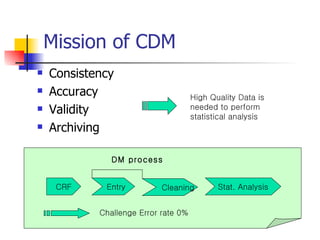
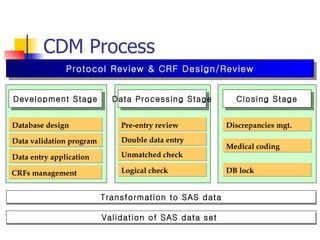
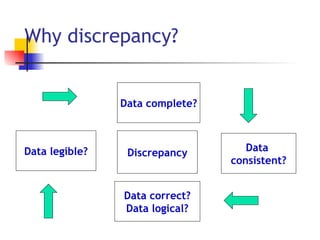
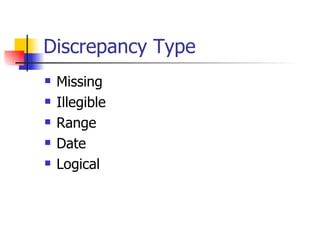
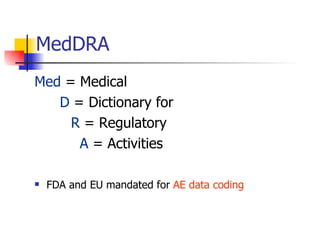
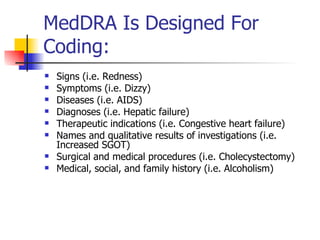
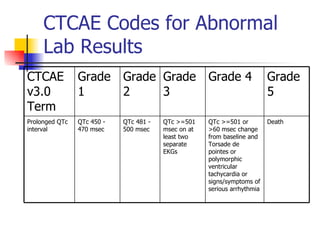
The document provides an overview of clinical data management (CDM) responsibilities and processes. It discusses the CDM mission of ensuring high quality, consistent, accurate and valid data collection. Key CDM responsibilities include protocol review, database design, data entry, verification, coding, query resolution and ensuring data quality. The CDM process involves multiple stages from database design to data transformation and locking. Medical coding systems like MedDRA are used to standardize adverse event and medical condition terms. Case report forms and logging procedures are also outlined.