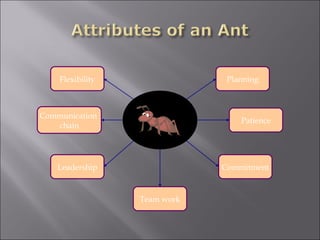
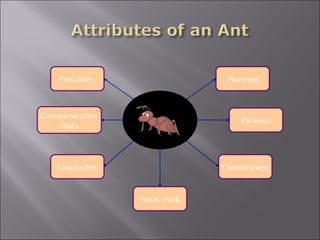
The document discusses environmental sustainability and the challenges posed by environmental degradation. It notes that [1] environmental problems exist due to both human and natural factors, and poor, rural populations are often most affected. It then outlines several drivers of environmental degradation, including [2] population growth, consumption patterns, economic factors, and climate change. Finally, it recommends [3] reforms like mainstreaming environmental costs, regulating subsidies, improving governance, and investing in sustainable agriculture and education to promote environmental sustainability.