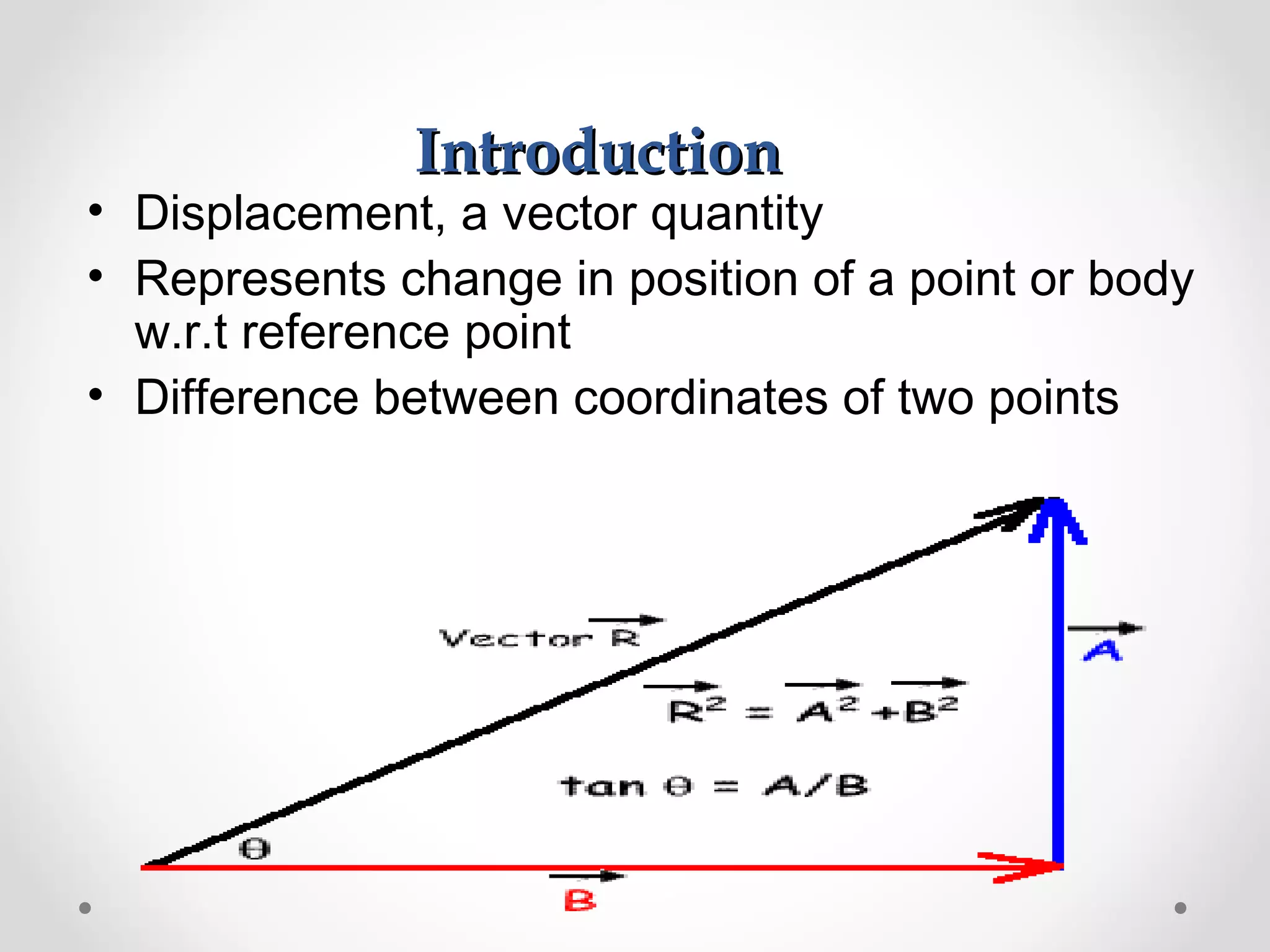
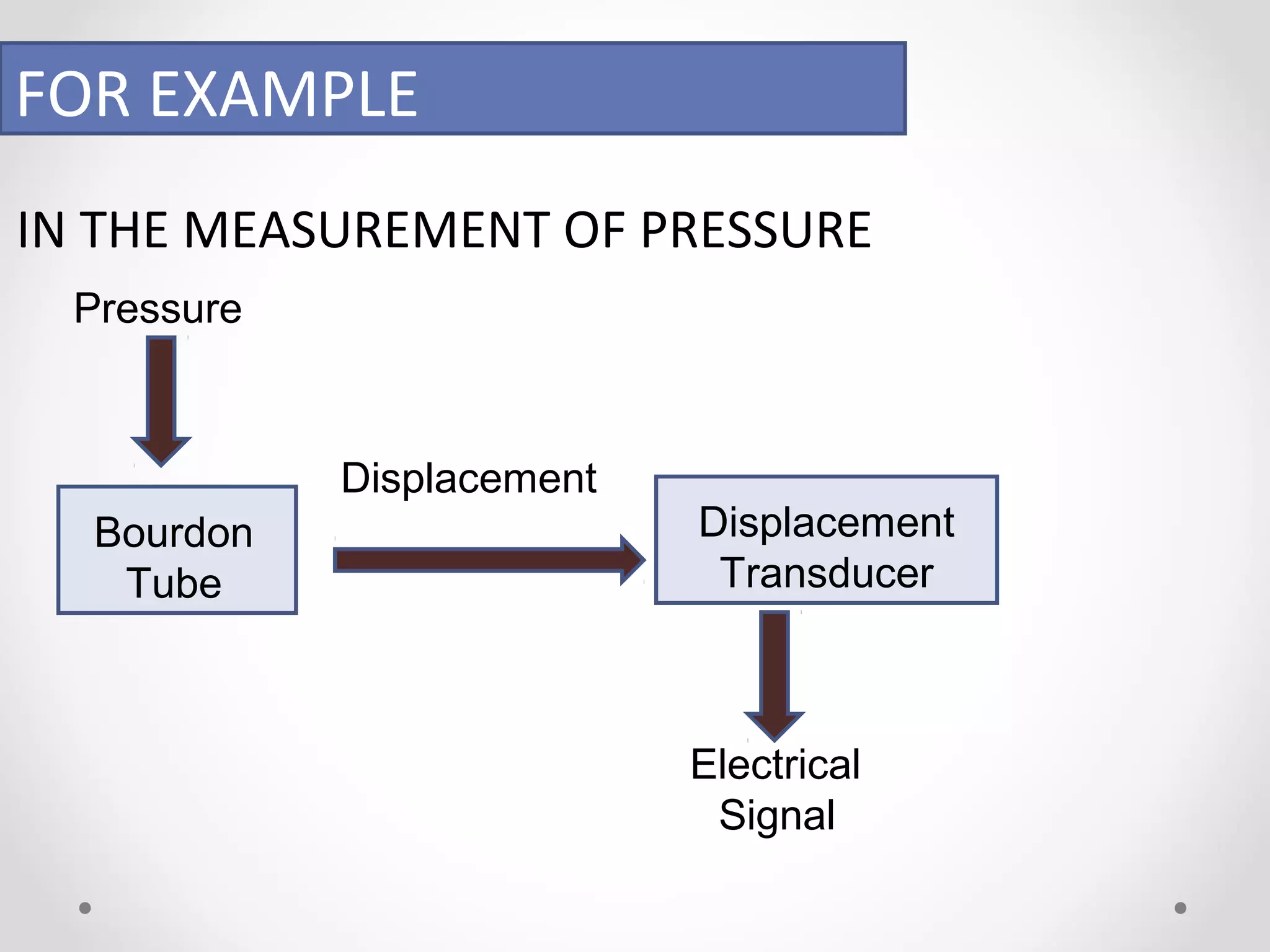
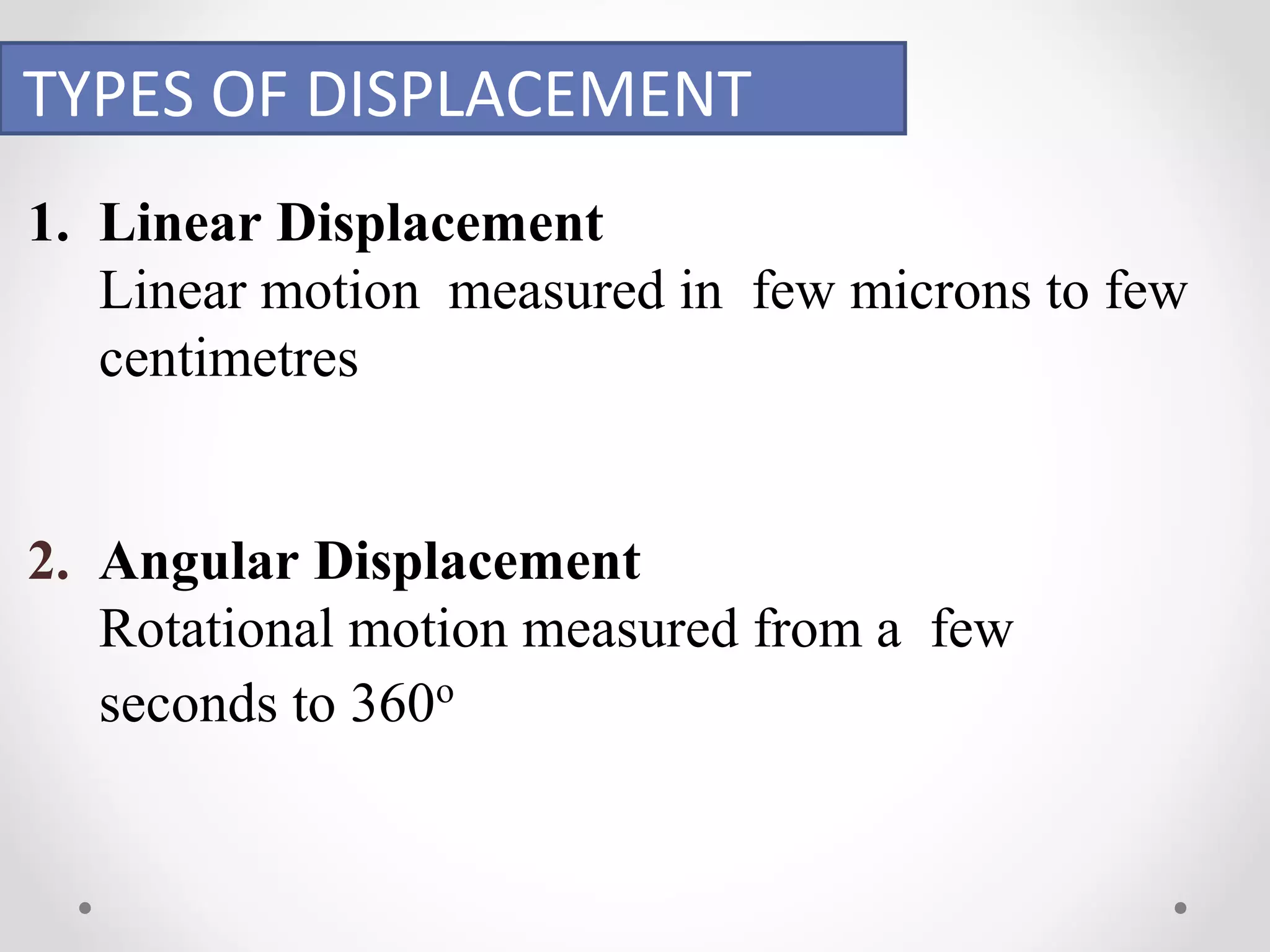
