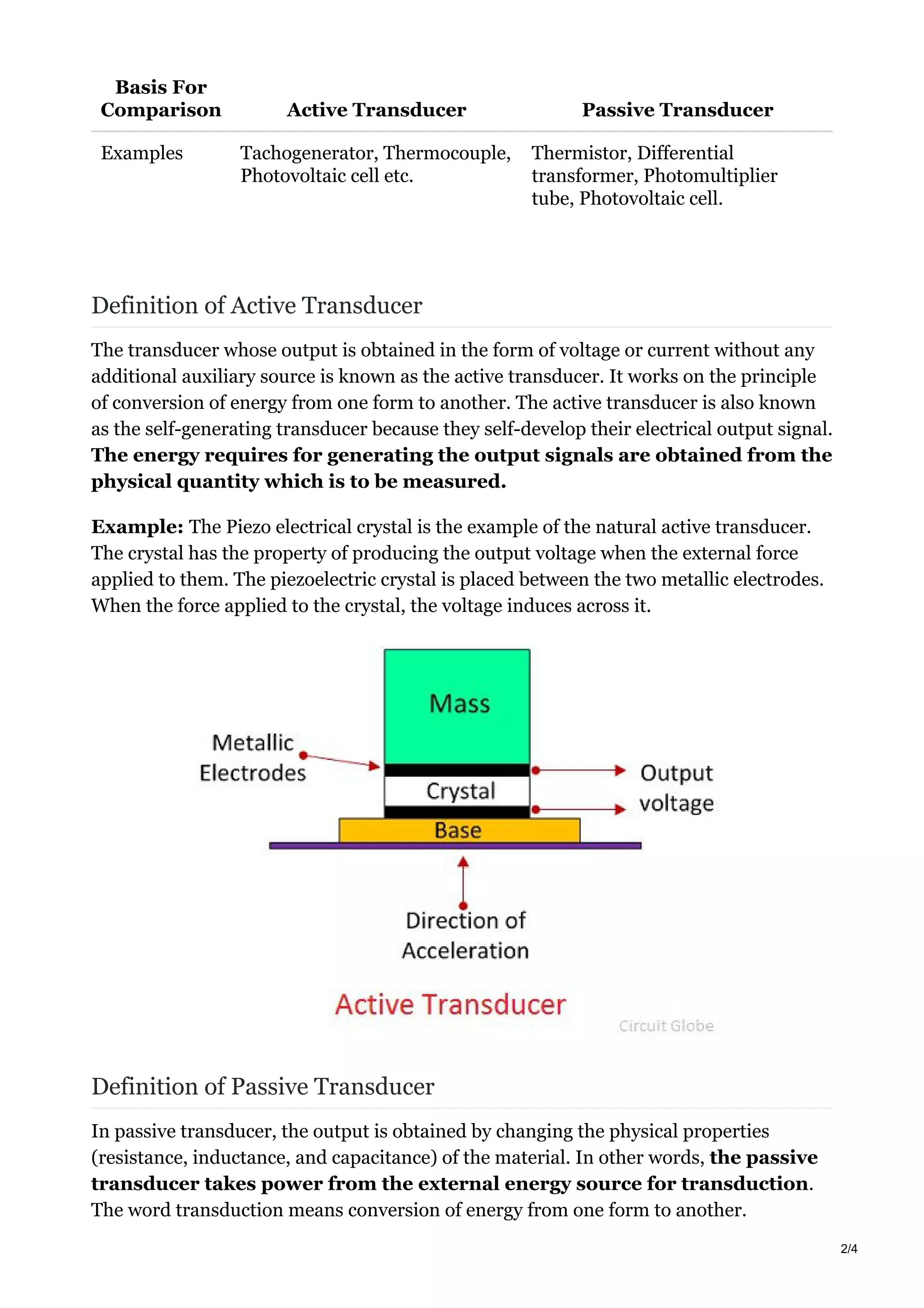
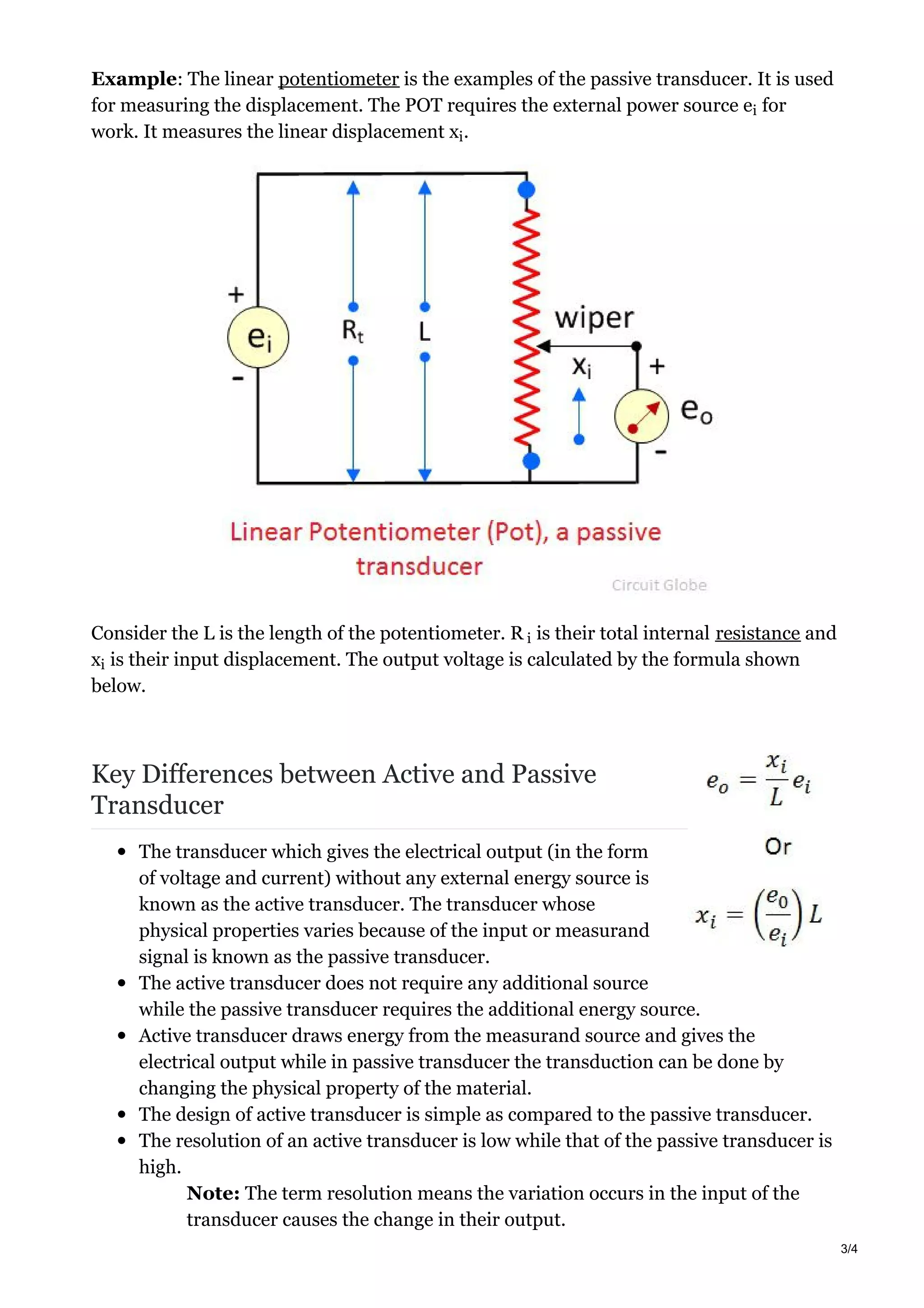
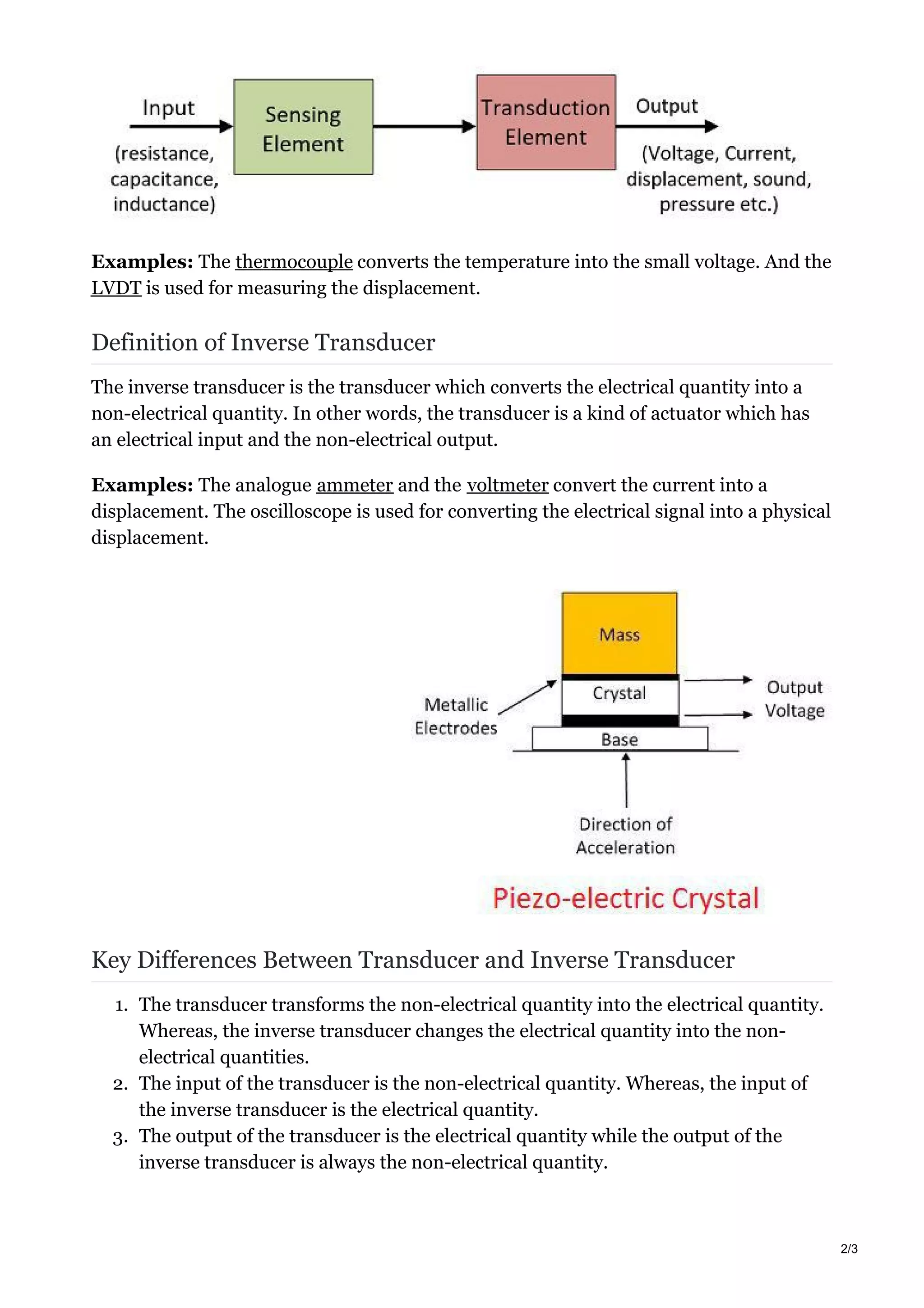
