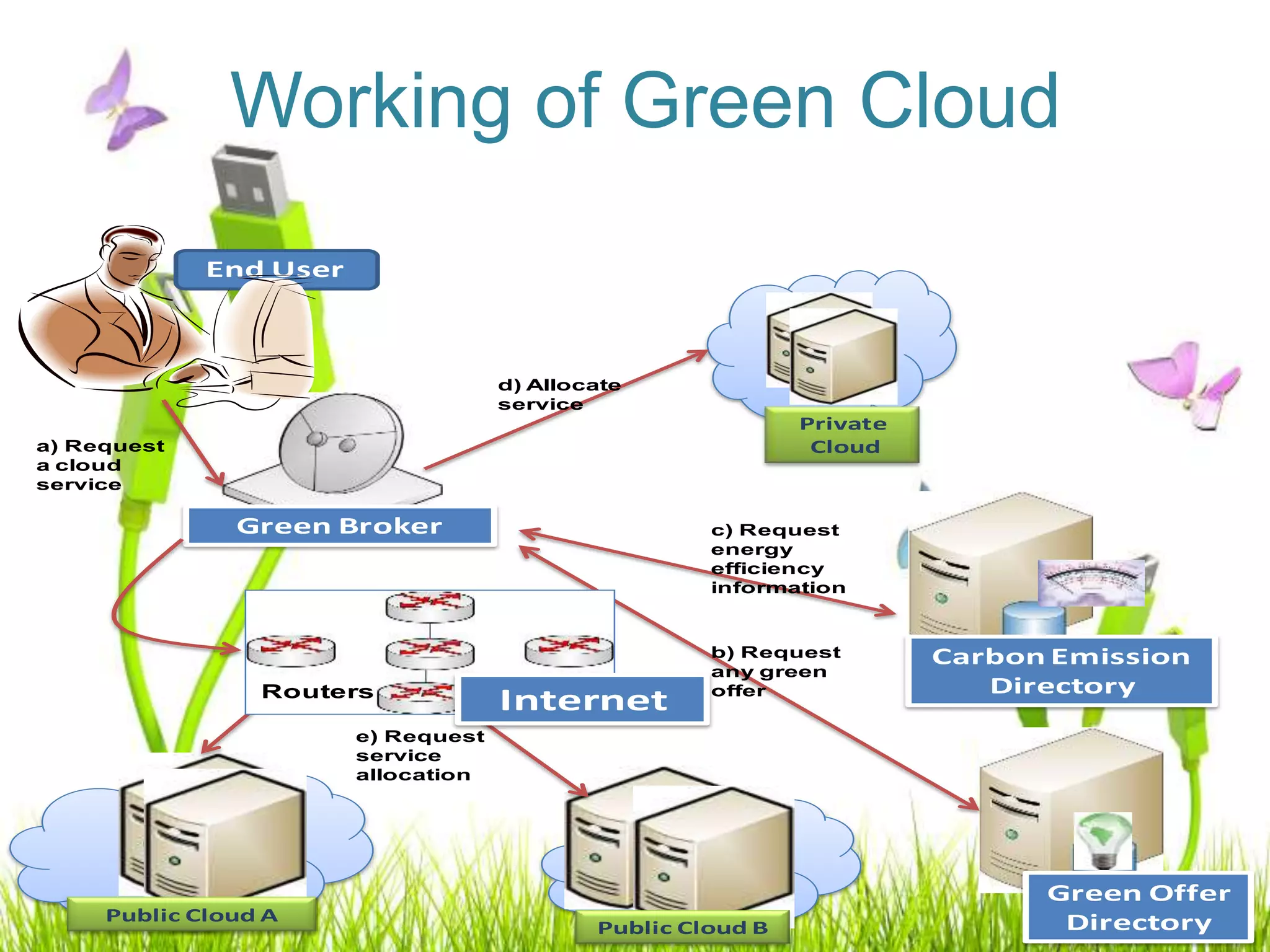
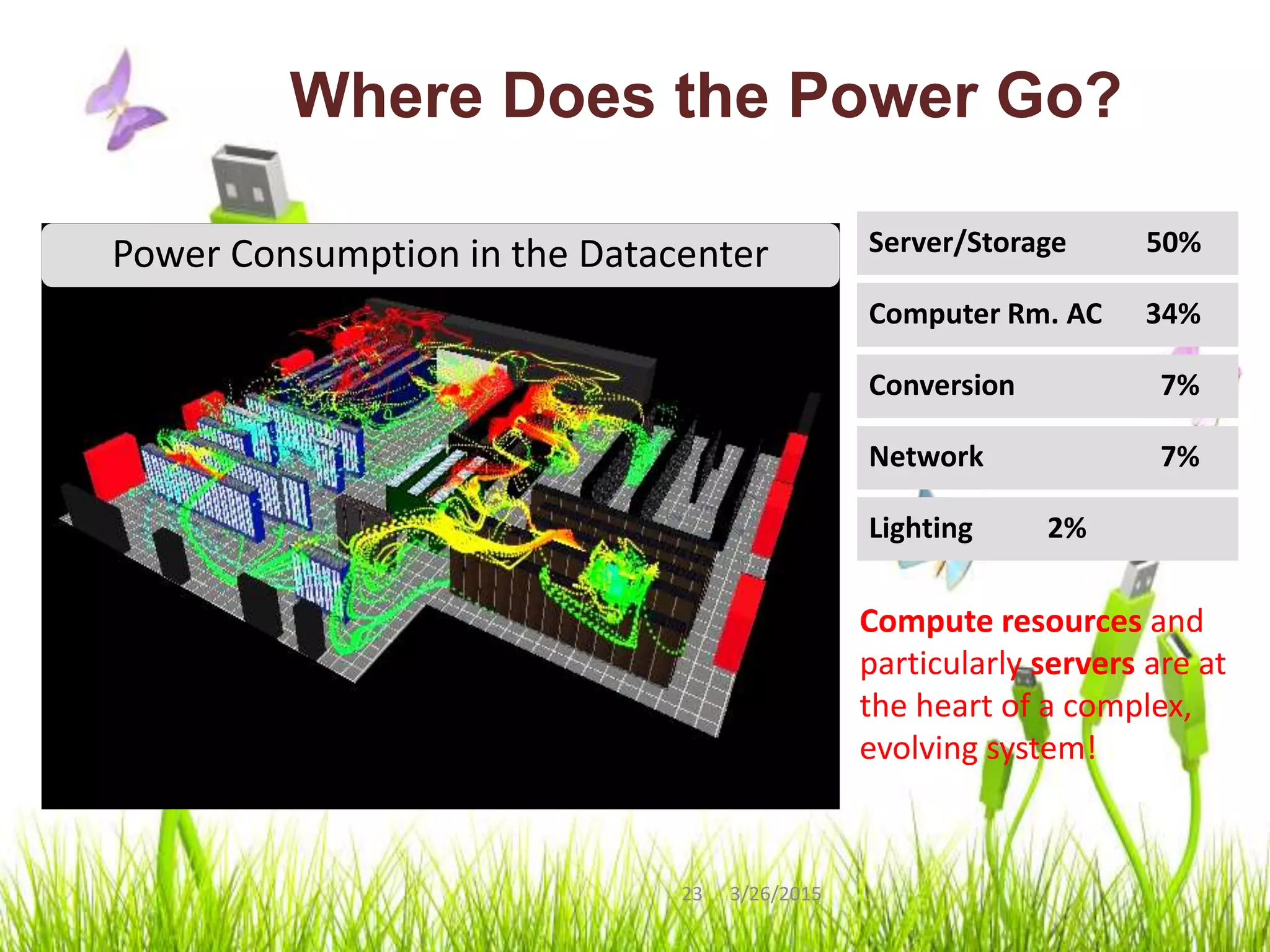
Green computing refers to using computing resources efficiently and minimizing environmental impact. It involves implementing energy-efficient policies and practices when setting up and operating IT systems. The goals of green computing include minimizing energy consumption, purchasing green energy, and reducing employee/customer travel requirements. Green cloud computing aims to achieve efficient infrastructure utilization and processing while minimizing energy usage. It uses techniques like dynamic resource allocation and powering down underutilized servers.