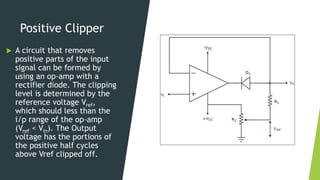
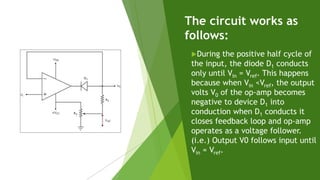
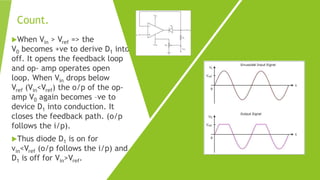
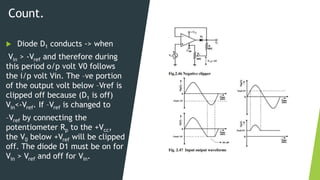
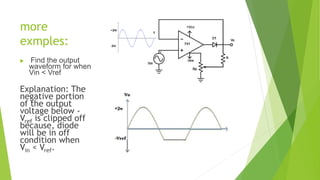
This document discusses clipper circuits, which are wave shaping circuits that remove parts of an input signal above or below a reference value. There are two main types of clippers: positive clippers, which clip off positive parts of the signal above the reference value, and negative clippers, which clip off negative parts below the reference value. Clipper circuits use diodes and op-amps to clip portions of the waveform and are commonly used in applications like signal separation, limiting noise spikes, waveform generation, and voltage protection.