The document discusses transducers, which convert one form of energy into another. Specifically, it discusses:
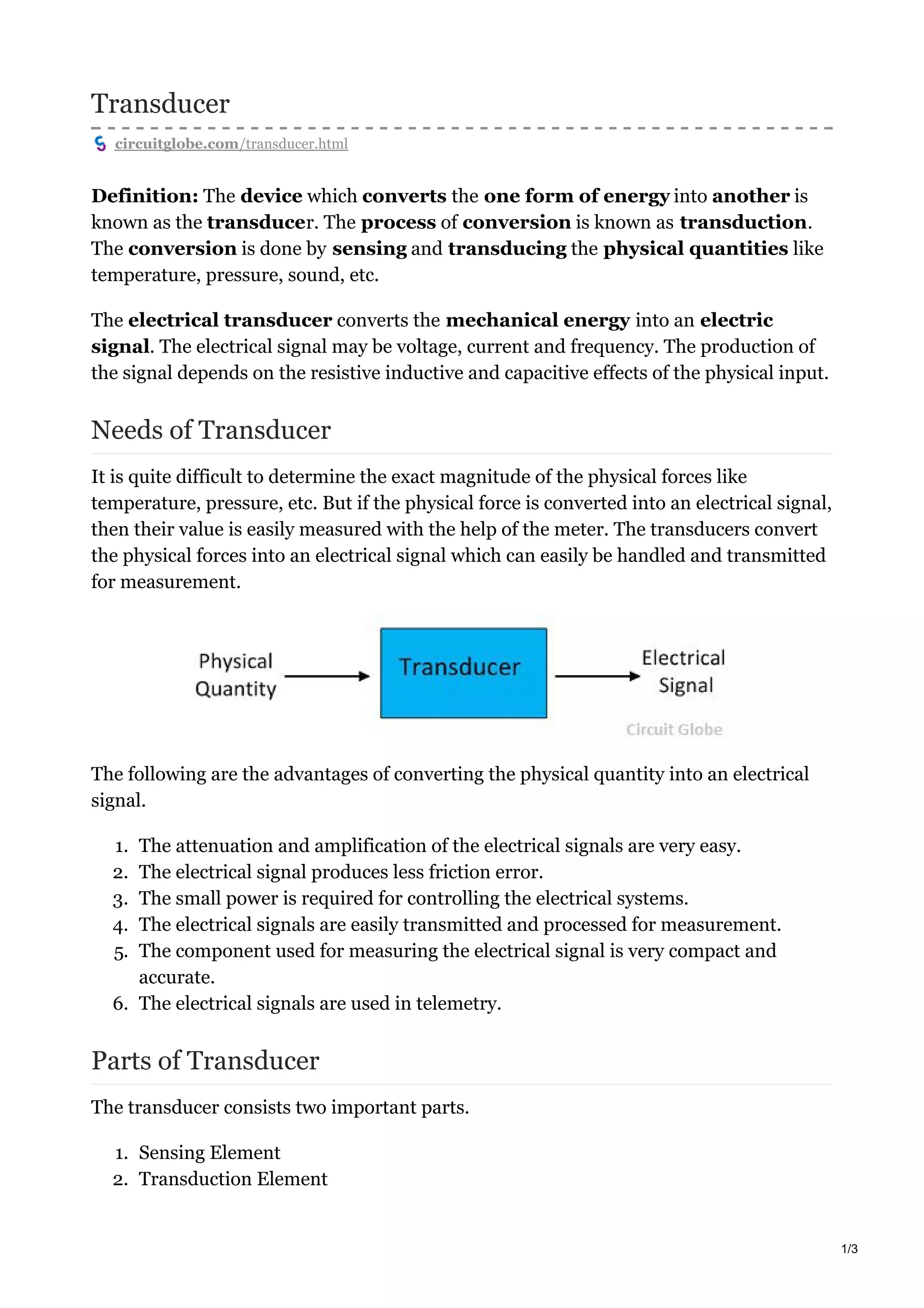
1. Transducers convert physical quantities like temperature, pressure, and sound into electrical signals. This makes the values easier to measure with instruments.