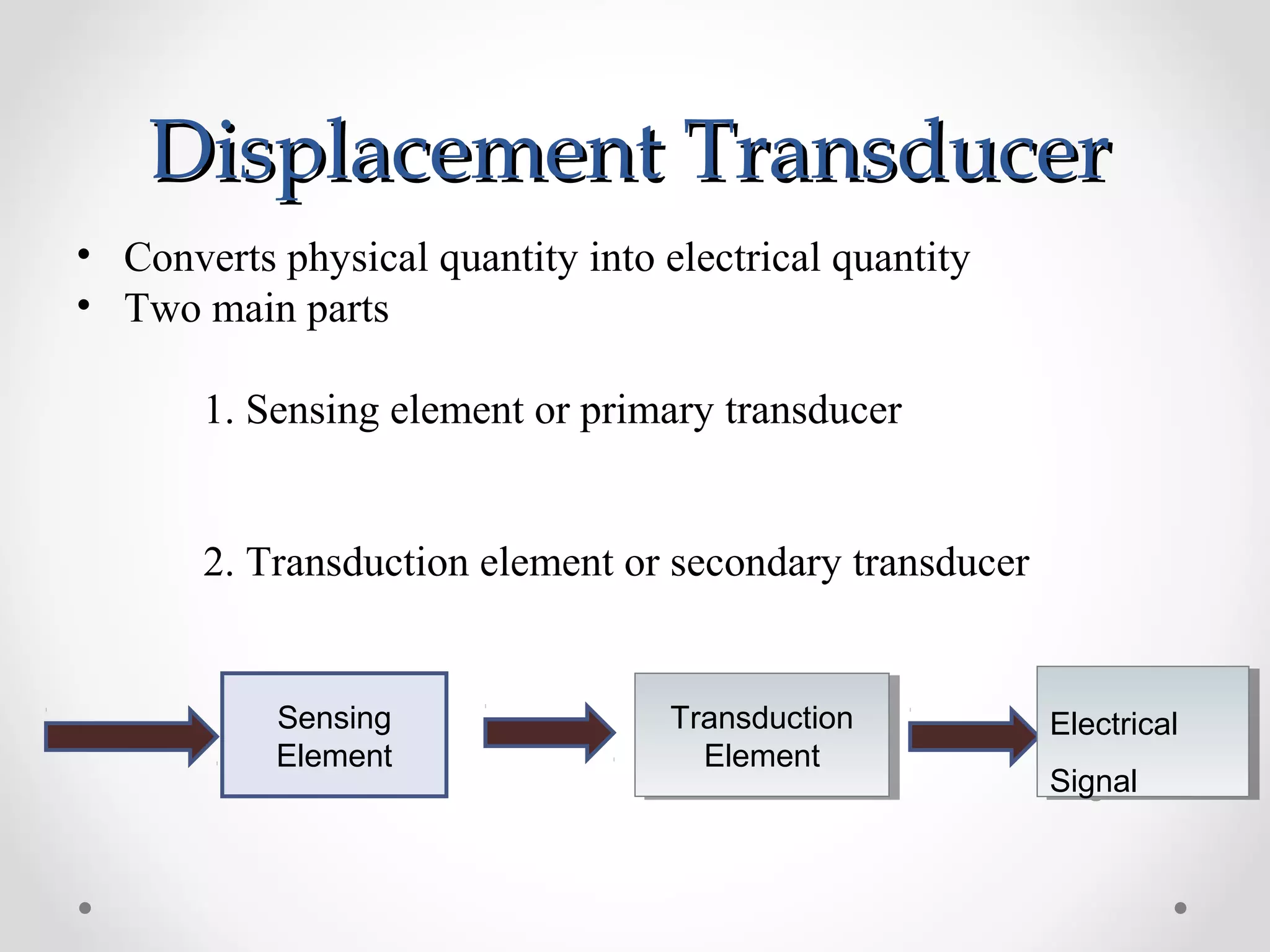
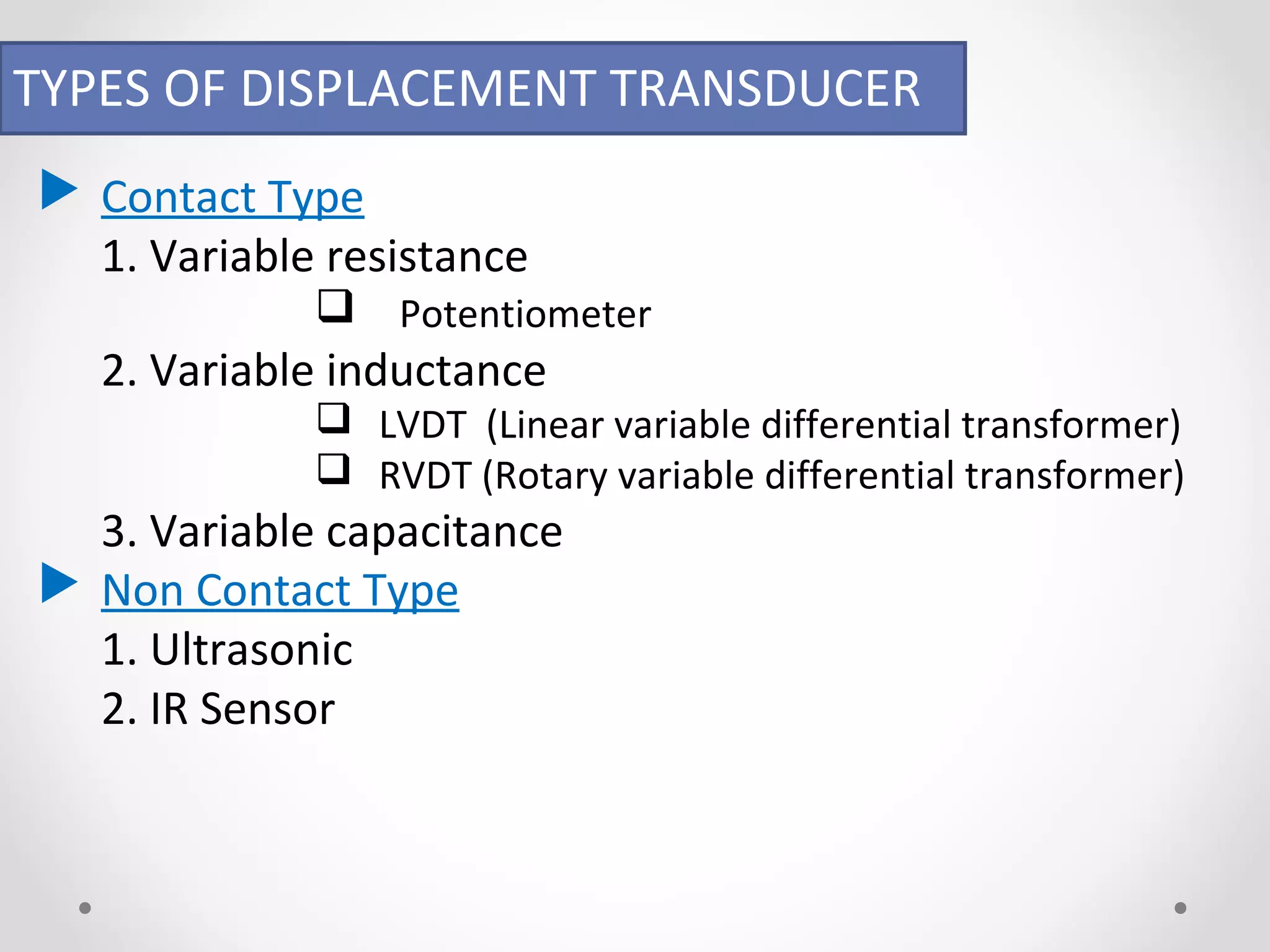
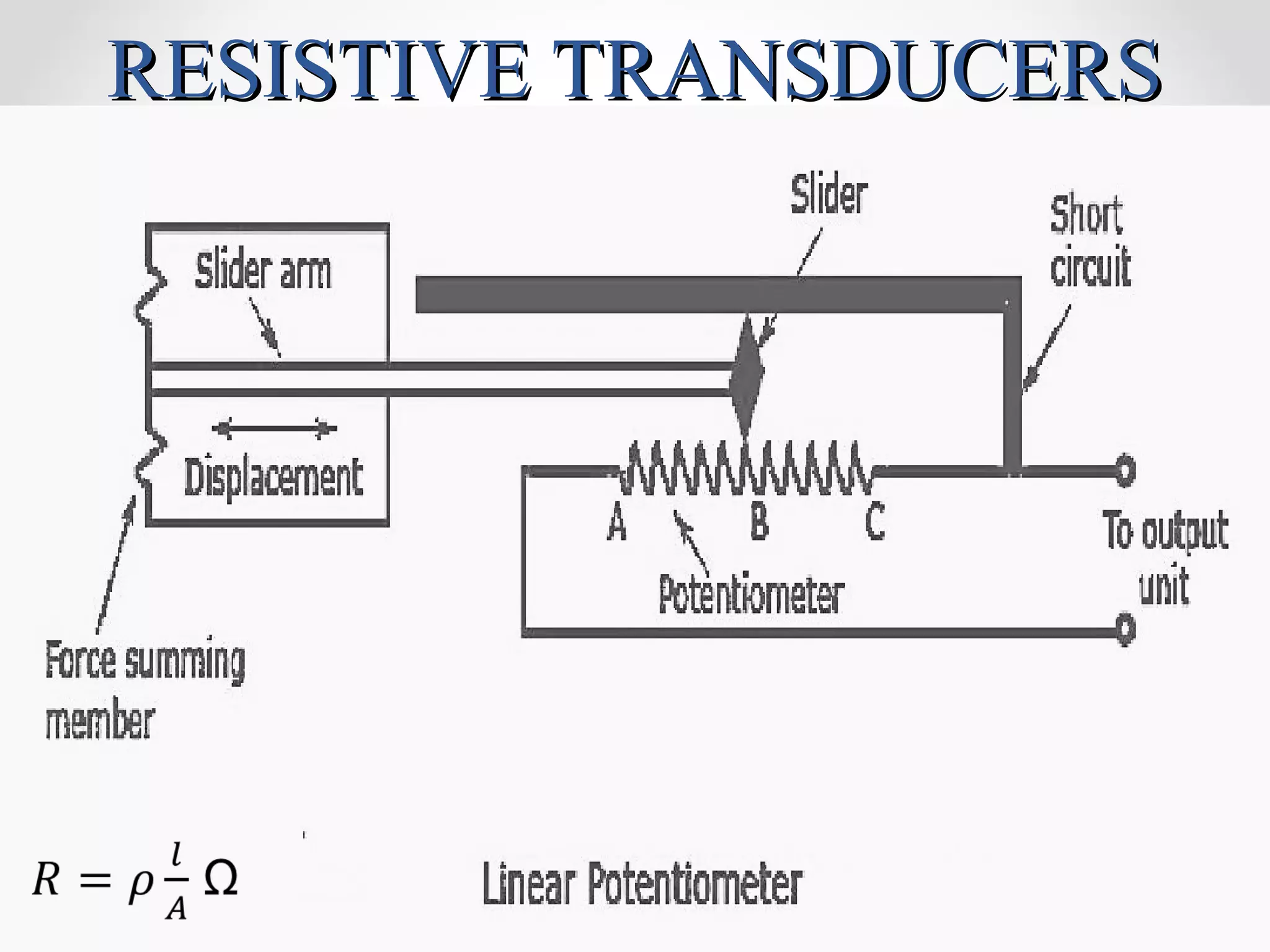
