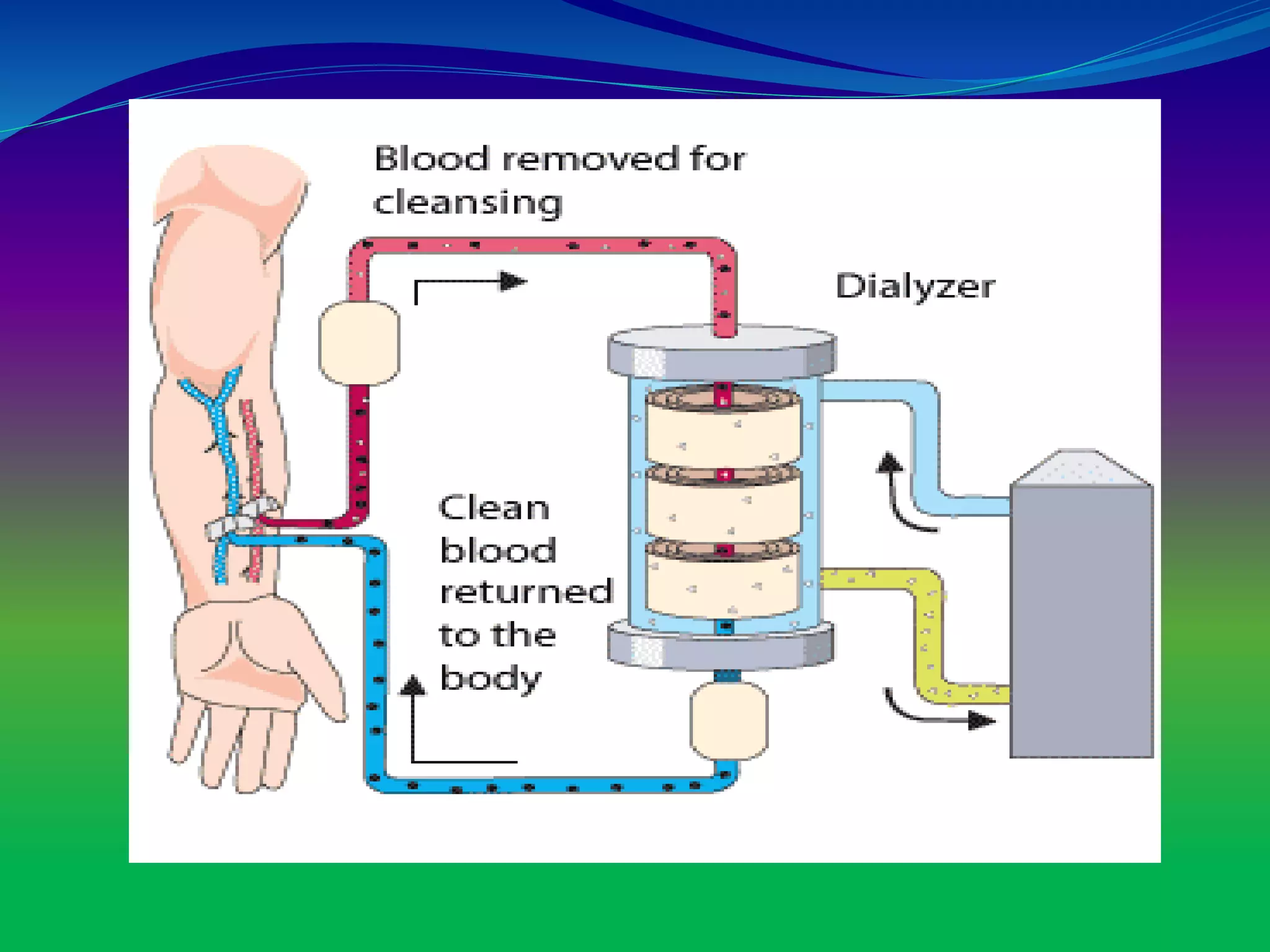
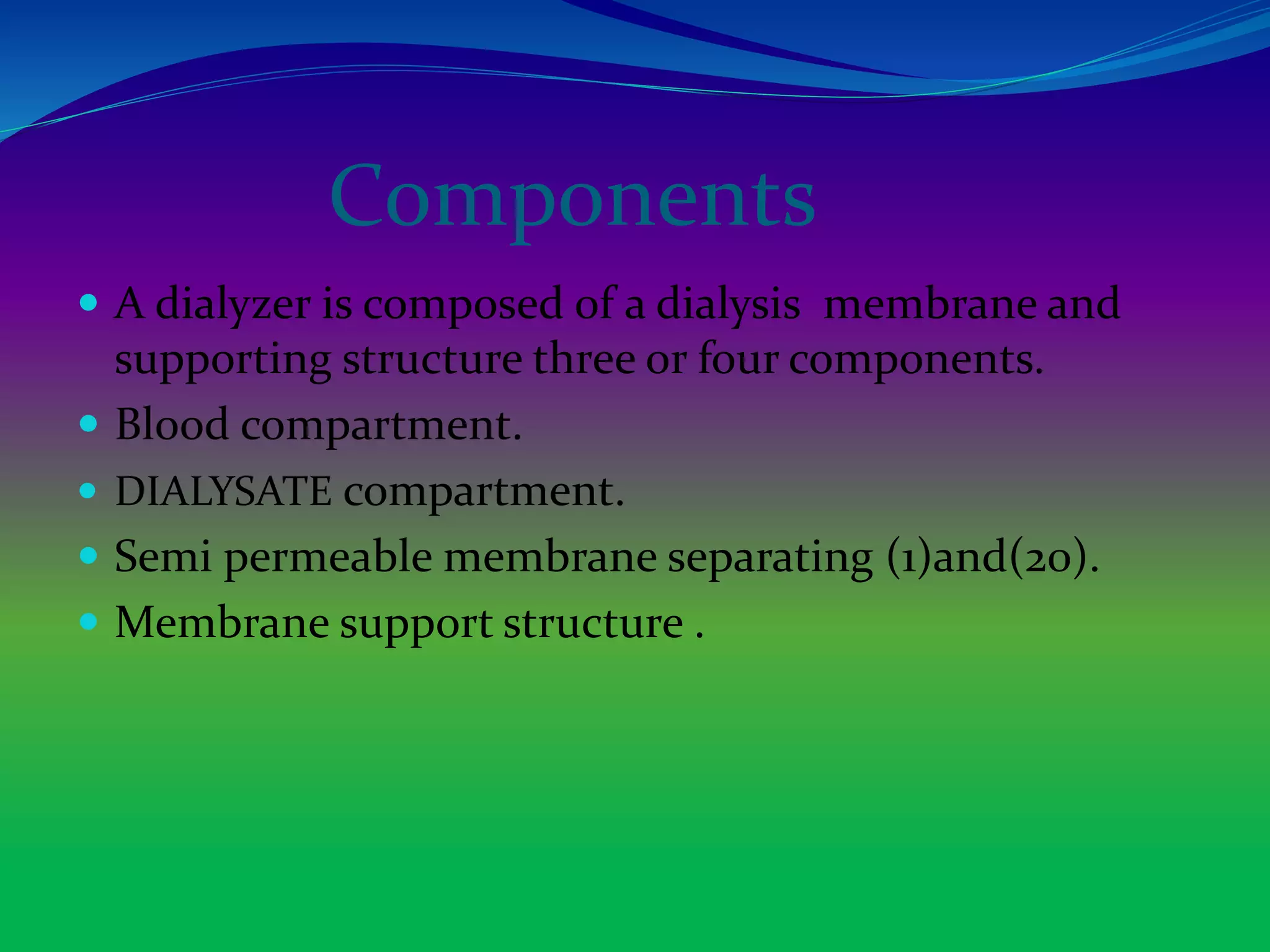
The document discusses dialysis machines, which act as artificial kidneys for patients experiencing renal failure, utilizing hemodialysis to cleanse blood. It traces the history of dialysis back to Dr. Willem Kolff, who invented the first dialyzer in 1943, and explains the machine's components, principles, advantages, and disadvantages. Key points include the process of blood filtration and the challenges faced by patients regarding diet and fluid intake.