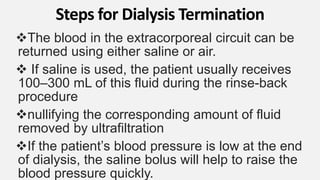
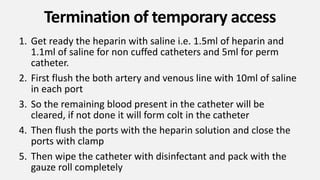
This document outlines the steps for terminating a dialysis treatment session through either saline or air rinse. It describes disconnecting the patient from the dialysis machine by using saline or a saline-air mixture to displace the remaining blood in the extracorporeal circuit and return it to the patient. It notes that air rinse increases the risk of air embolism so must be carefully supervised. The document also provides instructions for caring for vascular access sites after treatment and in emergency situations.