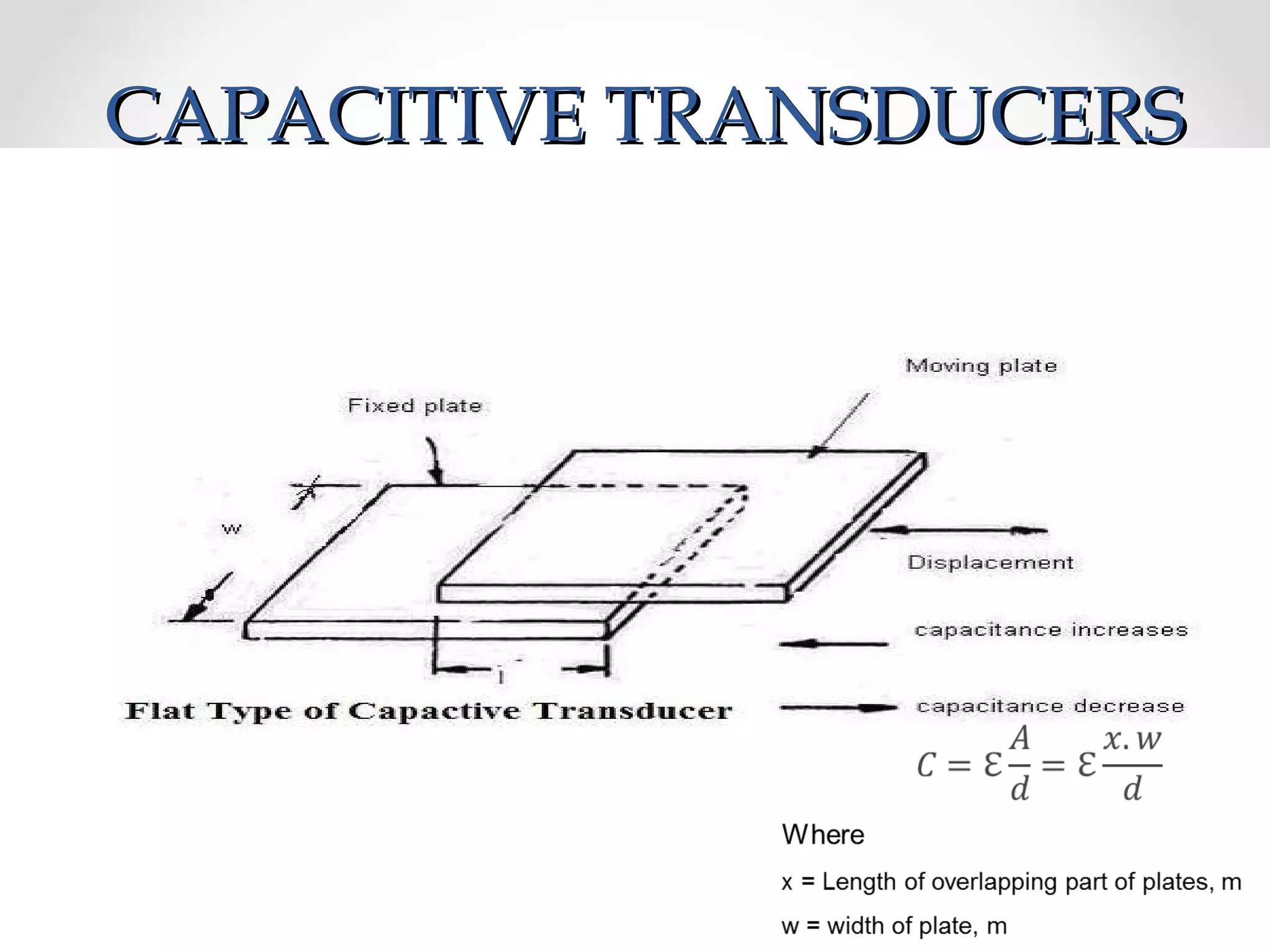
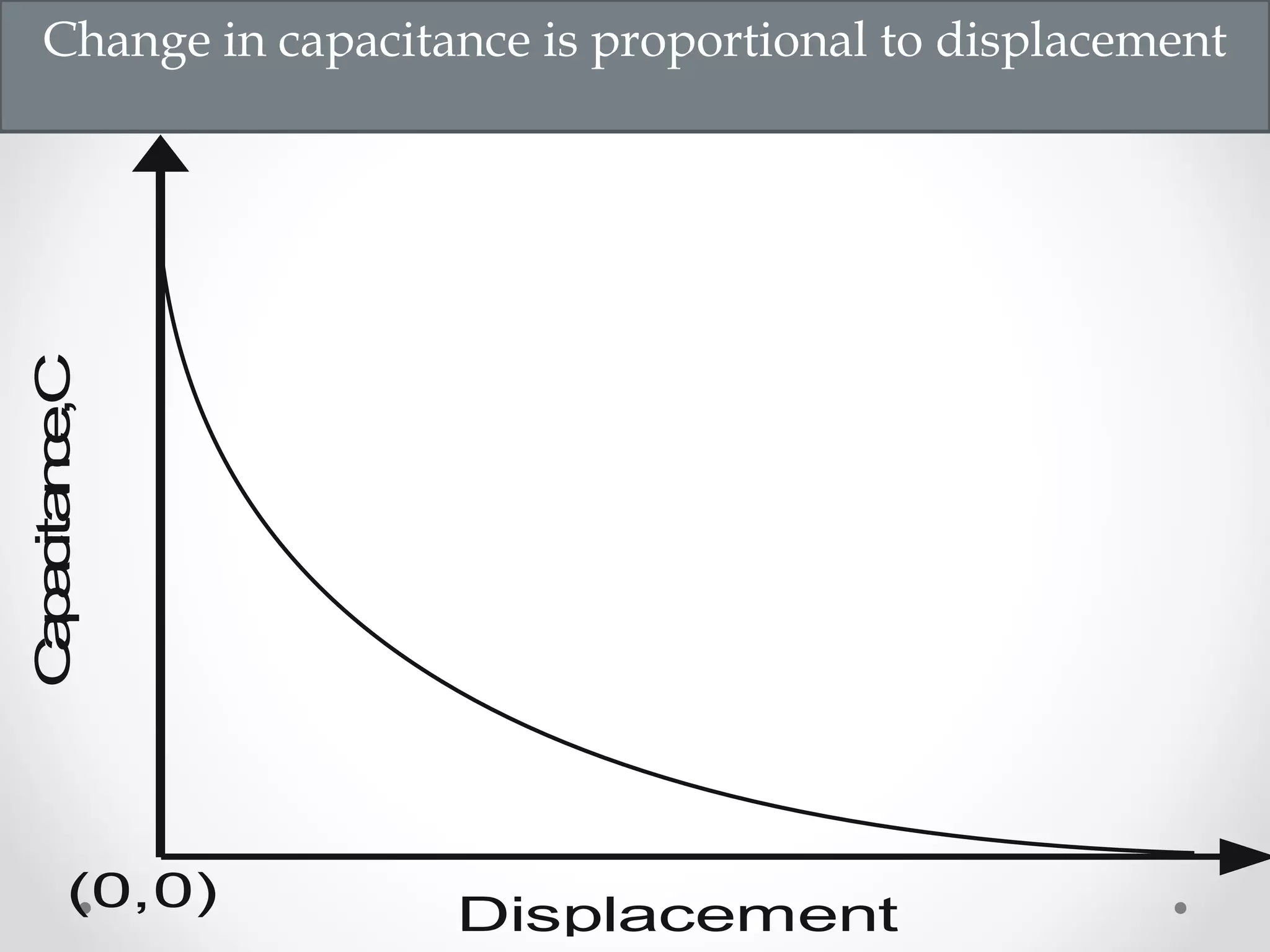
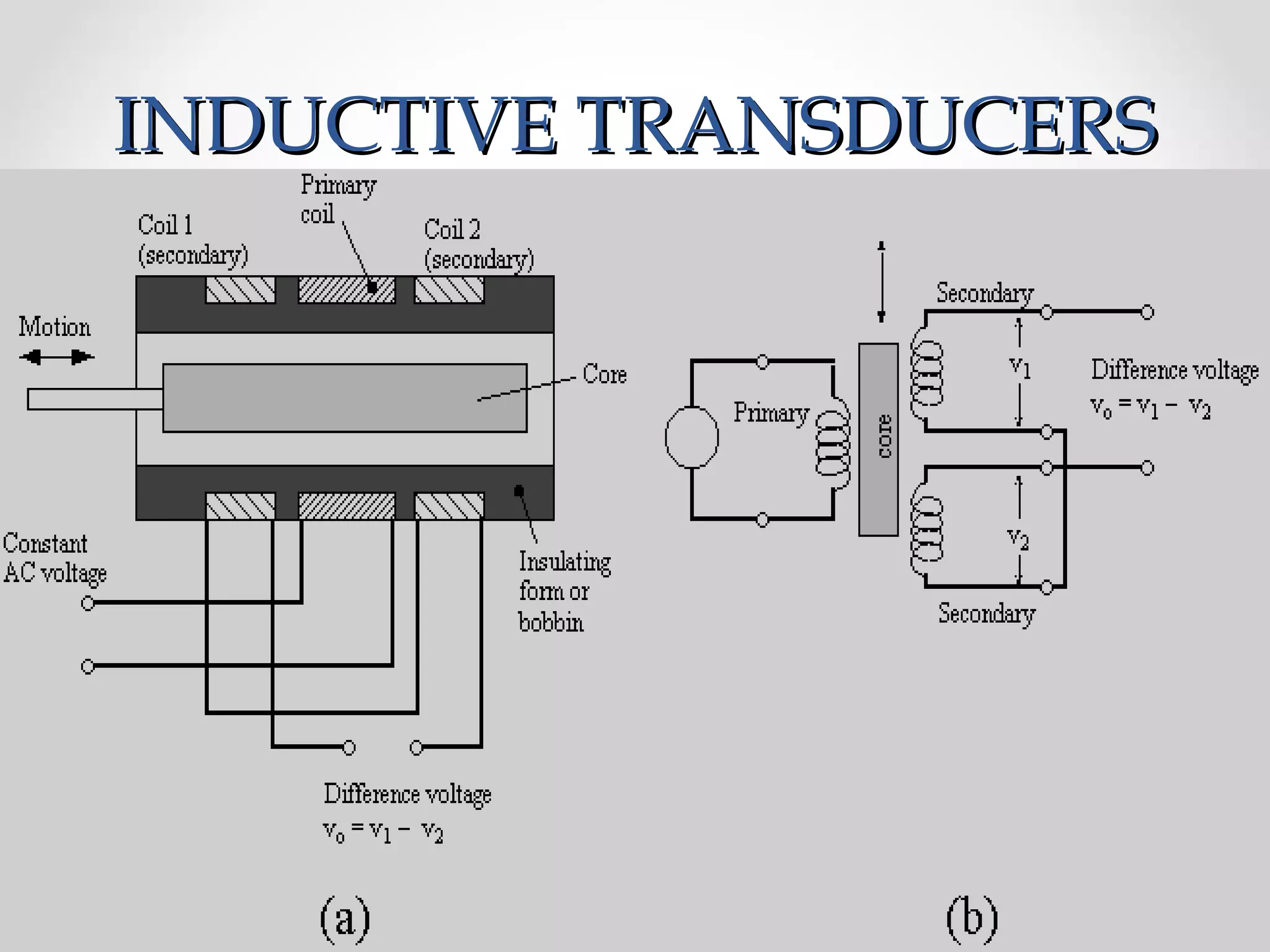