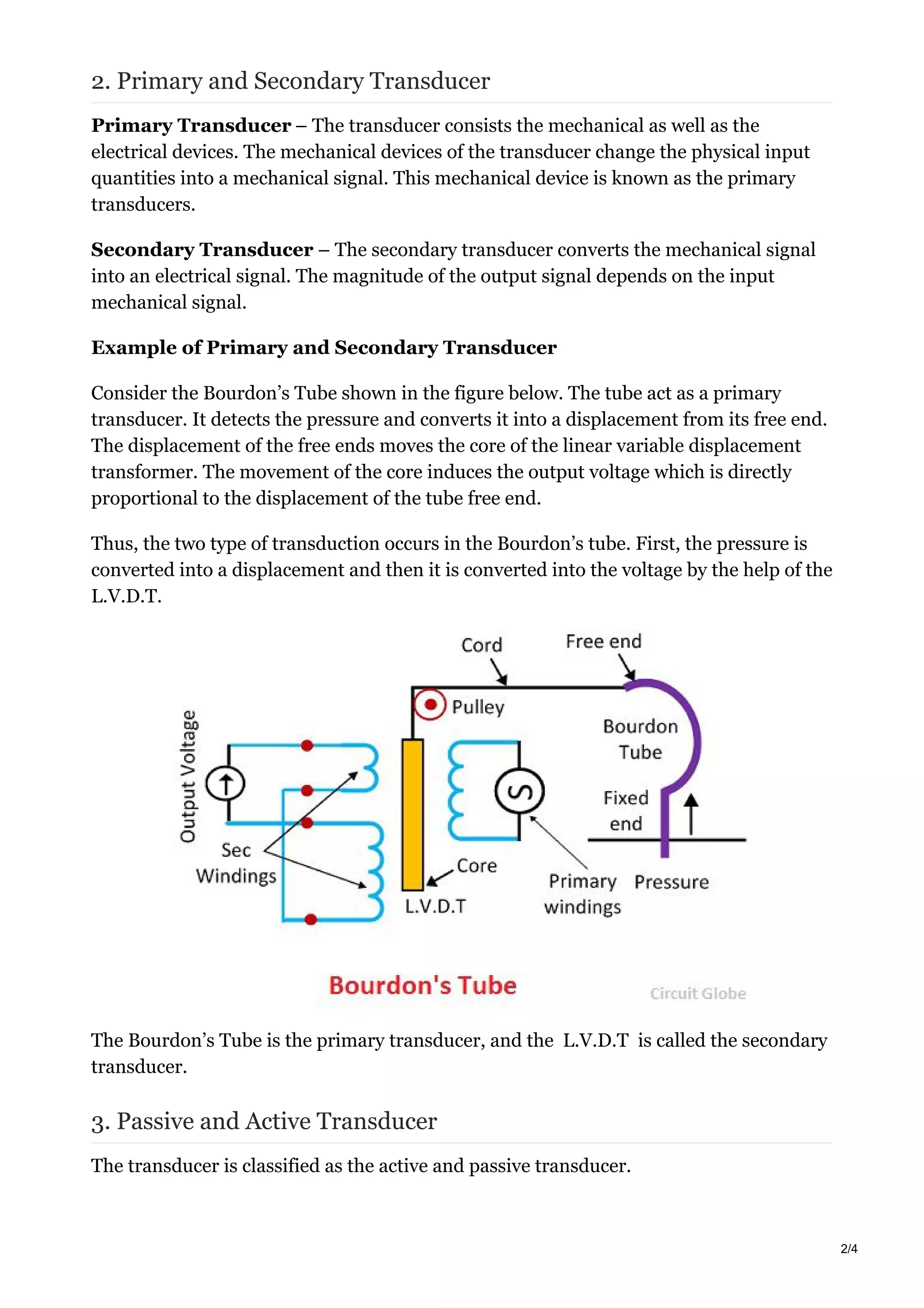
2. Transducers have two main parts - a sensing element that responds to physical stimuli, and a transduction element that converts the sensor output into an electrical signal.
