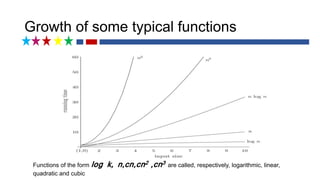
An algorithm is a sequence of unambiguous instructions to solve a problem and obtain an output for any input in a finite time. Euclid developed one of the earliest algorithms to find the greatest common divisor in 300 BC. Performance of an algorithm is evaluated based on time and space complexity. Time complexity measures the total time required and is classified based on functions like constant, logarithmic, linear, quadratic or cubic. Space complexity measures the memory required excluding input space.