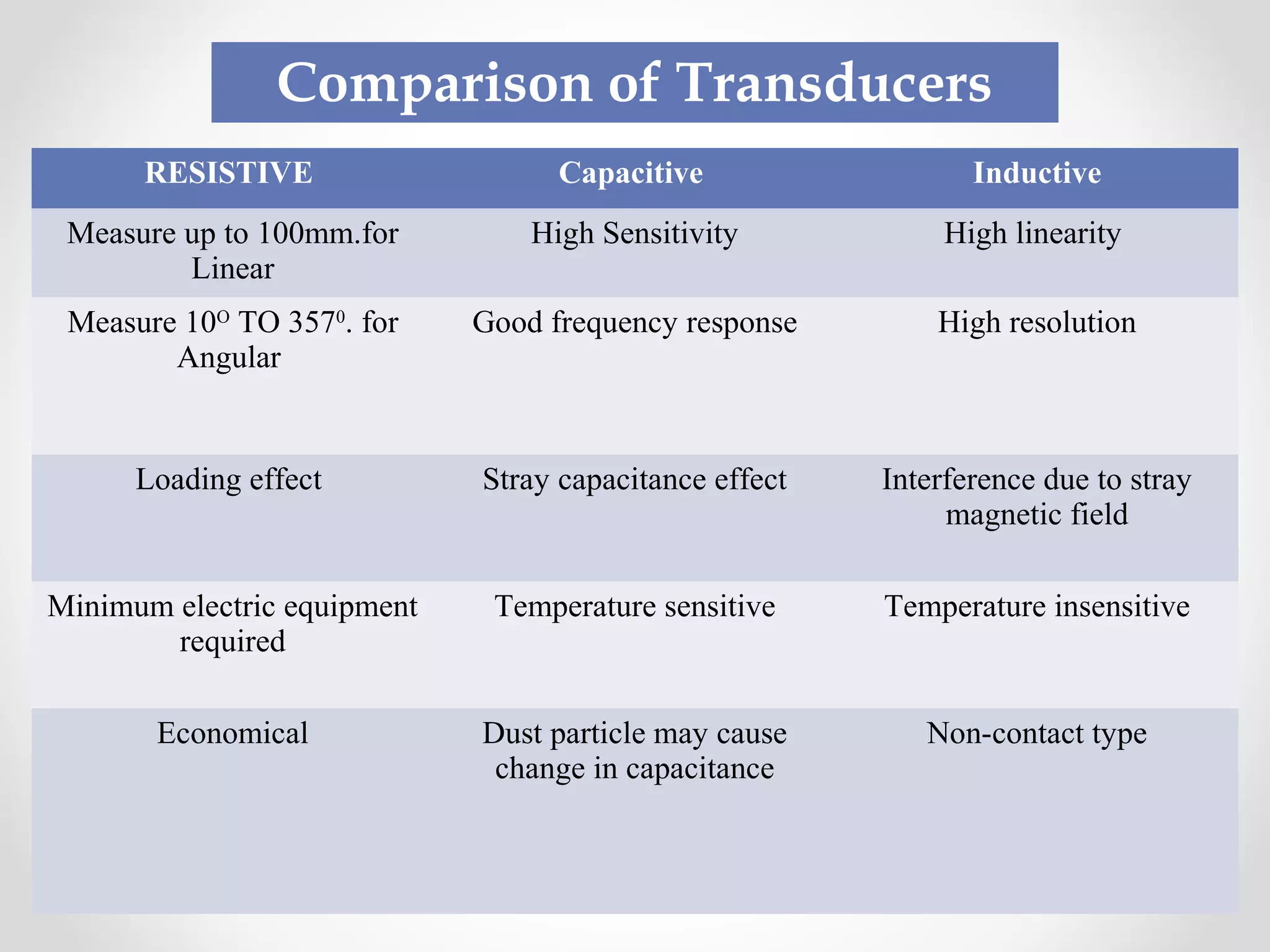
The document discusses displacement transducers used for measuring physical quantities like force, pressure, velocity and acceleration. It describes different types of displacement including linear and angular, and factors to consider when selecting a displacement sensor like required range, resolution and cost. Common displacement transducer types are described as contact types like potentiometers and LVDTs, and non-contact types like ultrasonic and IR sensors. Resistive, capacitive and inductive transducers are compared in terms of their measurement capabilities, sensitivities, resolutions and limitations.