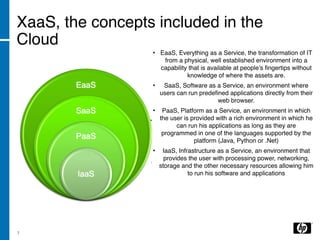
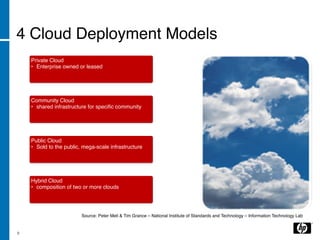
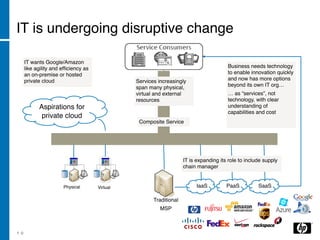
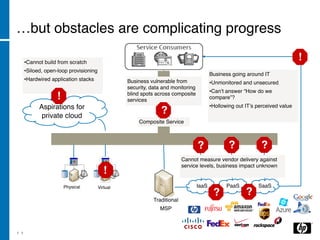
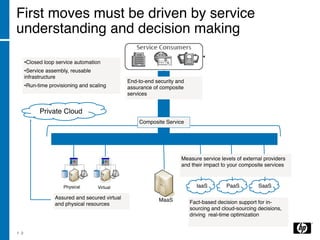
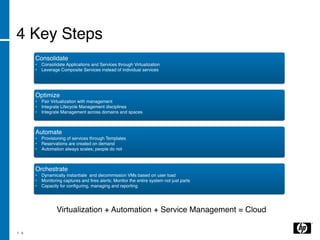
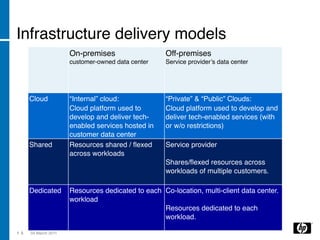
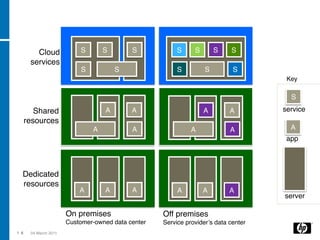
The document discusses the transition to cloud computing, emphasizing its definition, various deployment models, and the importance of service management. It outlines four key steps to achieve successful cloud implementation: consolidation, optimization, automation, and lessons learned from past experiences. The presenter highlights the need for a strategic approach, addressing obstacles, and ensuring security while integrating cloud solutions.