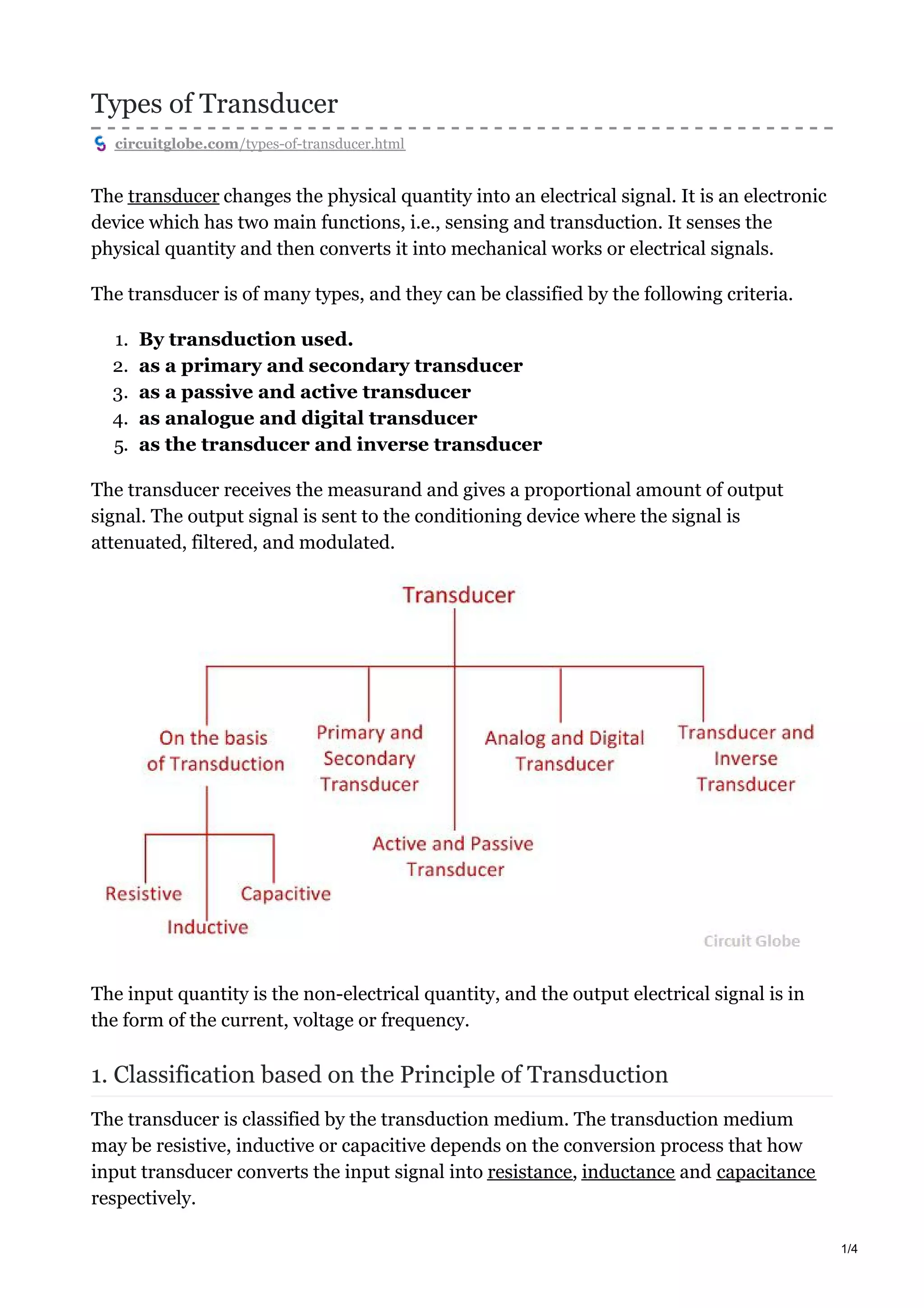
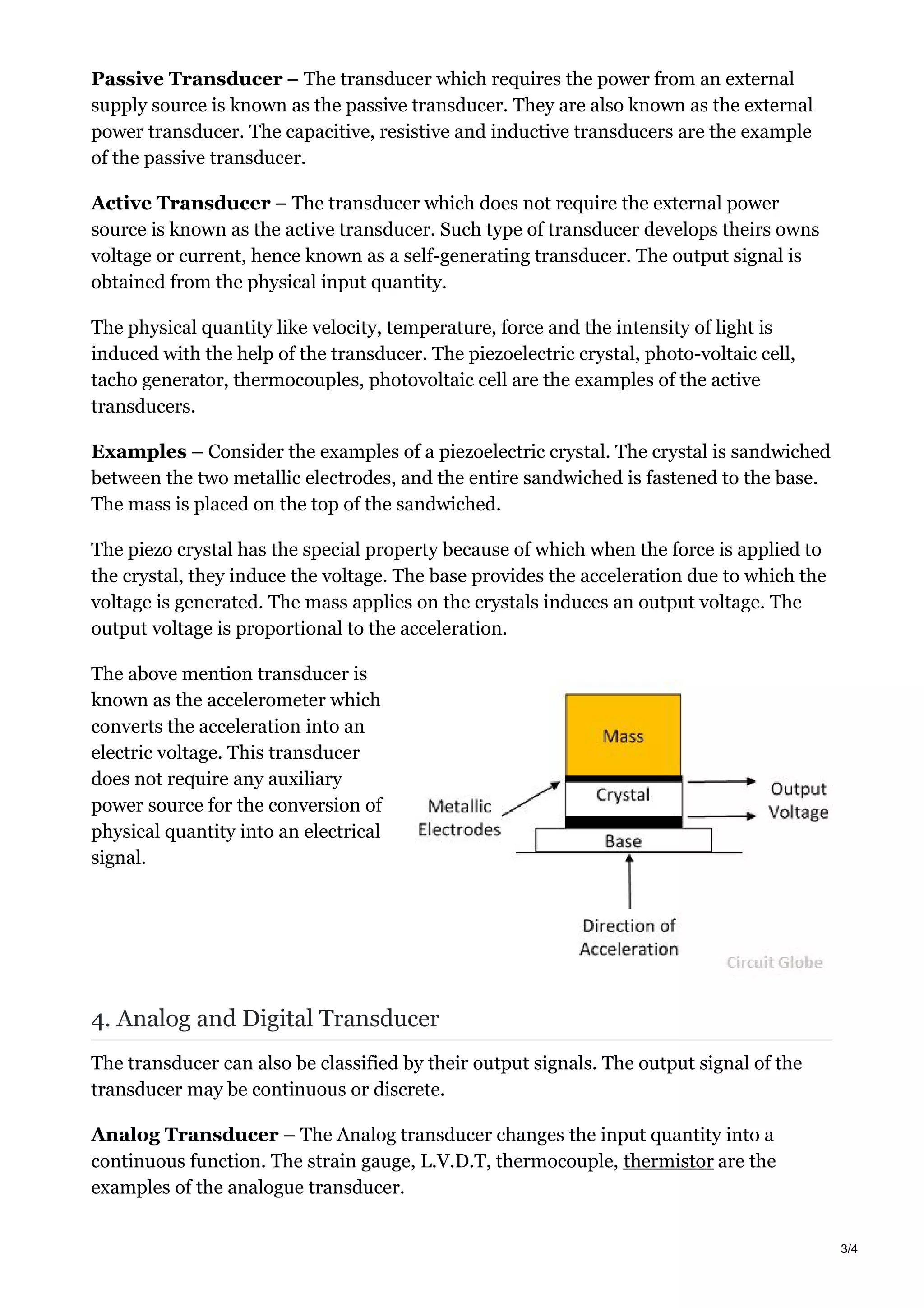
3. Transducers are classified based on their operating principle (resistive, inductive, etc.), whether they require external power (passive) or generate their own output (active), and if their output is analog or digital.