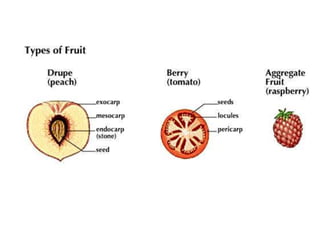
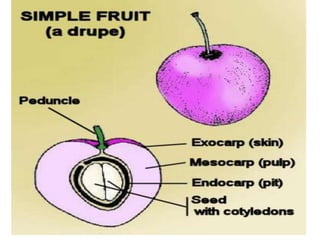
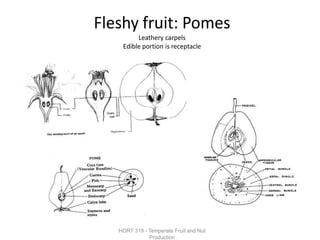
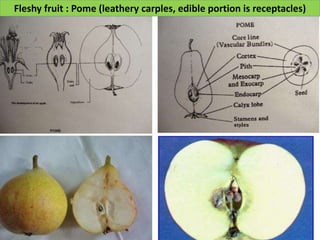
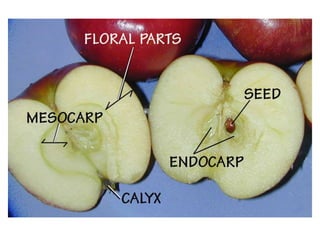
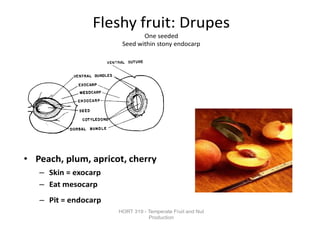
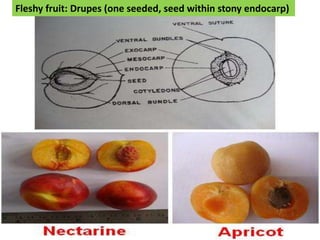
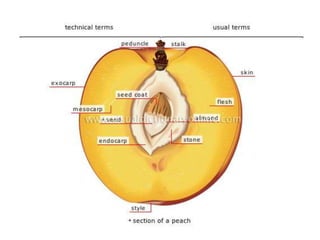
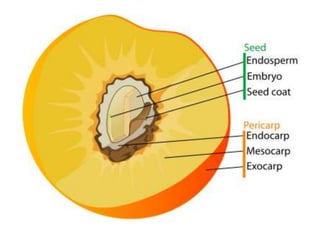
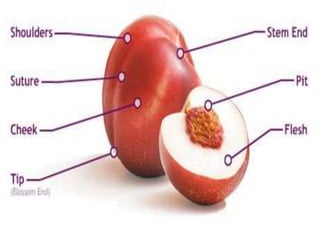
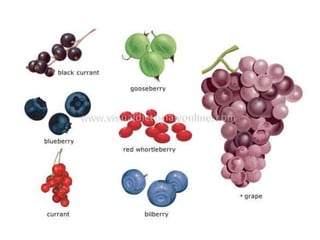
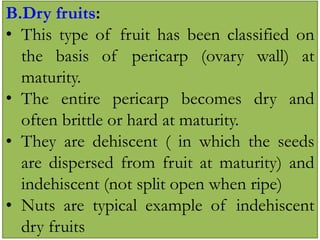
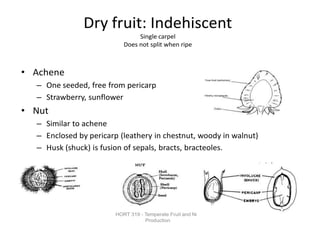
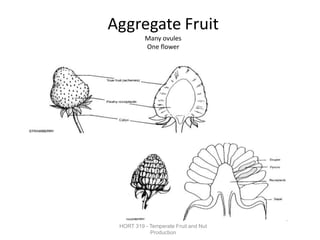
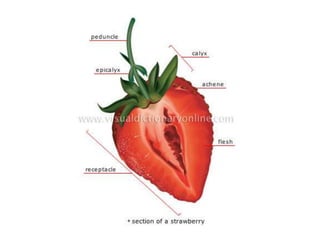
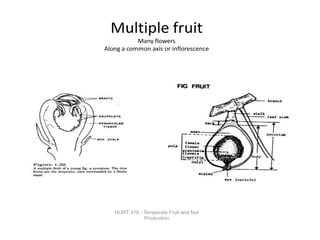
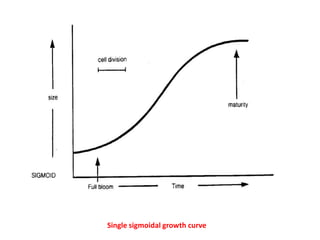
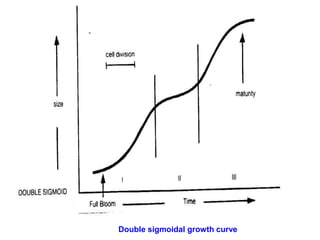
Temperate fruit plants are those that grow in climates with distinct winter cold periods. They require chilling temperatures to break dormancy and initiate growth. Examples include apple, pear, stone fruits, berries, nuts, and cherries. These plants are classified based on factors like plant structure, fruit morphology, bearing habit, and growth pattern. Fruits are categorized as tree fruits, small fruits, or nuts. Classification helps identify relationships and suggest cultural requirements. Common temperate fruit types include pomes like apple; drupes like peach; and dry fruits like nuts.